


Gospower P221B/P222B Maintenance Manual
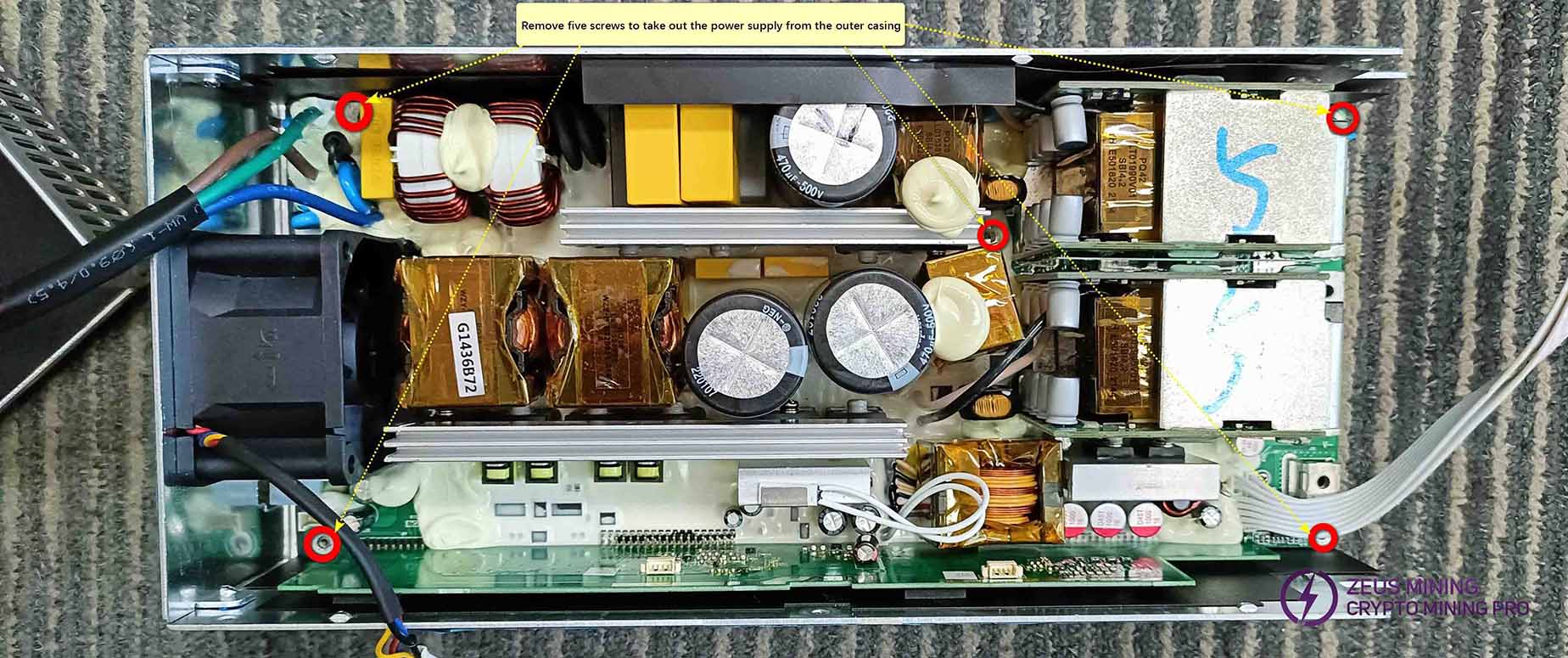
1. Remove the entire power circuit from the power supply box

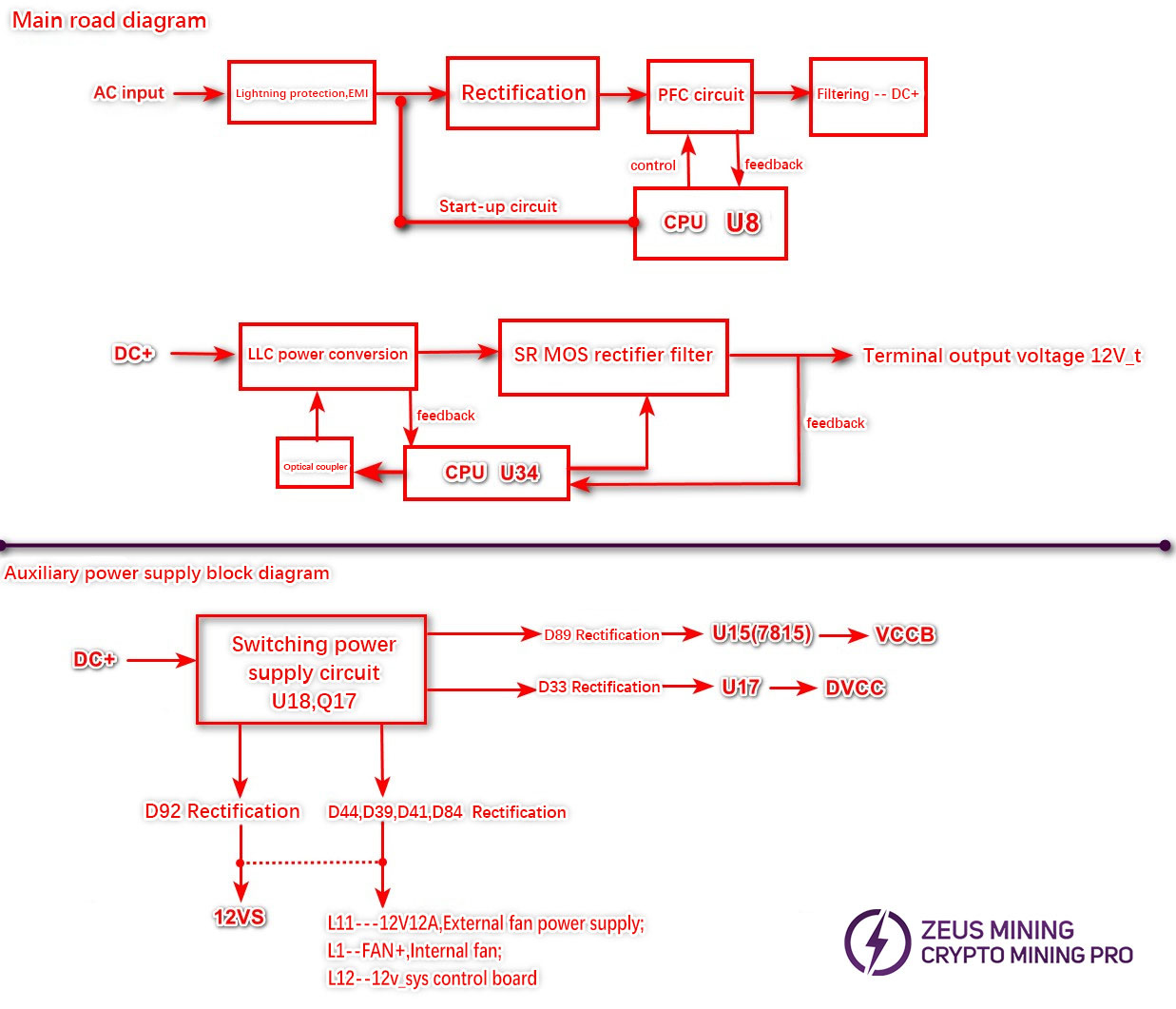
2. Circuit Structure Block Diagram
The L and N AC inputs are filtered through the fuse, interference capacitors CY5, CY6, and CX2, the lightning protection varistor VR1, and the interference inductors LX1 and LX2, then fed to the rectifier bridges BD1 and BD3 for rectification. After filtering by C68, C23, and C122, the rectified voltage from the switching power supply equals twice the input AC voltage (311V). The DC output is approximately 300V, with a peak of around 311V. When the PFC circuit operates, the filter capacitor voltage increases by 100V, reaching about 400V. The PFC circuit includes PFC inductors L8 and L9, PFC MOS transistors Q6, Q86, Q84, and Q21, their driver circuits, PFC driver chips U13 and U14, and the CPU control and feedback circuit.
NT1 and NT2 are soft-start thermistors, while RLY1 is a soft-start relay.
The LLC circuit comprises two parallel branches: one branch consists of LLC MOS Q1, Q13, L6, T1, C3, C10, and their driver circuits, while the other branch consists of Q37, Q85, L13, T5, C261, C252, and their driver circuits. The combined output is then delivered to the rectifier MOS module to generate the final voltage.
The front-end CPU processes the front-end feedback sampling voltage and temperature s,igna ands RT,2, RT5 to control the PFC circuit and relays. The rear-end CPU processes the rear-end feedback sampling voltage and temperature signals, RT3 and RT4, to prevent the LLC circuit, the rectifier MOS output circuit, and the internal fan.
The auxiliary power supply provides voltage for all chips, while the fan power is supplied through a rectified output from the transformer's primary winding, passing through D44, D39, D41, and D48.
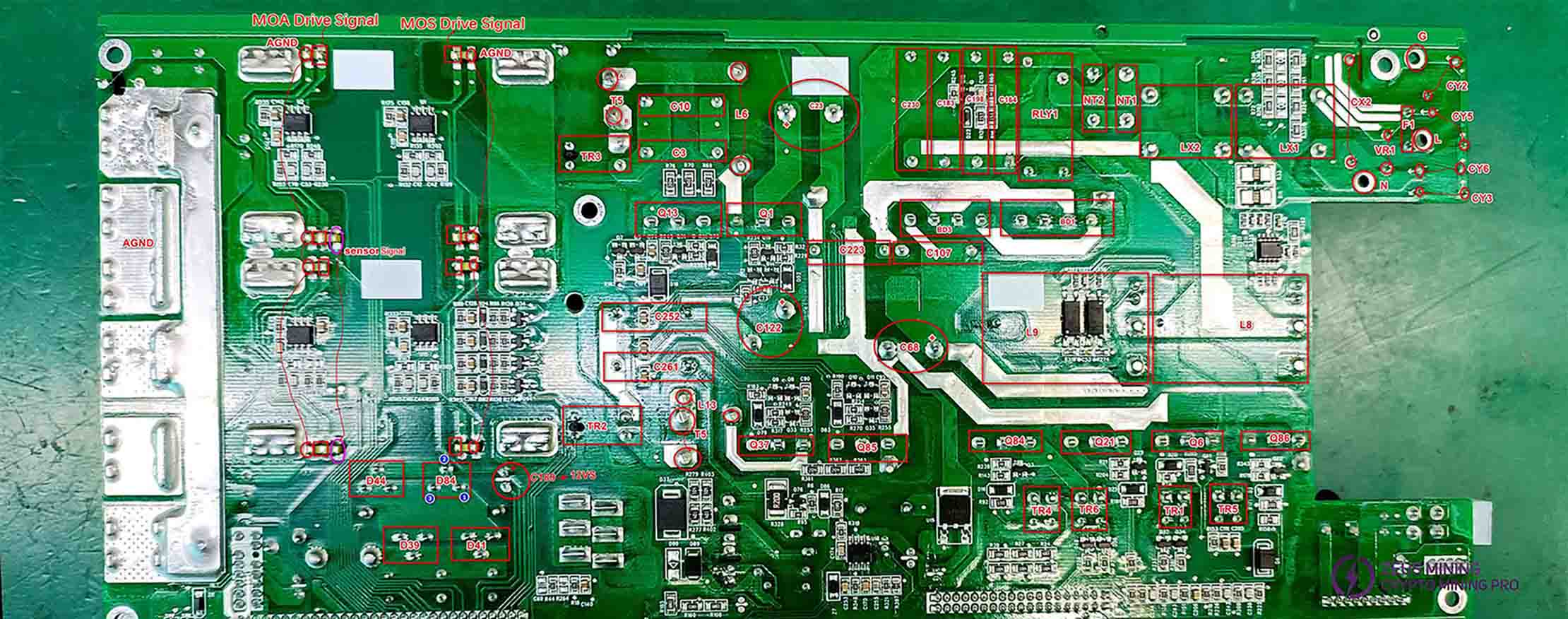
Surface-mounted components of the plugin: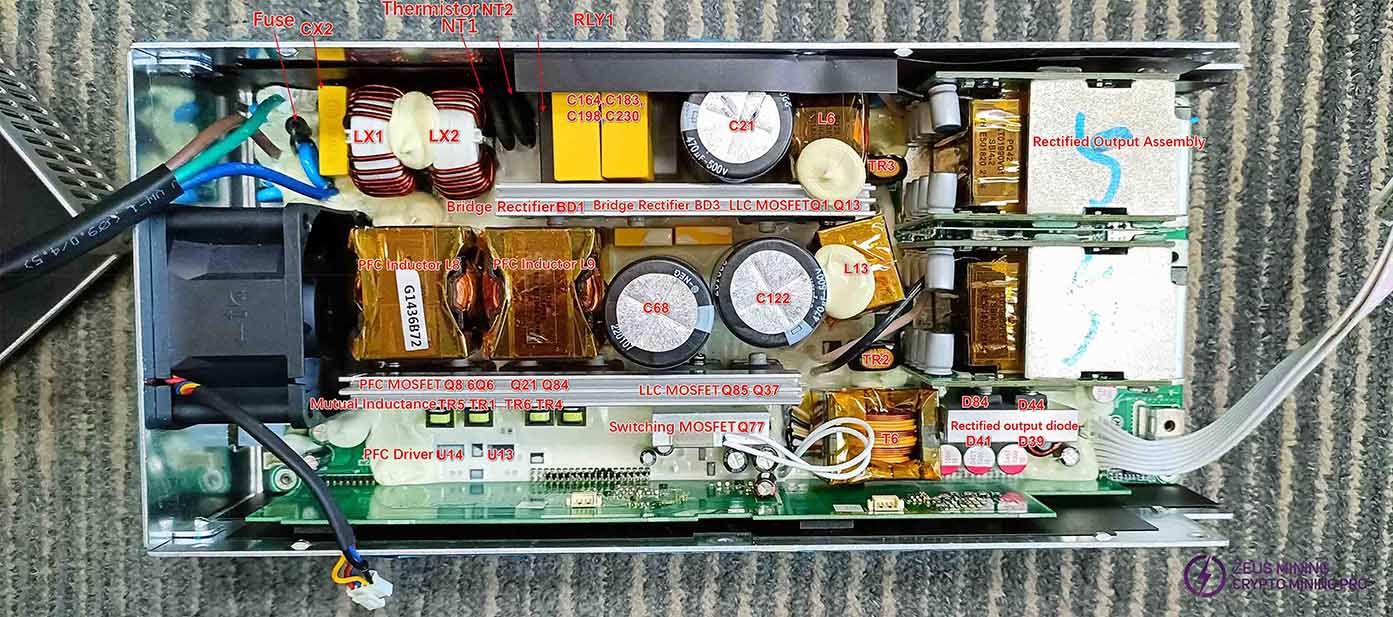
The plugin is on the back side of the pin:
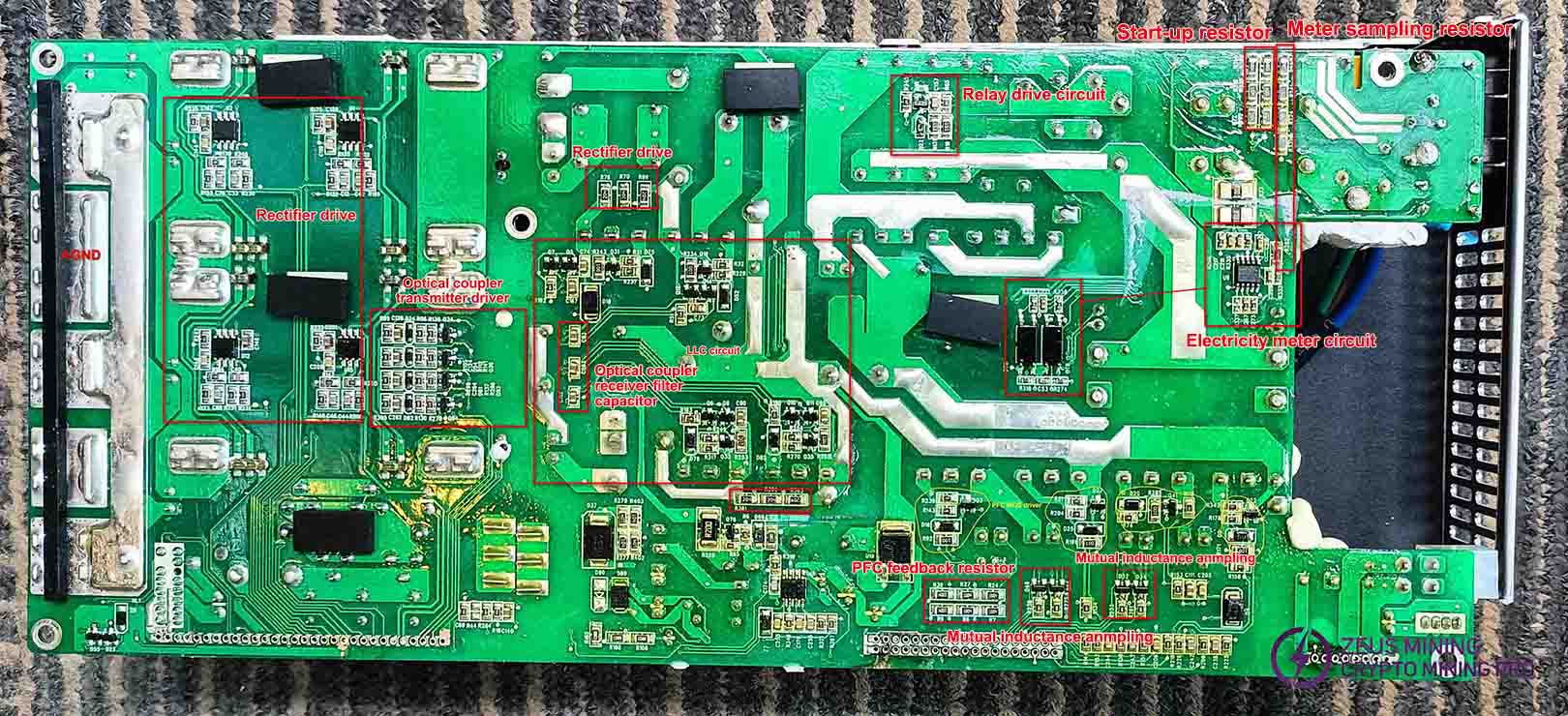
Surface Mount Component Functions:
Plugin patch component position: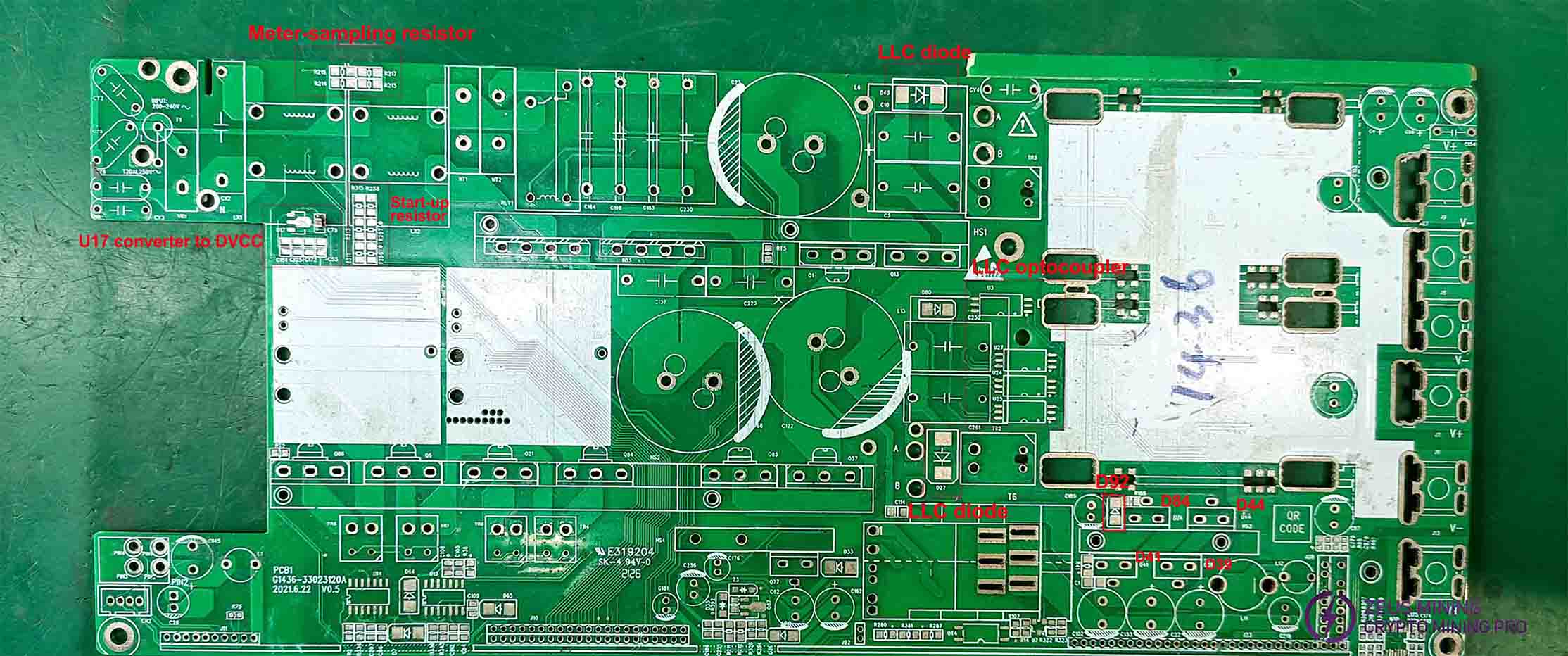
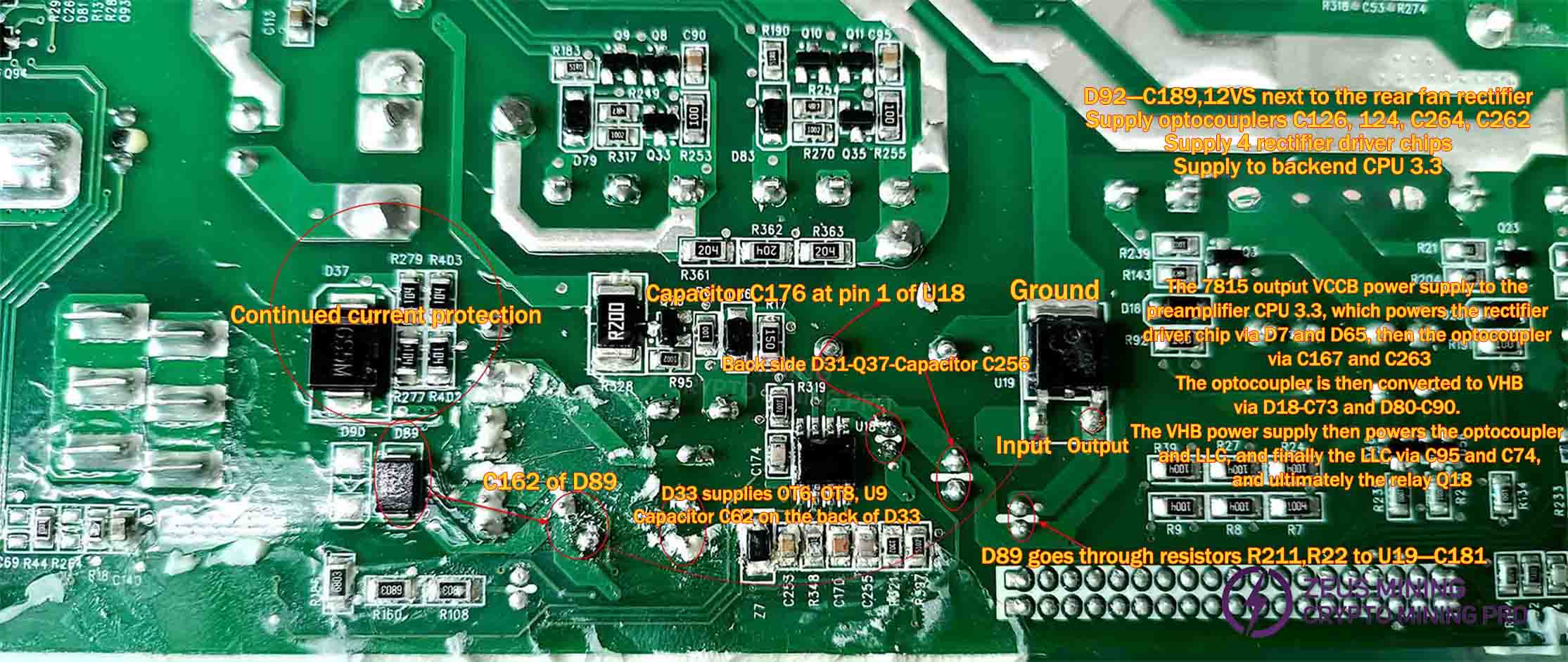
The auxiliary circuit voltage is supplied by:

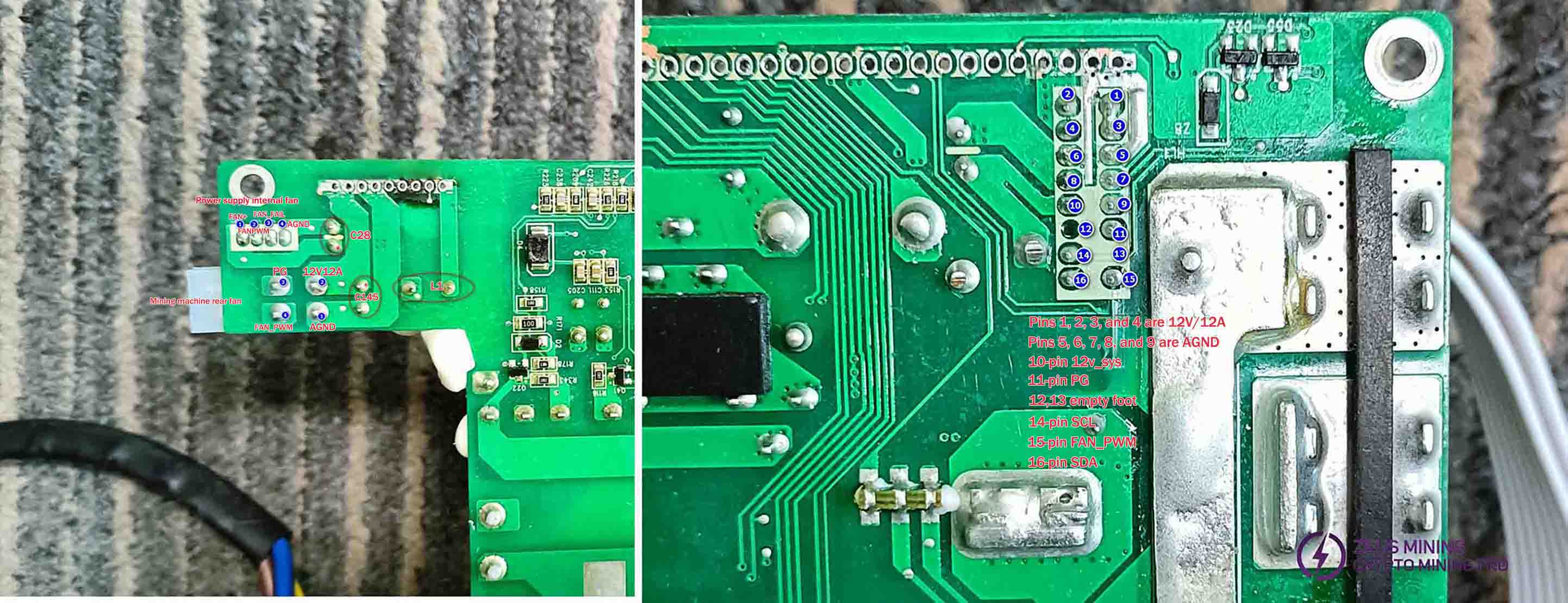
Interface pin functions: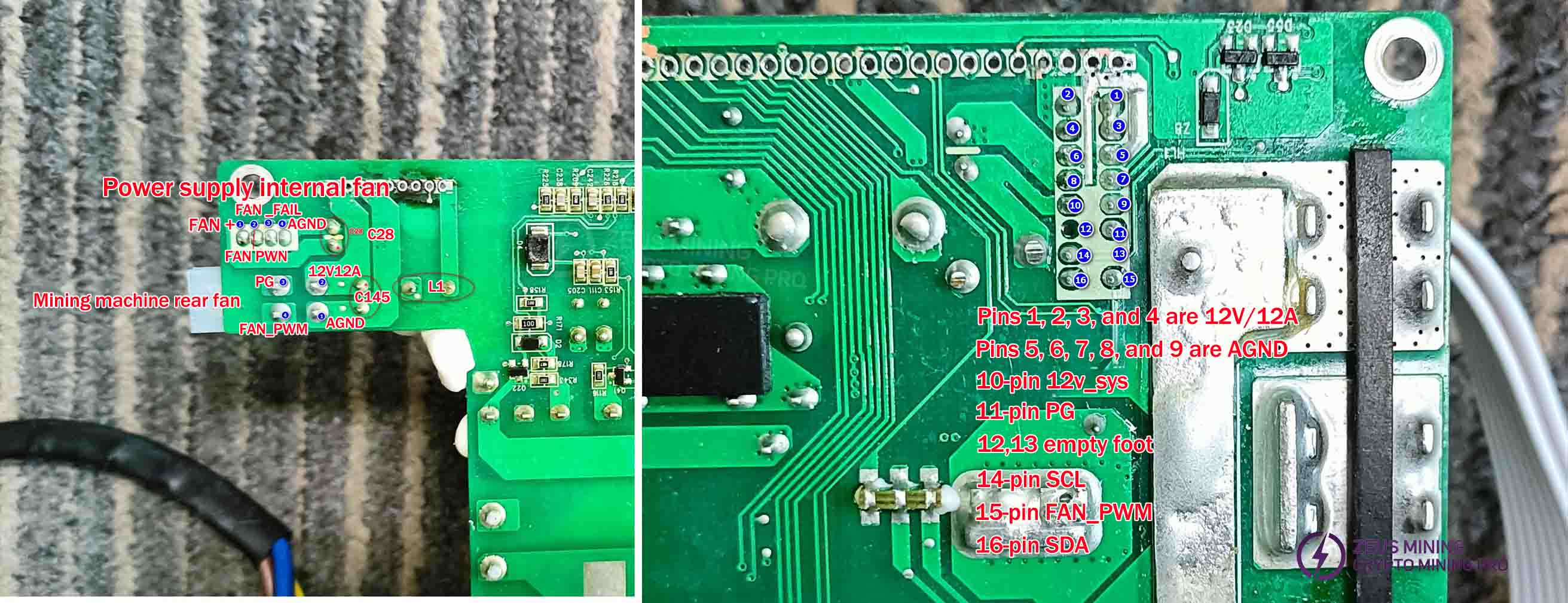
Rectifier output component: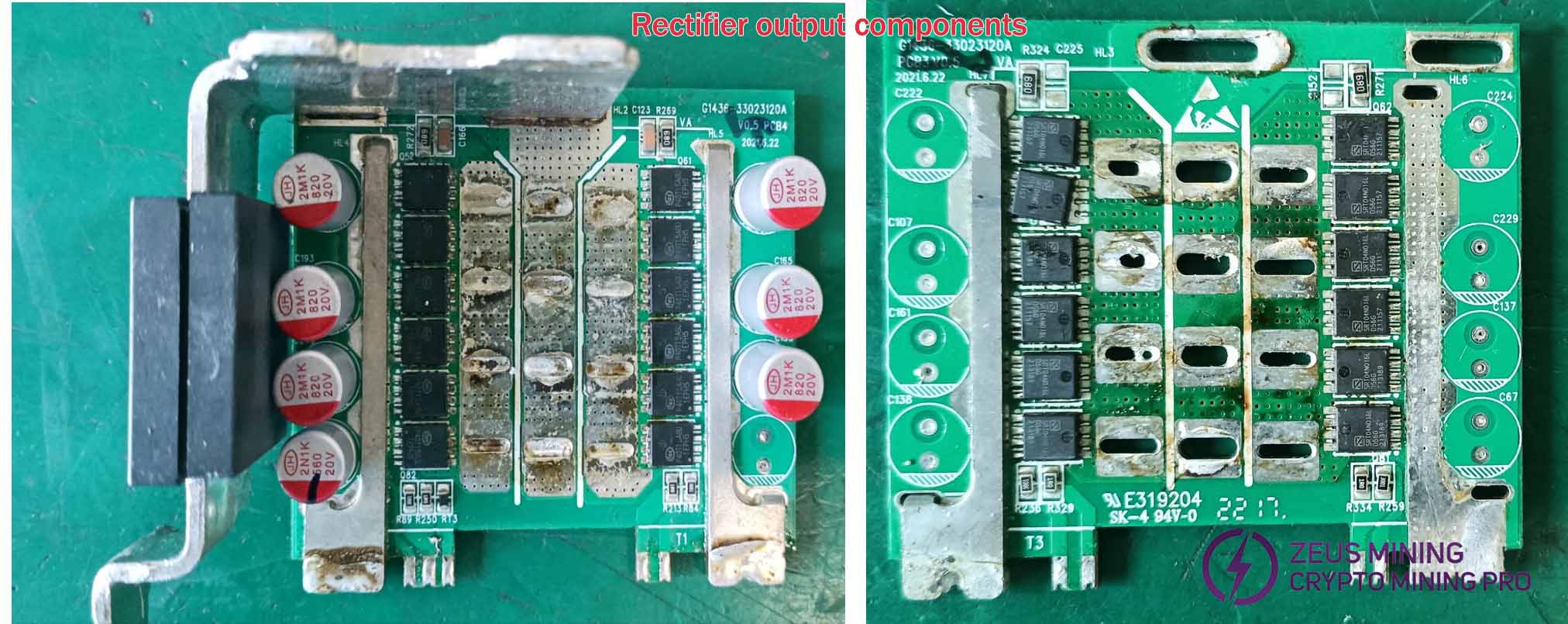
Control board: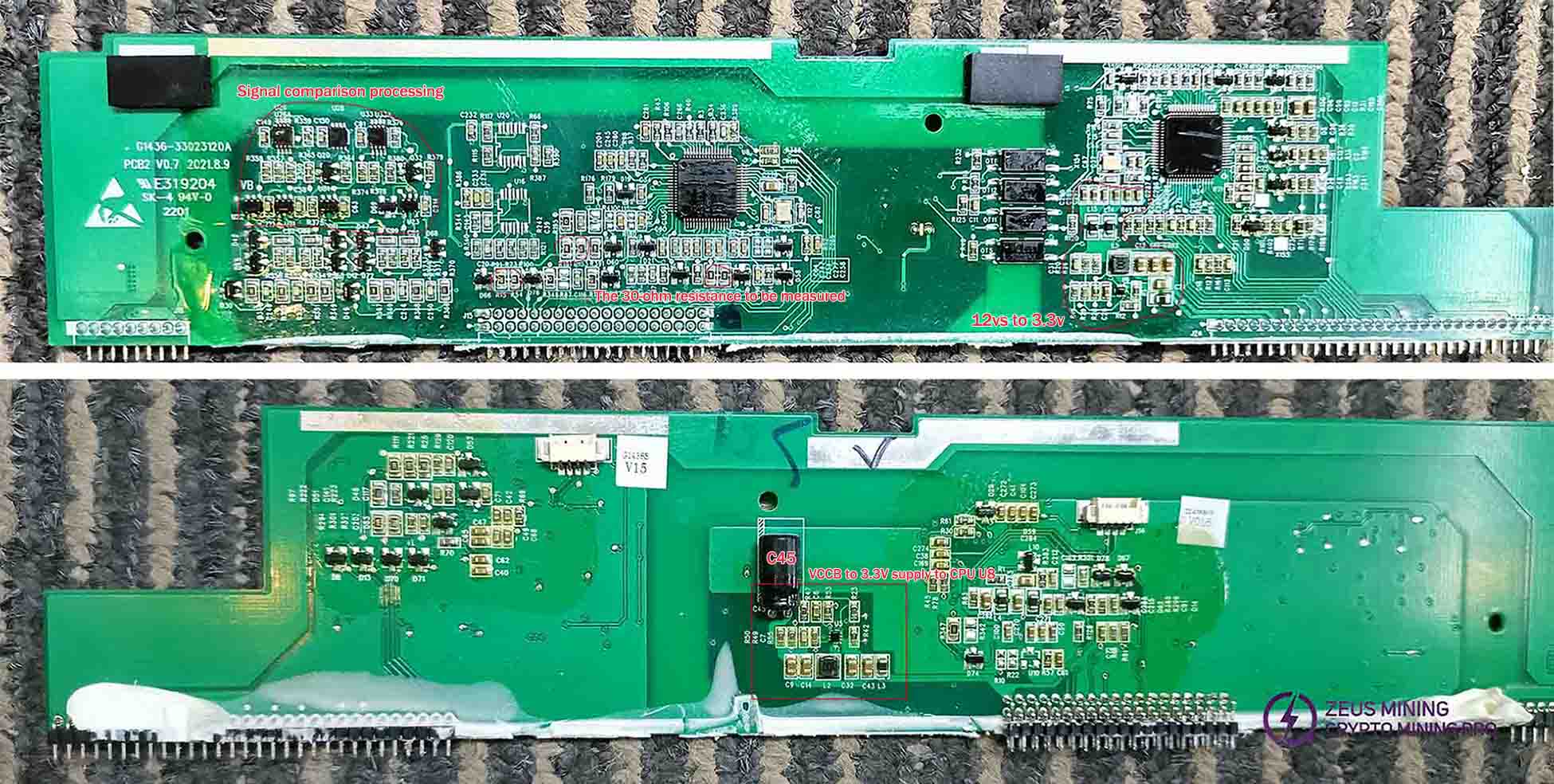 Repair procedure:
Repair procedure:
1. For live-line maintenance
First measure the resistance at the AC input. If the circuit is open, the internal fuse will blow. If no blowout occurs, the fault is minor. In either case, perform internal component inspection before power-on testing. After opening the cover, visually inspect for burnt components or broken copper layers. Replace any burnt components immediately.
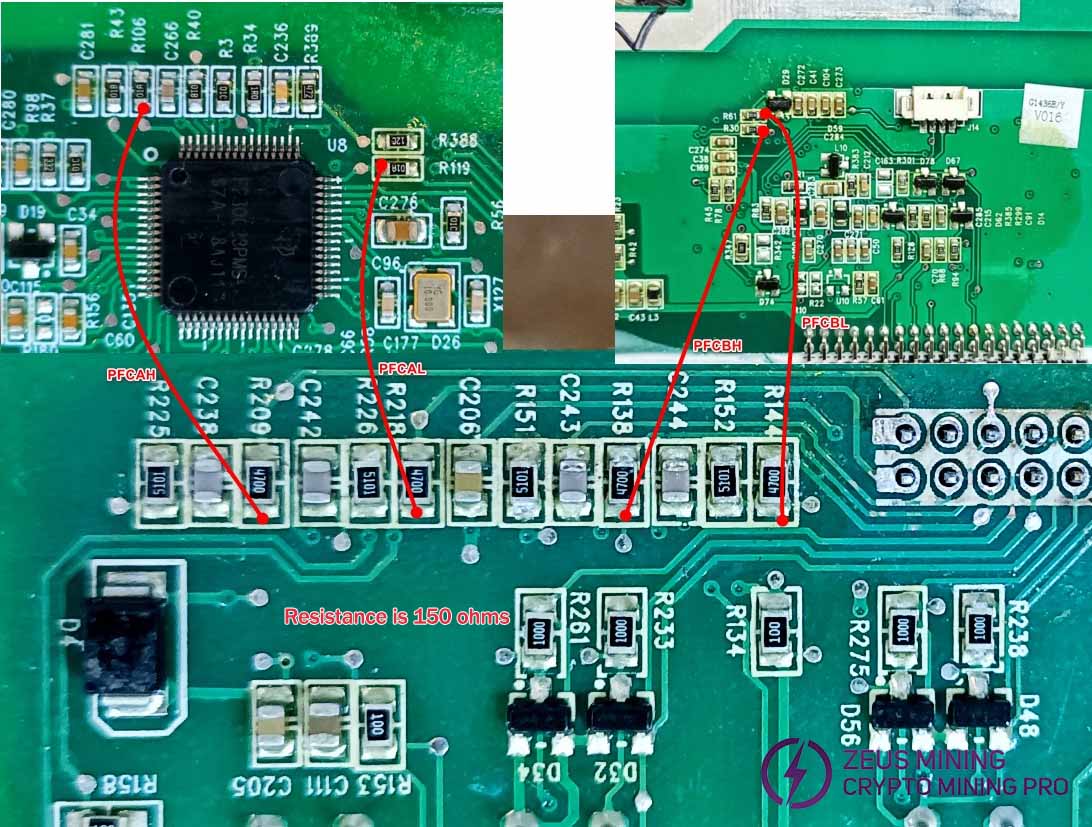
PFC circuit inspection: Measure the diode values of the driving transistors Q3, Q23, Q41, and Q22 on the PFC MOS transistor, as well as the 1st and 3rd pins. The forward resistance should be around 0.56Ω, and the reverse resistance around 1.73Ω. If the values are too high, consider an open 10-ohm resistor. If the values are too low, the driver chips U13 and U14 may be burnt out, and the MOS transistor could be damaged.
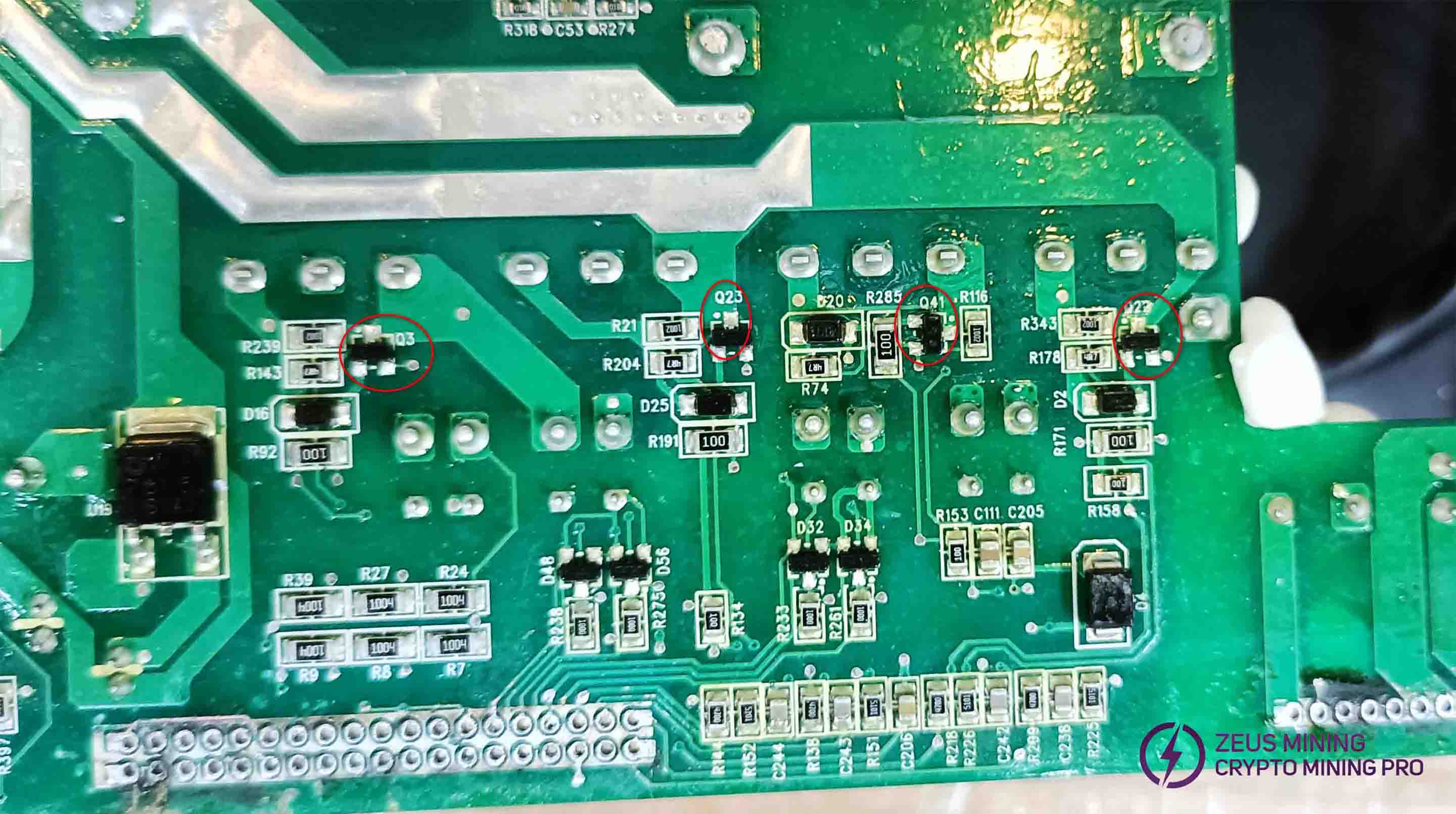
Four mutual inductors (RT5, RT1, RT6, RT4) may be burnt out, or the PCB traces could be damaged. Use a multimeter to check the connectivity between the inductors and the MOSFET pins, as shown in the diagram.
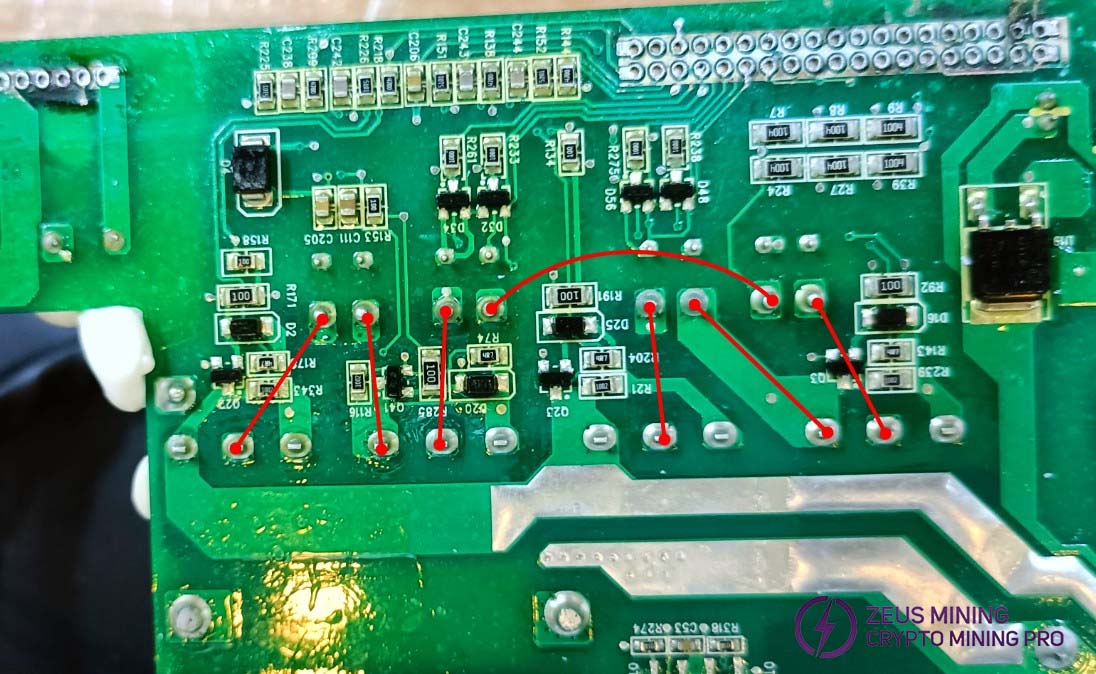
If a PFC MOS transistor fails, all four PFC MOS transistors in the same power supply must be replaced with identical brand and model to ensure consistency. For PFC tube failure, check the corresponding driver chip and verify if the capacitor resistance is abnormal.
 The driving signal has approximately 150 ohms between its two terminals.
The driving signal has approximately 150 ohms between its two terminals.
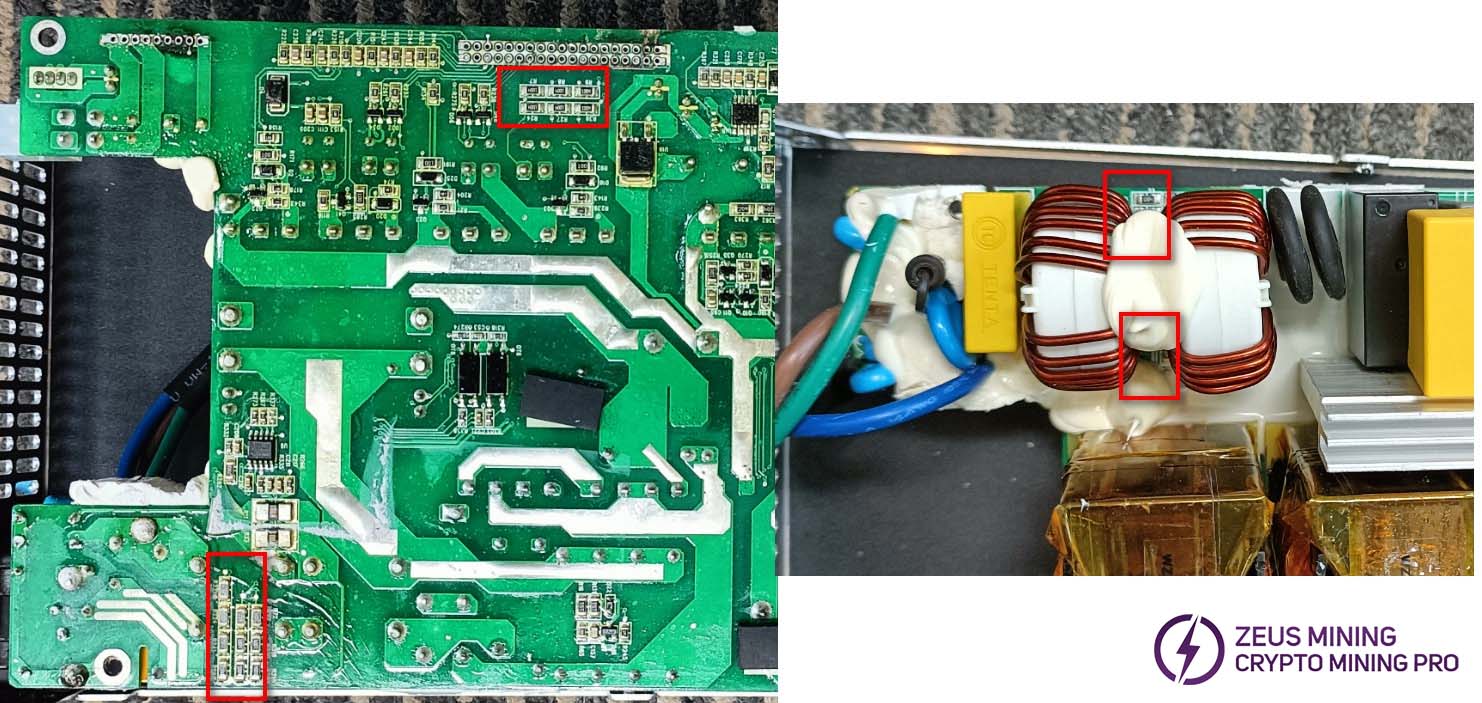
Check whether any wires in the coil circuit are burned out.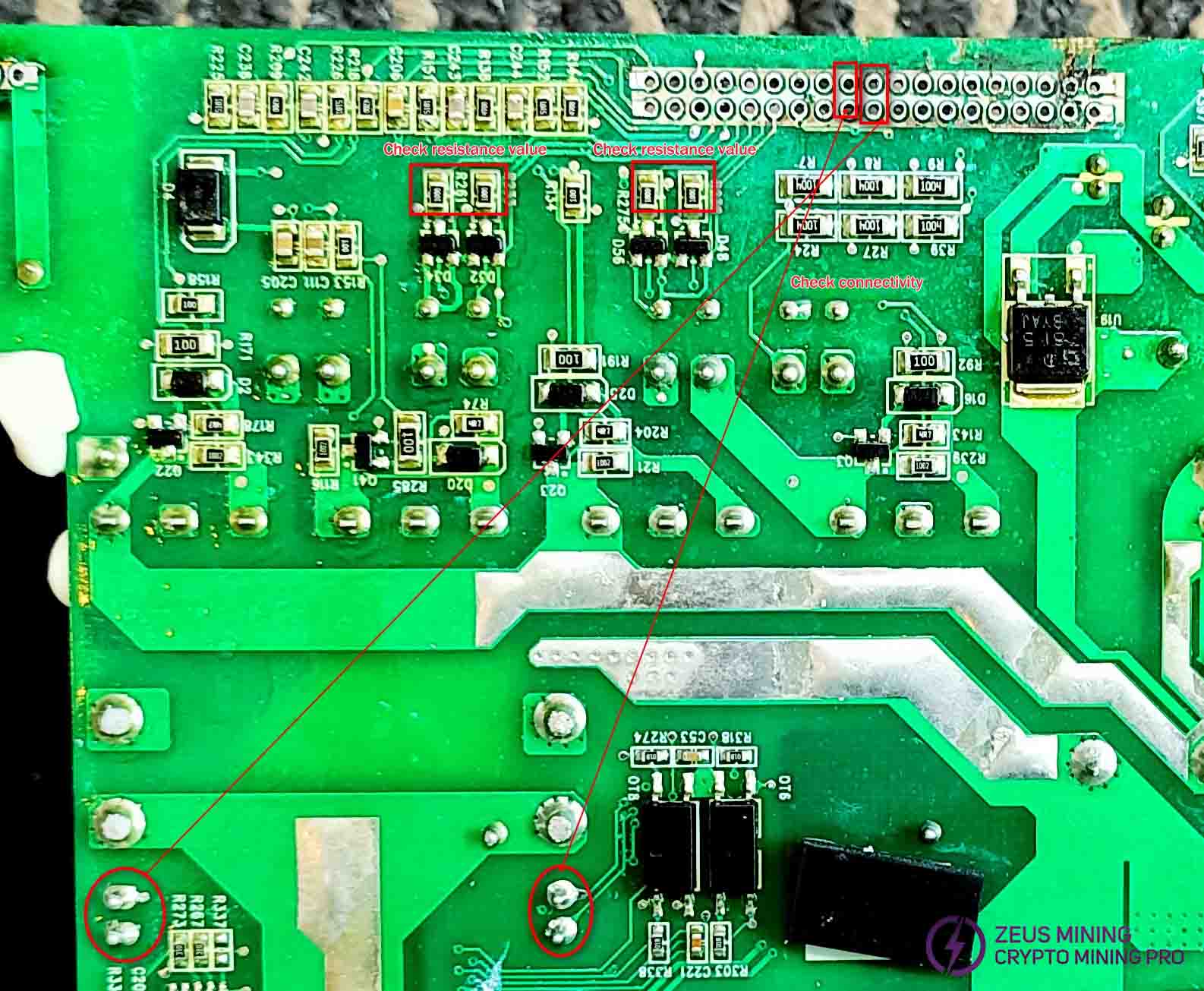 Check the start-up resistor and sampling feedback resistor for dust accumulation, leakage, or burnout.
Check the start-up resistor and sampling feedback resistor for dust accumulation, leakage, or burnout.
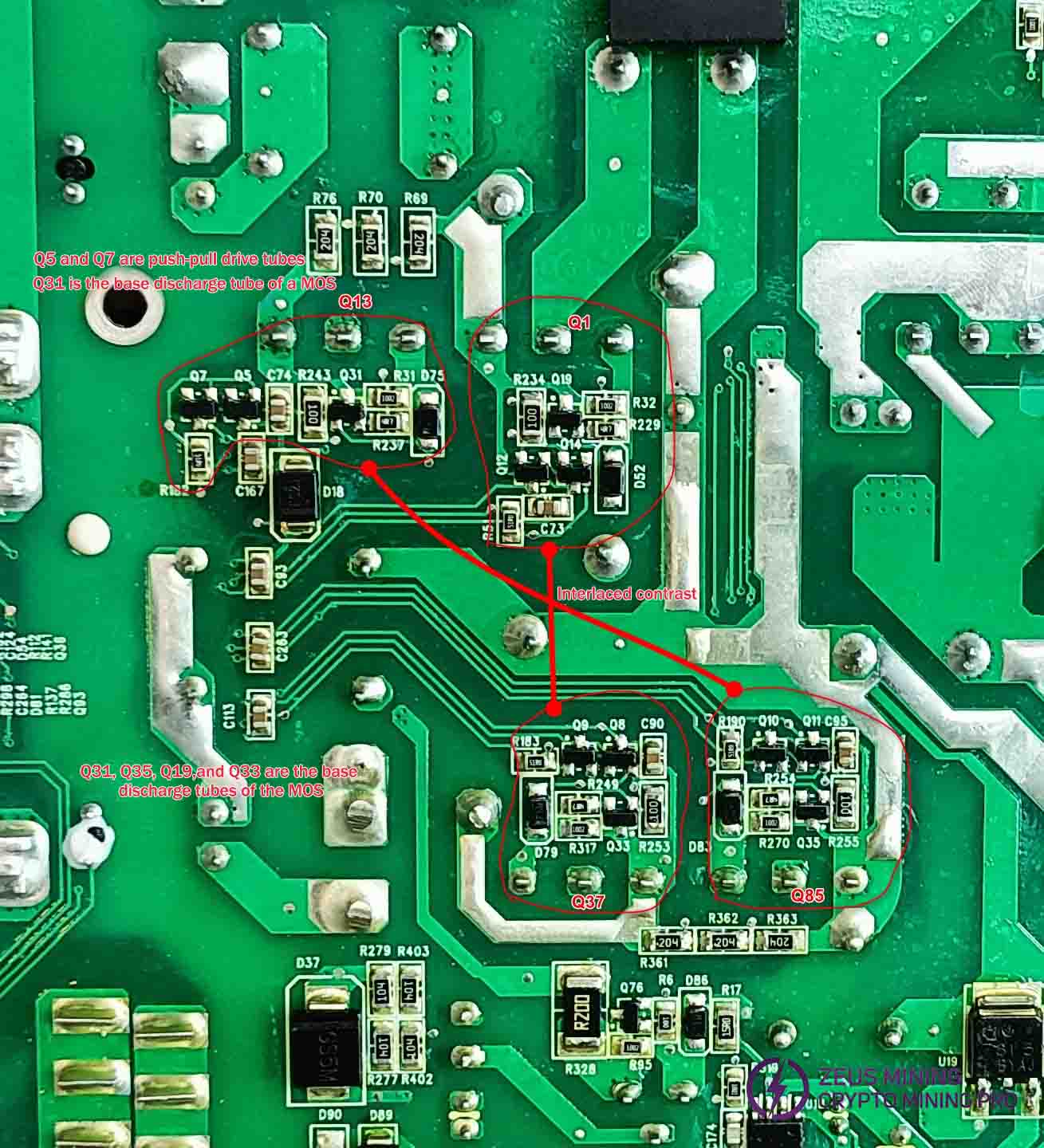
LLC circuit inspection:
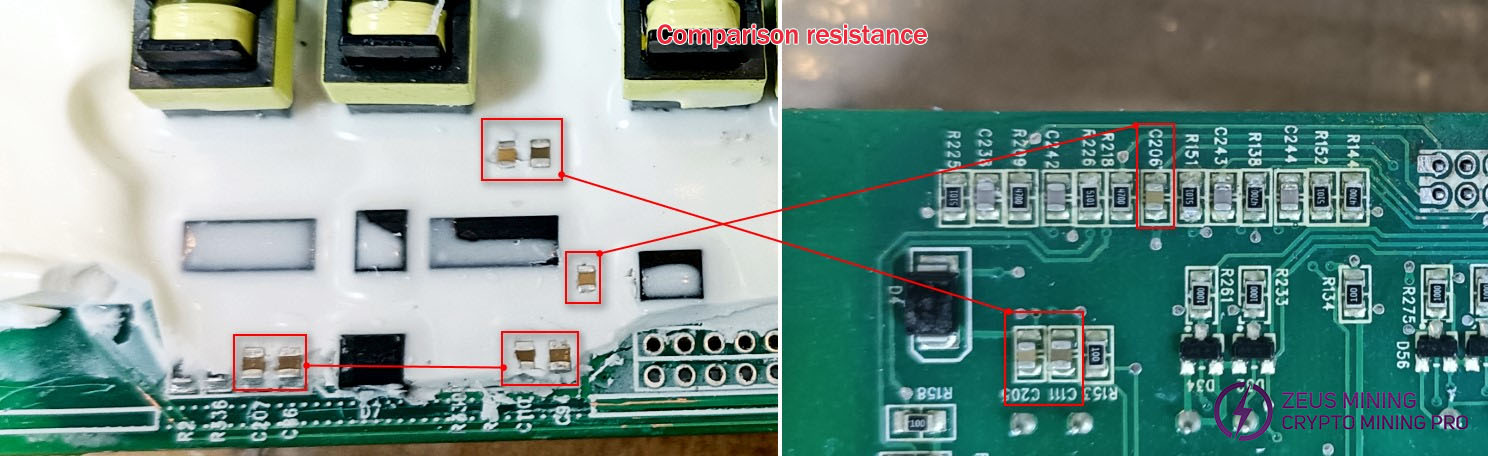
Compare the diode values of pins Q1 and Q37 for MOS transistor Q1, and Q13 and Q85 for MOS transistor Q37. If the circuit is functioning normally, the diode values should be nearly identical. A value that is slightly lower indicates a short-circuit failure in the MOS transistor. If the value is significantly higher, further testing of the auxiliary driver transistor and resistor is required. All components in the circuit should be measured with alternating comparisons.
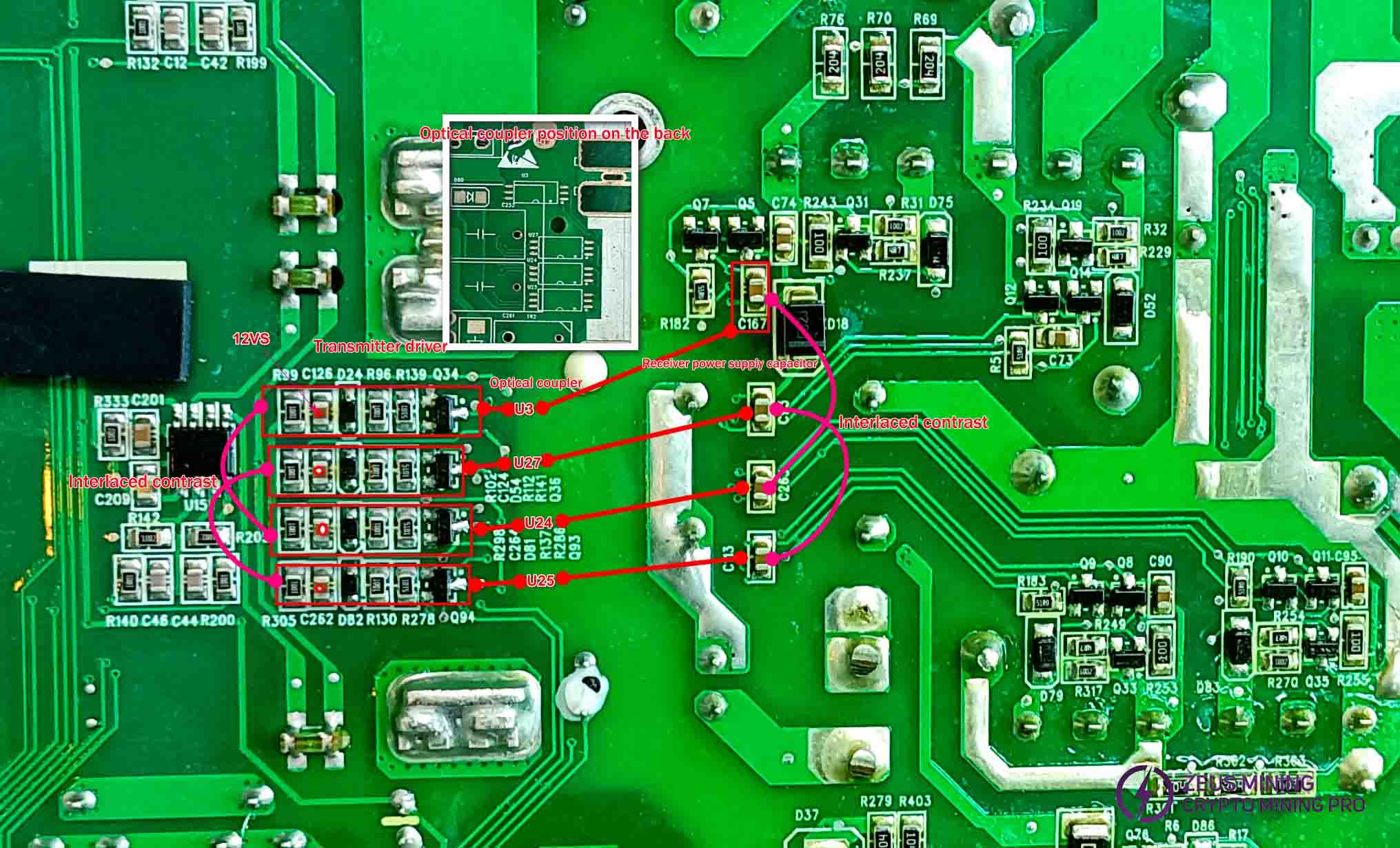
 Check the optocoupler circuit
Check the optocoupler circuit
The optocoupler circuits U3 and U24, U27 and U25 perform cross-checking of diode values. At the receiving end, C167 compares with C263, while C93 compares with C113 to detect short circuits or diode value discrepancies. At the transmitting end, corresponding-side transistor diode value differences are compared: Q34 with Q93, Q36 with Q94. The optocoupler is mounted on the plug face. During replacement, the rectifier output assembly must be removed using a soldering iron.
 Check the output rectifier section:
Check the output rectifier section:
Check capacitors C142, C158, C146, and C201 for abnormal resistance or short circuits, and verify the chip's normal operation by comparing resistance values at corresponding pins. 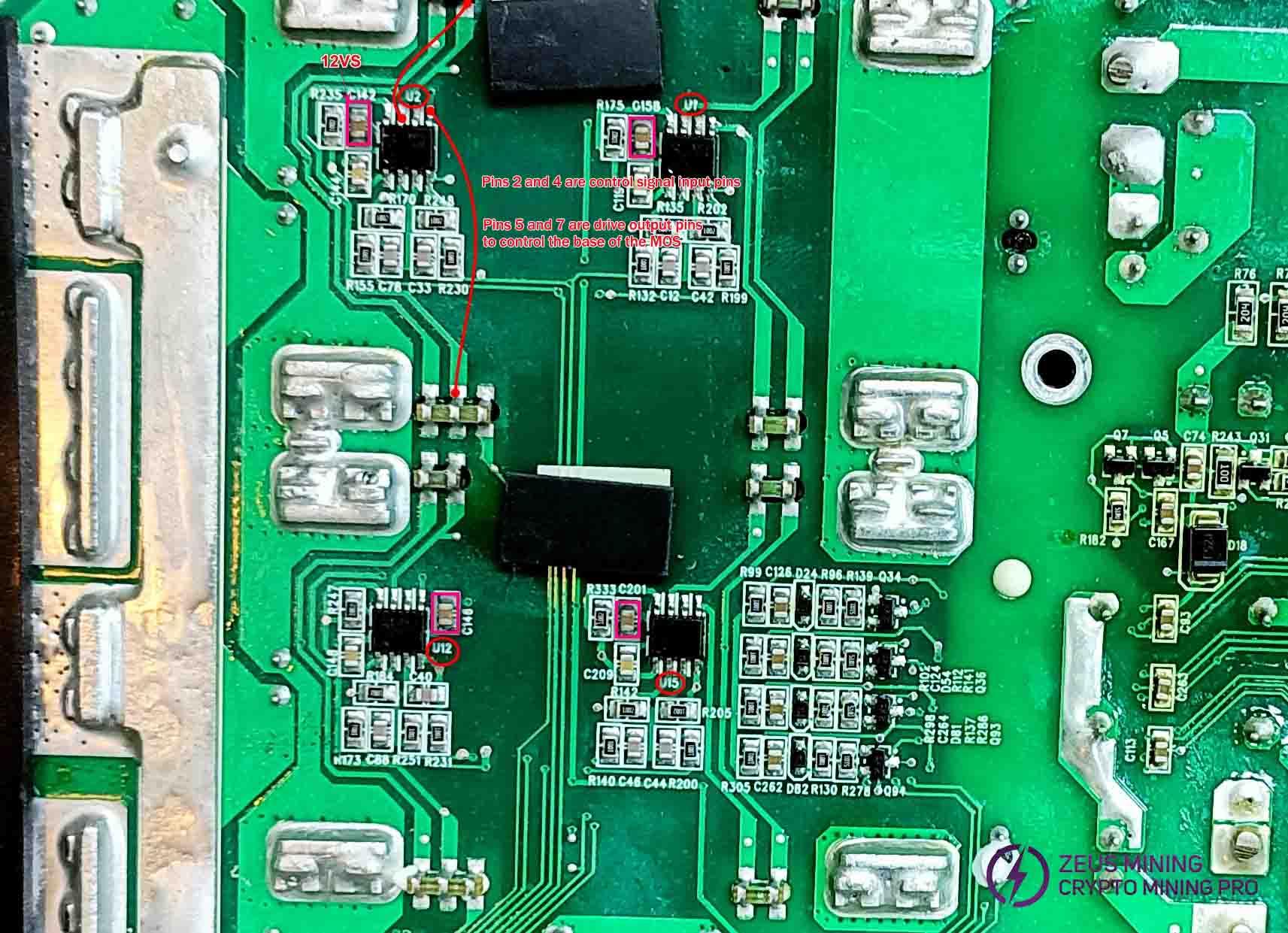
Compare the resistance values of MOS driver signals to identify the faulty rectifier component. Remove the component from the soldering iron and replace the damaged rectifier MOS. In the rectifier circuit with the faulty MOS, measure the resistance of each MOS pin 4. The component with the lowest resistance is the faulty MOS. After replacement, measure again. If discrepancies persist, replace the component with the lowest resistance. If continuous testing reveals more than three faulty MOS, replace the entire rectifier MOS group. 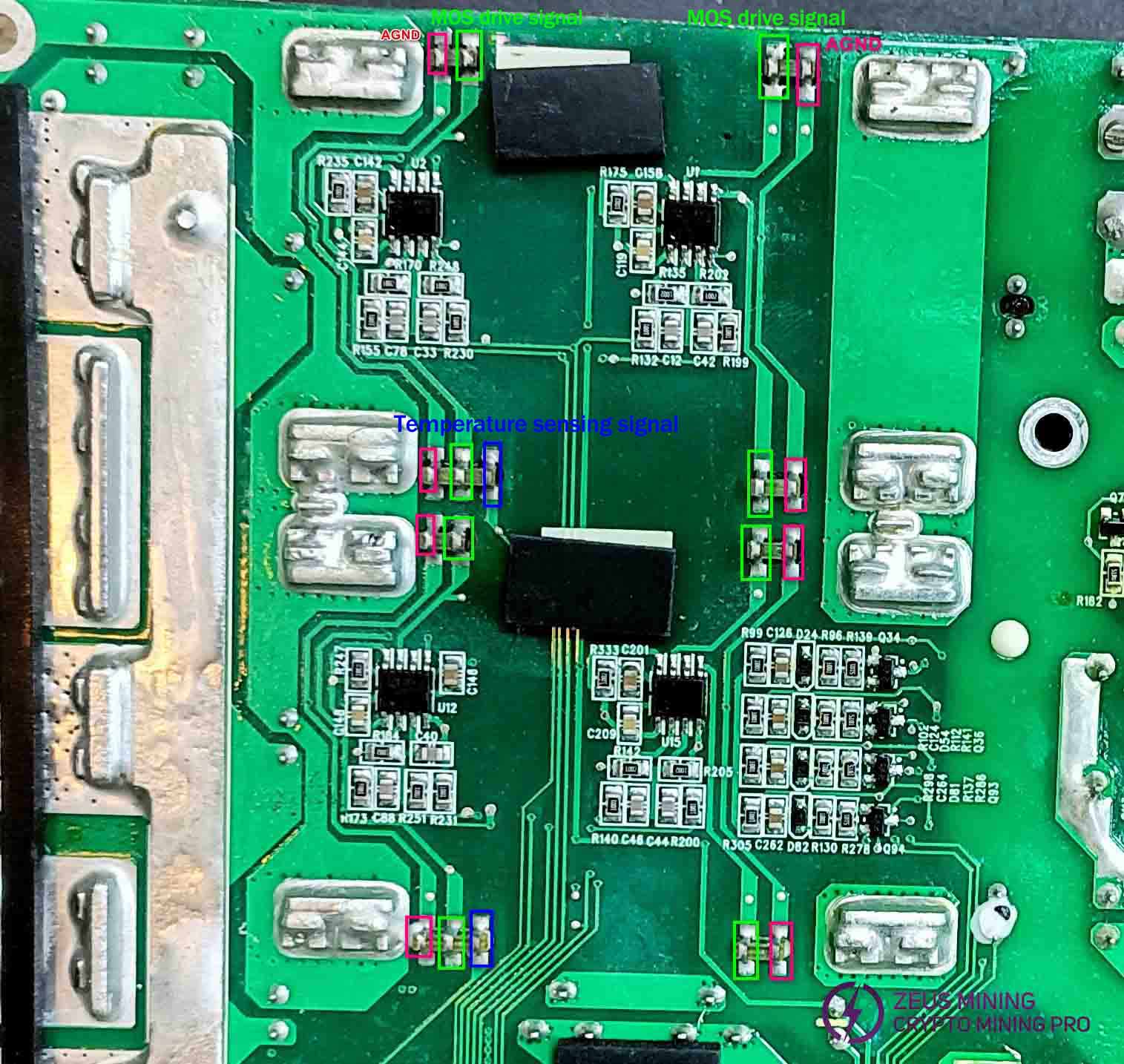
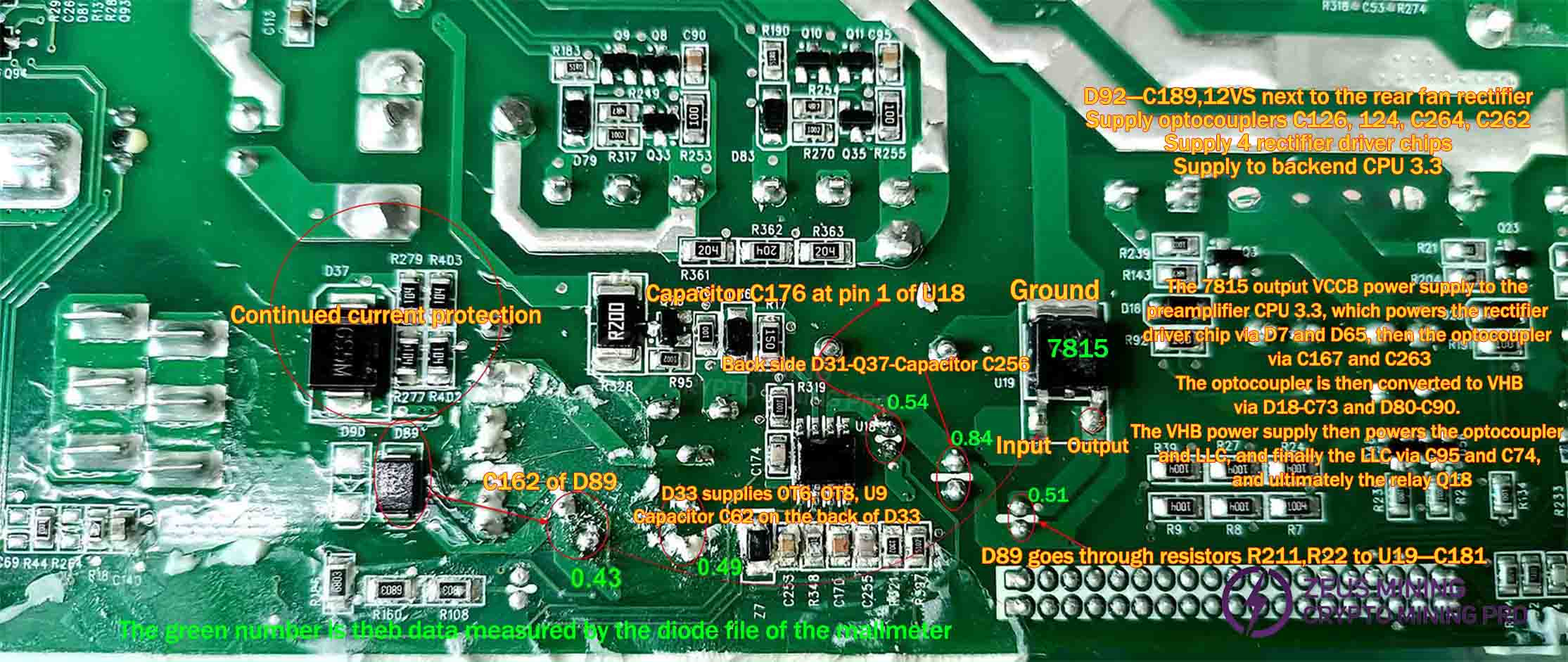
Auxiliary circuit voltage control system maintenance:
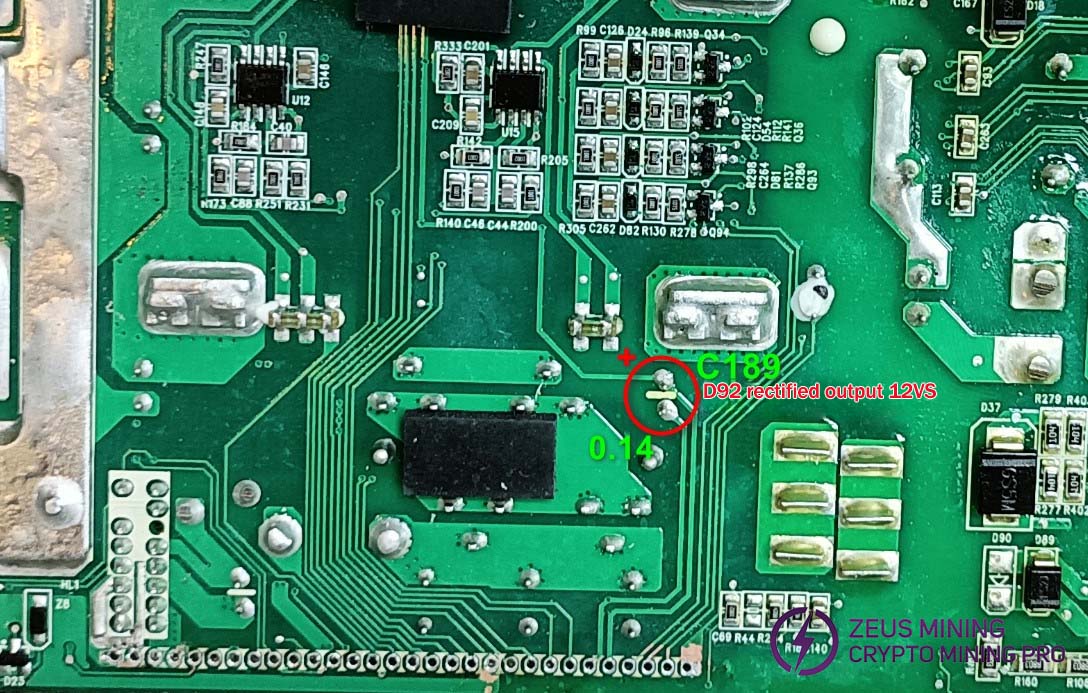
D89 rectification, C162 filtering, send 7815 output VCCB, if only 12V,11V, then replace 7815, at least 13.5V.
The D92 rectifier and C189 filter deliver a 12V output. D44, D39, D41, and D84 rectifiers provide 12V/12A to the fan. D33 rectifier and C62 filter supply U17 with DVCC, powering the meter chip. Q77 acts as the switch, while Q76 serves as its discharge transistor.
Test steps:
1) Verify the resistance values of corresponding resistors;
2) Upon power-on, check the voltage across corresponding capacitors.
 Check the CPU circuit:
Check the CPU circuit:
The 3.3V power supply is filtered by C45 and supplied to U8. The diode's forward resistance is approximately 0.37Ω, while the reverse resistance should normally range between 0.6-0.9Ω. If the measured value falls outside this range, remove U8 and retest C45. If the value returns to the specified range, it indicates a faulty U37. If the issue persists, the U5 is faulty. 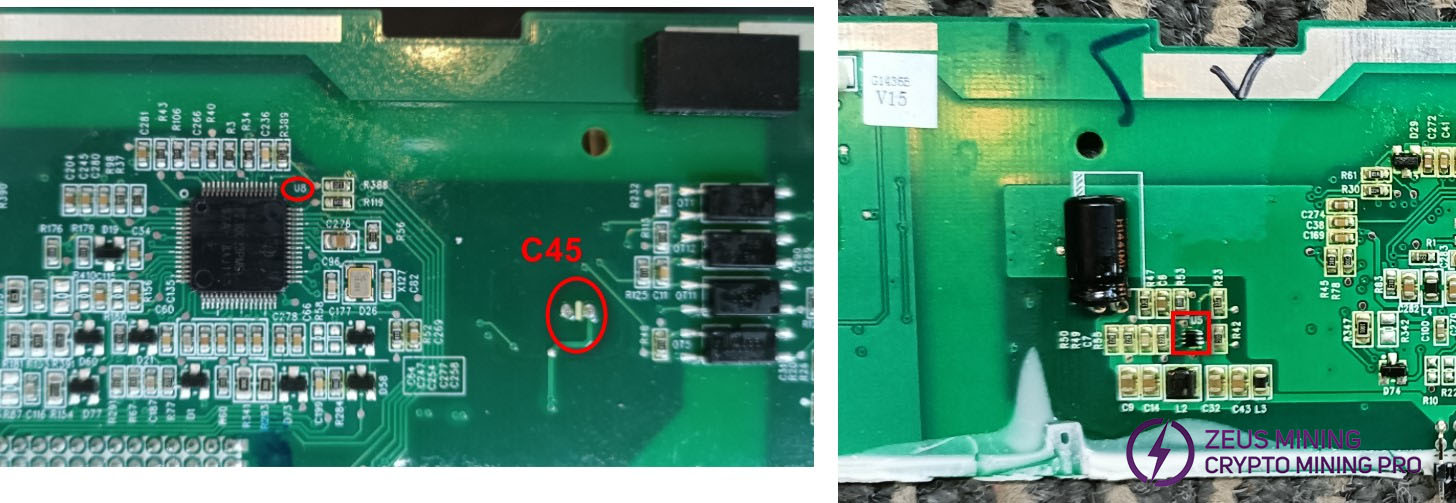
Rectifier bridge inspection:
Before powering on for circuit maintenance, measure the large filter capacitor C68 again with a diode. The forward measurement should be around 0.48, and the reverse measurement should be open. If the measurement values differ significantly or the reverse measurement is not open, recheck the rectifier bridge BD1, BD3, and the MOS transistor of PFC.LLC.
After completing the non-powered comprehensive inspection and maintenance, the powered check can be performed for confirmation:
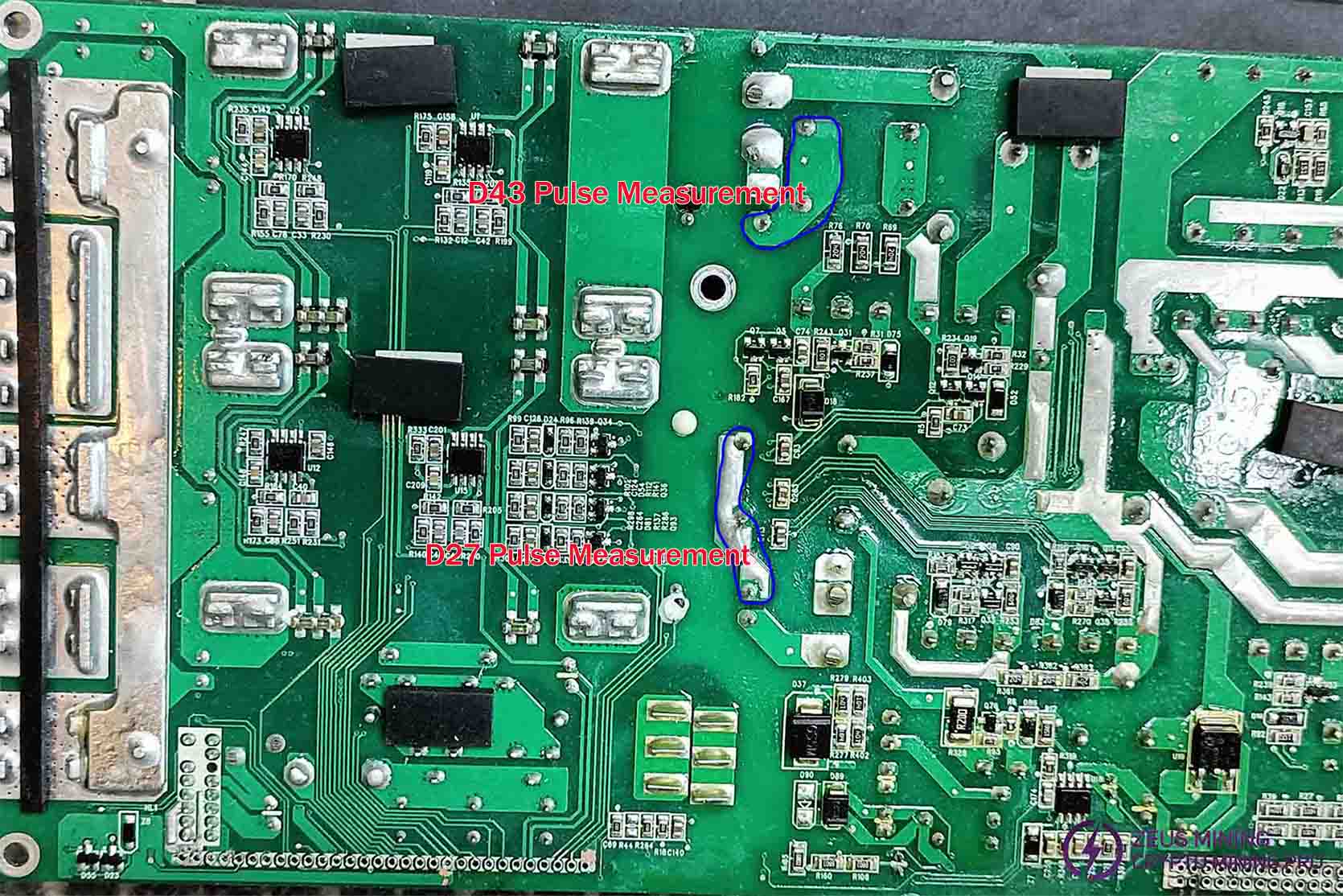
If you hear a clicking sound when the relay closes after power-on, the system is likely functioning normally. Measuring approximately 400V on capacitor C86 confirms proper PFC circuit operation. Check auxiliary control voltage C181 for around 14V output. Normal output indicates proper auxiliary circuit voltage. Connect the unlock control board and use the multimeter's voltage range to measure D27 and D43 for 12-120V pulse voltage fluctuations. Observe whether the decimal values show periodic fluctuations. Absent fluctuations or minimal range suggests malfunction in the LLC circuit. If the output voltage is normal but the system fails to drive the load, possible issues include PFC or LLC single-side operation, or capacitor aging. Test capacitance using a bridge: check LLC capacitors C3, C10, C252, and C261. The total output capacitance should be around 20mF. Insufficient capacitance requires capacitor replacement until proper capacitance is restored.
If the output protection activates after power-on and the output voltage drops to zero rapidly, check RT2, RT5, RT3, and RT4. The normal voltage should be around 3V.
LLC impulsive measurement :
 Fan failure:
Fan failure:
The power supply's internal fan is controlled by CPU U4. The PG signal (speed indicator) from the external fan is transmitted back to the mining machine's control board, which then sends PWM signals to both external fans.
Check if the power supply control board's connection pins to the mining machine's control board are properly connected to the corresponding pins on the power mainboard. If a burnout causes the connection to fail, use a jumper wire to reconnect the pins. For communication issues, inspect component U30 for scratches or missing parts.
CPU:
Front-end MCU U8: The pre-programmed MCU chip can be replaced. The rear-end MCU U34 requires parameter calibration after replacement and cannot be replaced arbitrarily.
The difference between P221B and P222B:
The P221B delivers 12 VDC, while the P222B provides 14 VDC. The two power supplies differ in their backend CPU (U34) programs, output filter capacitor capacities, and voltage ratings, though all other components remain identical.