


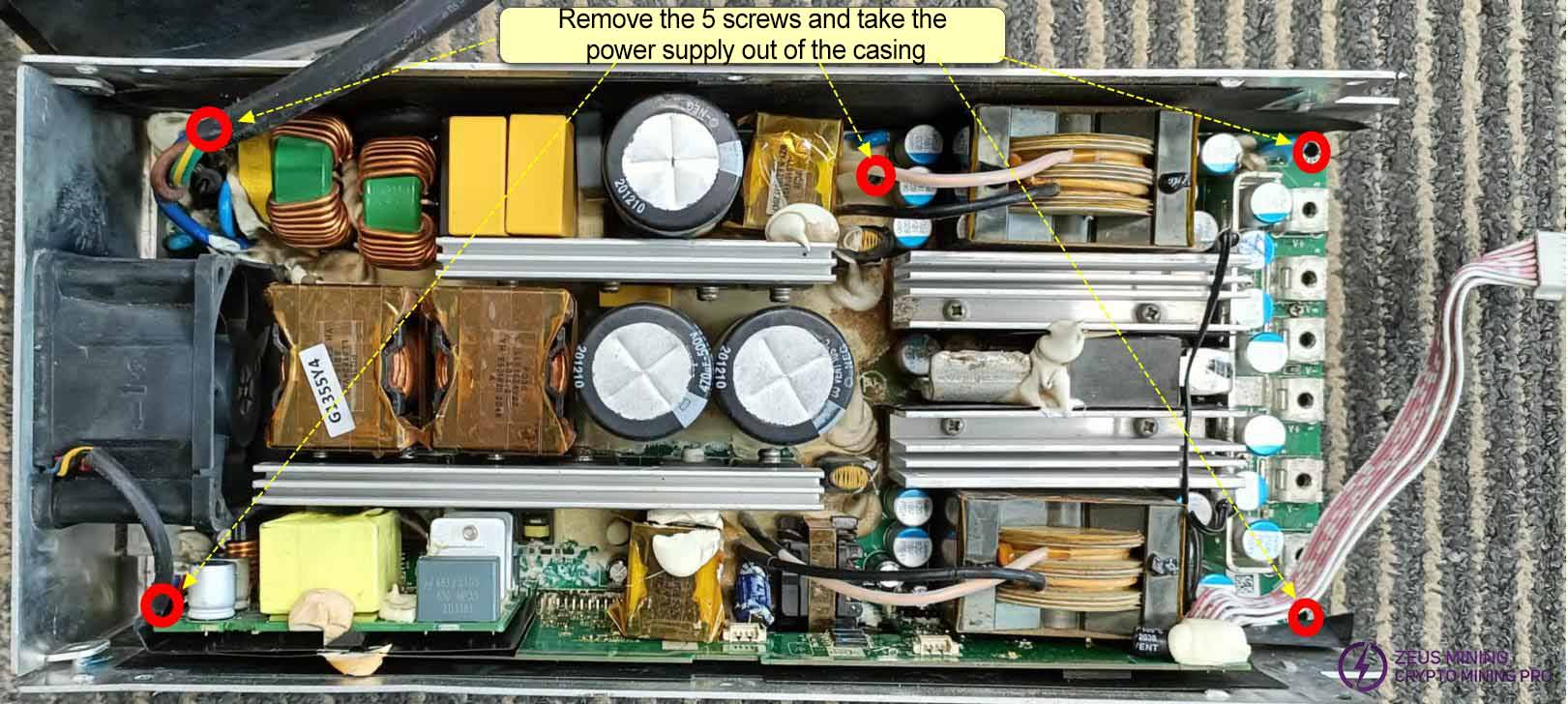
Gausspower P221C and P222C repair manual
Remove the entire power supply circuit from the power supply casing
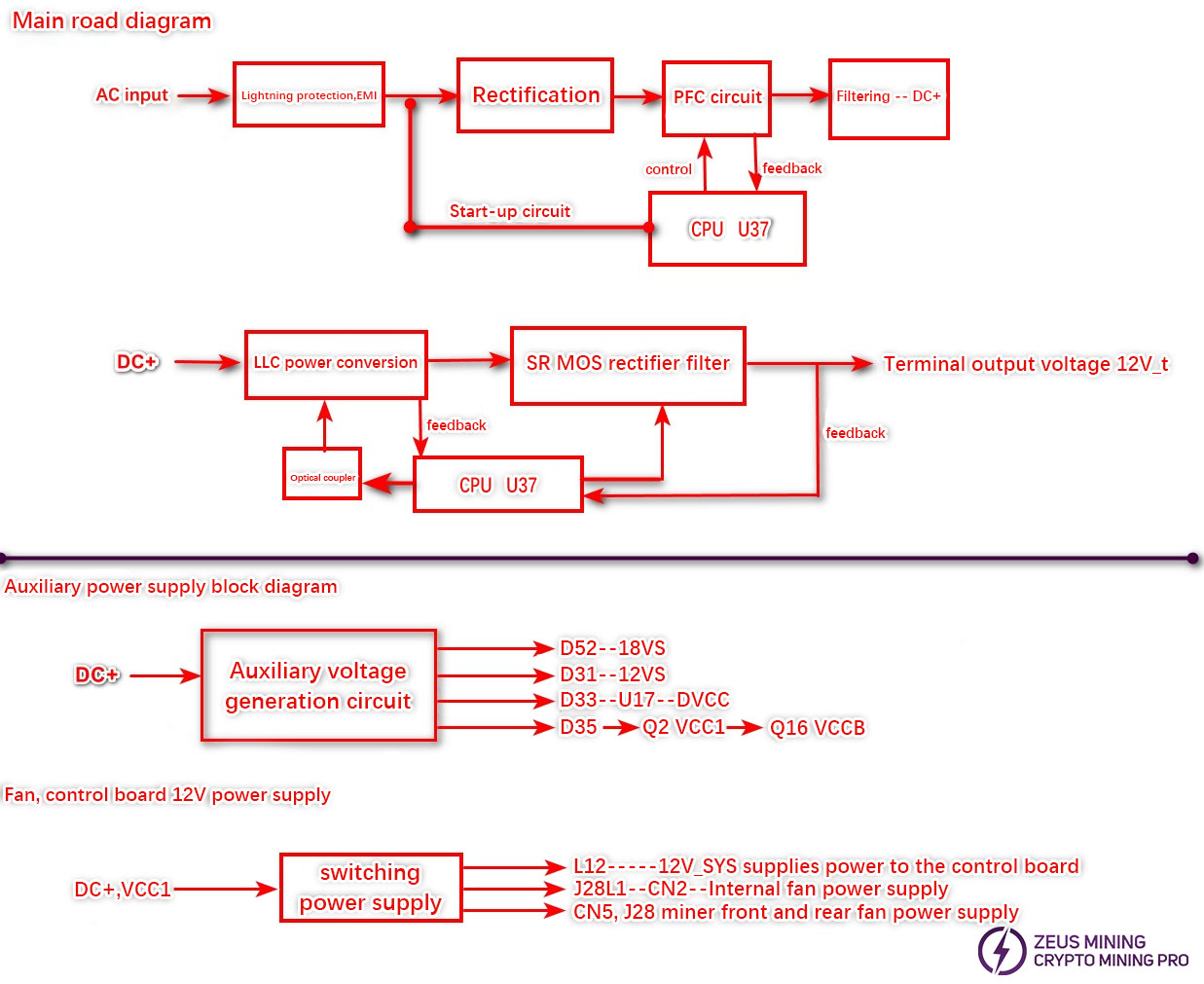
P221C/P222C Circuit Block Diagram
Working Principle:
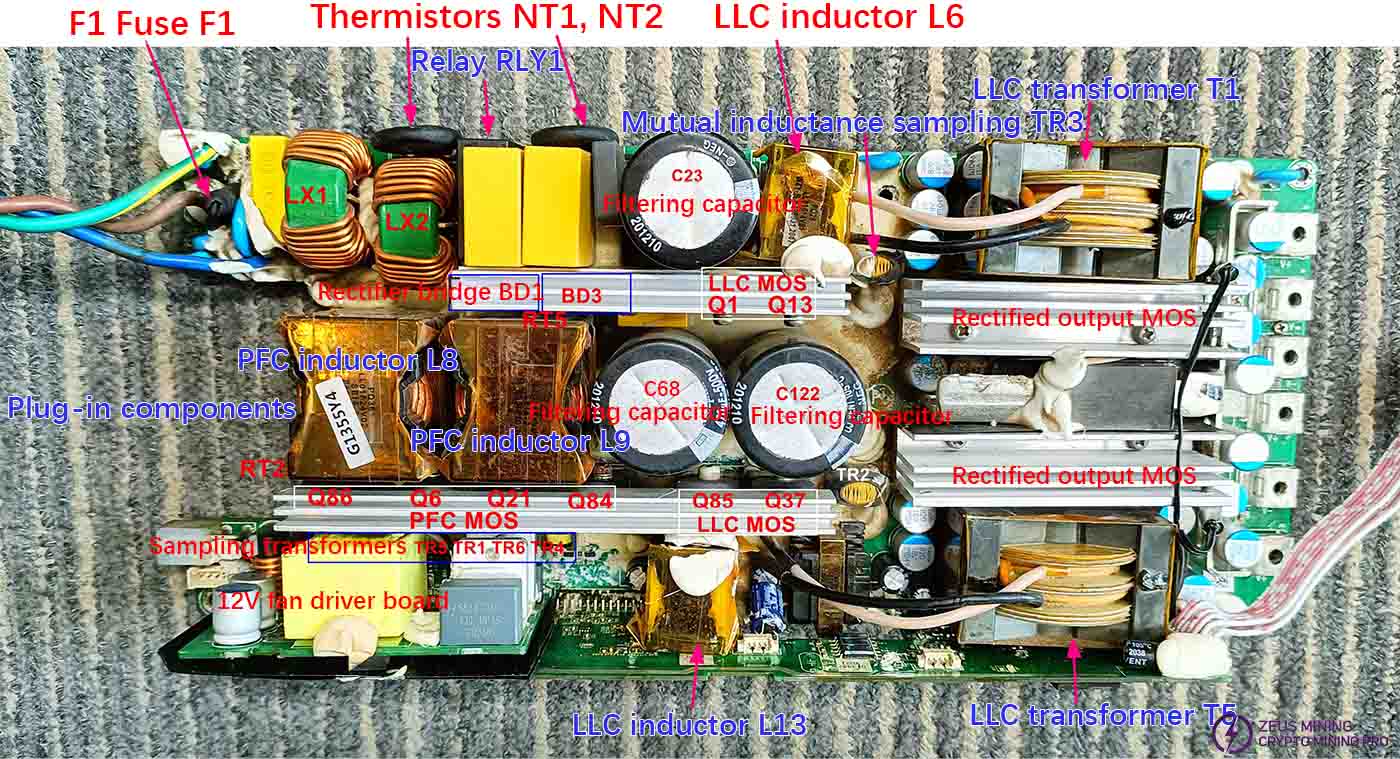
The AC input (L, N) passes through a fuse, interference suppression capacitors CY5, CY6, CX2, surge suppressor varistor VR1, and interference suppression inductors LX1, LX2, before being rectified by rectifier bridges BD1 and BD3. Capacitors C68, C23, and C122 filter the rectified voltage. The voltage after rectification of the switching power supply is approximately twice the input AC voltage, i.e., *220V = 311V. The DC voltage is generally around 300V, with a peak of approximately 311V. After the PFC circuit operates, the filter capacitor voltage increases by 100V, reaching approximately 400V (D+). The PFC circuit includes PFC inductors L8, L9, PFC MOS transistors Q6, Q86, Q84, Q21 and their driver circuits, PFC driver chips U13, U14, CPU control and feedback circuits. NT1 and NT2 are soft-start thermistors, and RLY1 is a soft-start relay. The LLC circuit consists of LLC MOS transistors Q1, Q13, L6, T1, C3, C10 and their driver circuits on one side, and Q37, Q85, L13, T5, C261, C252 and their driver circuits on the other side, which then feed the rectified MOS output to provide the final voltage.
The front-end MCU receives the front-end feedback sampling voltage and temperature sensing signals RT2, RT5 to control the PFC circuit and relay. The back-end MCU receives the back-end feedback sampling voltage and temperature sensing signals RT3, RT4 to control the LLC circuit and rectifier output circuit. The internal fan auxiliary power supply provides operating voltage for various chips.
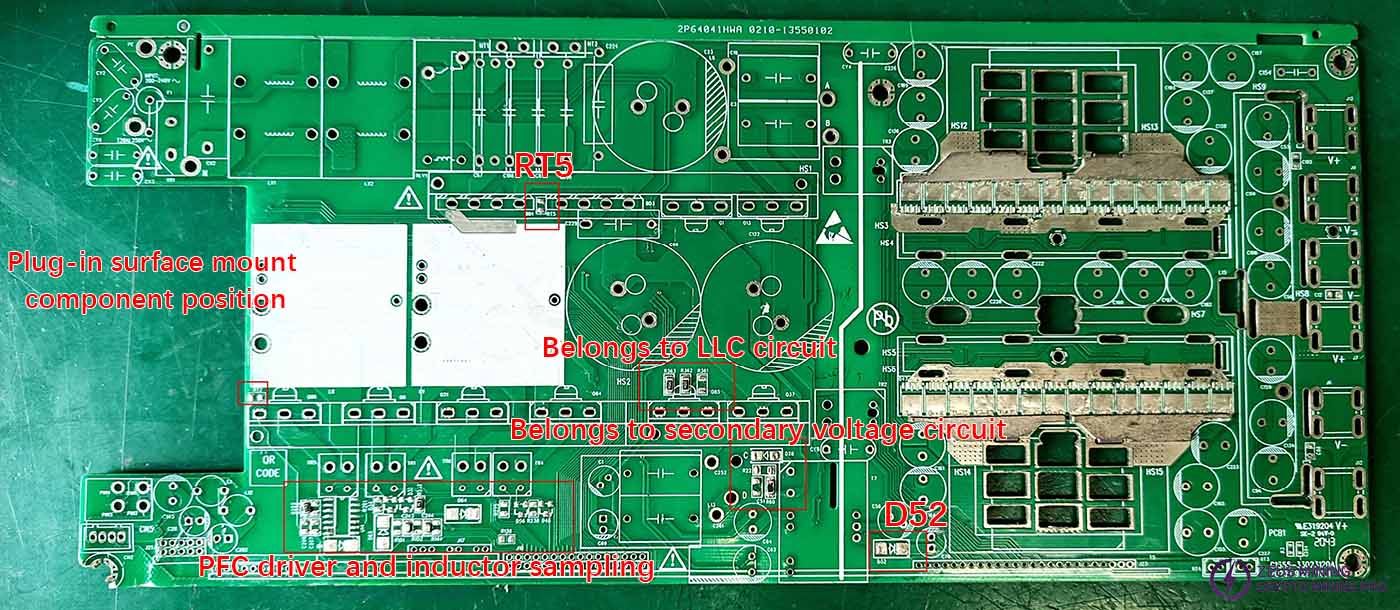
Plug-in component diagram
Pin diagram of through-hole components on the surface mount
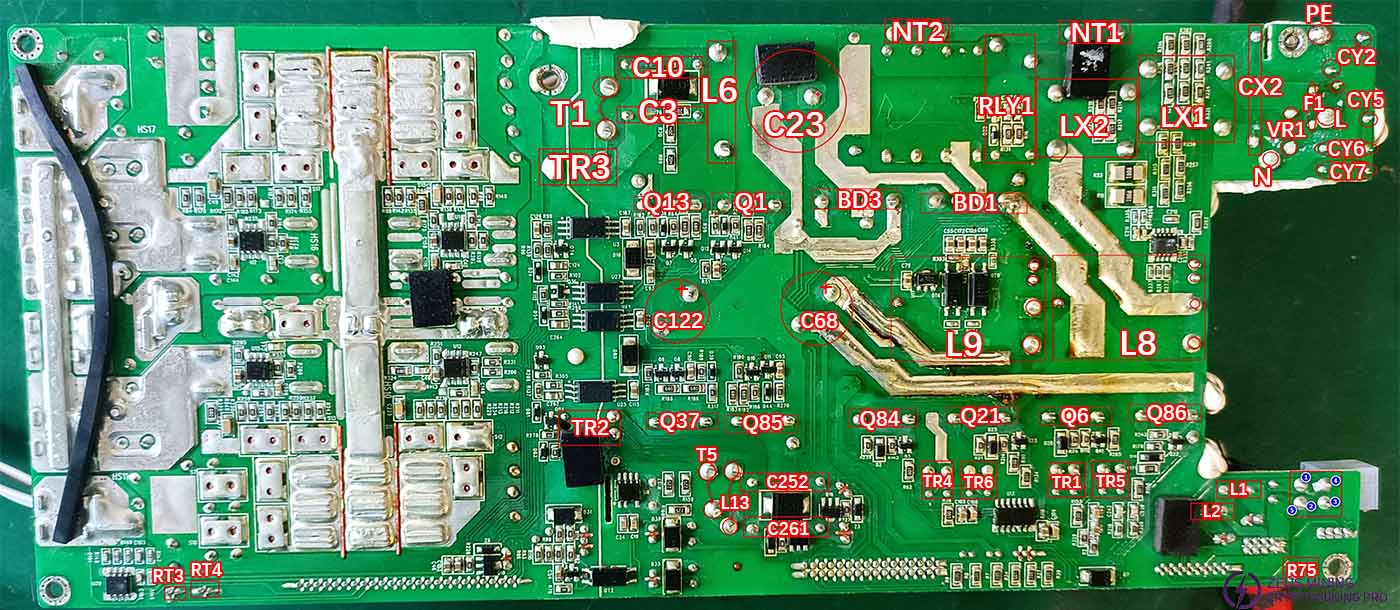
Functional differentiation of surface mount components
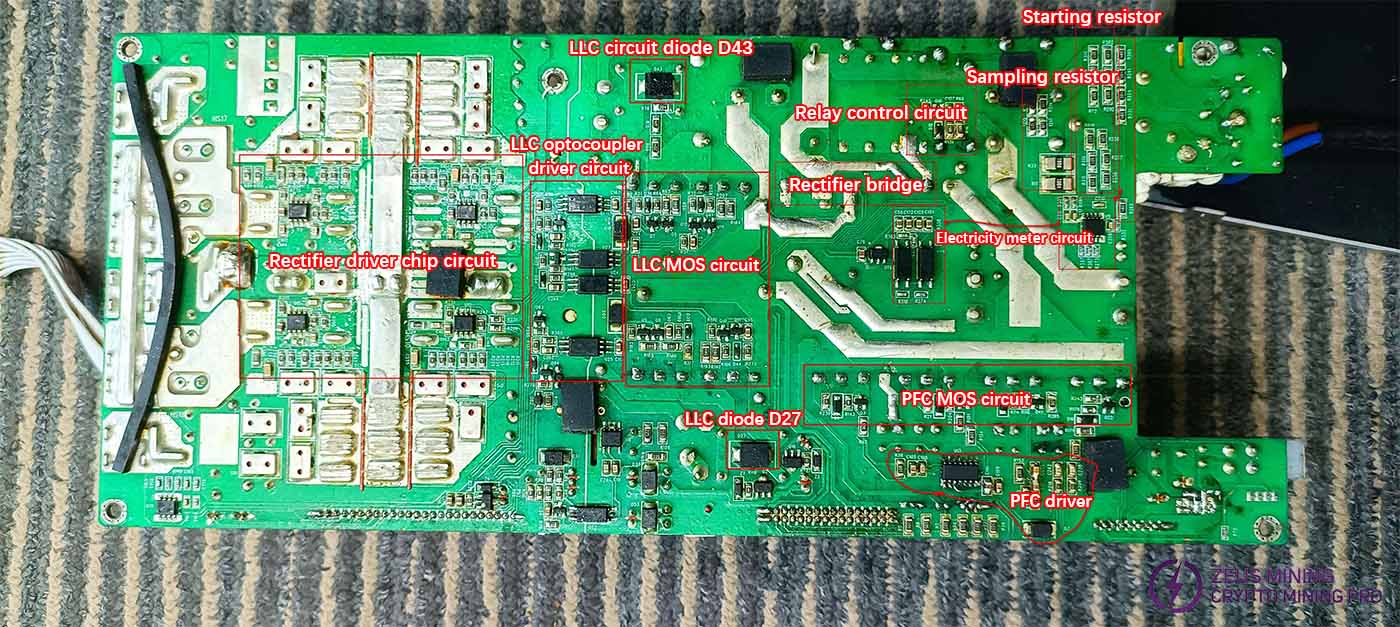
Position diagram of surface-mount components installed on the plug-in side
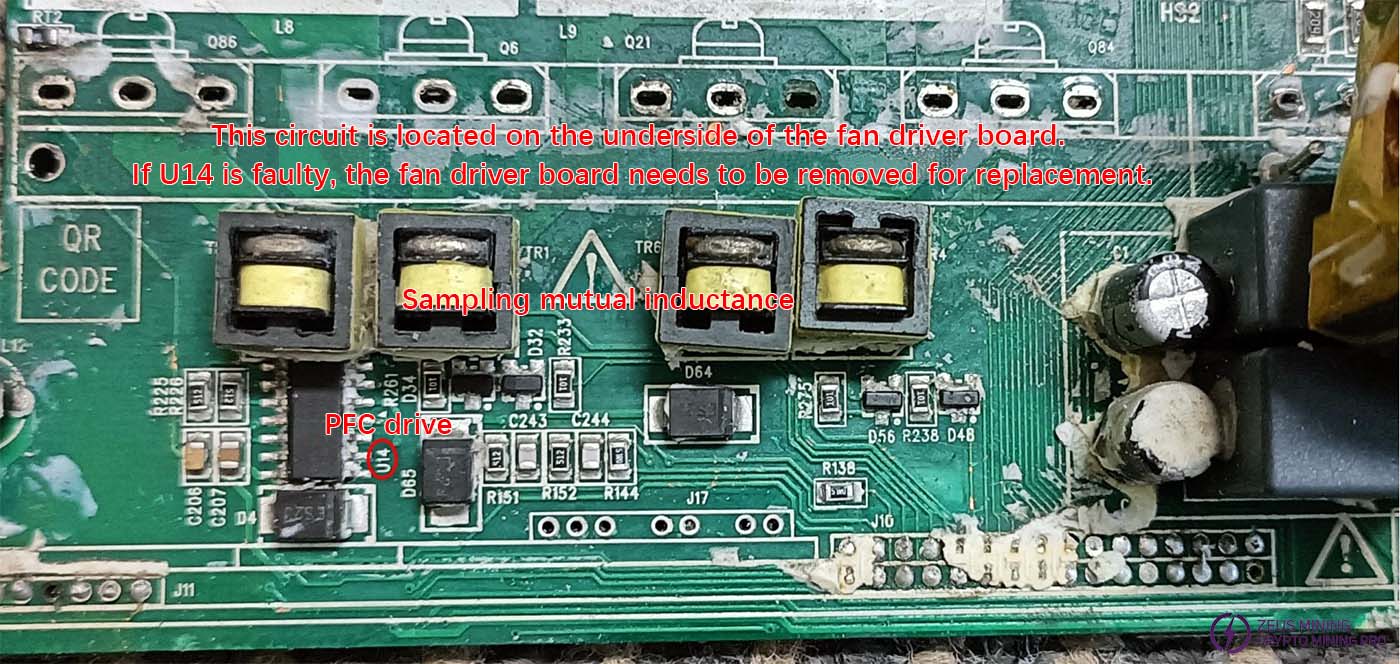
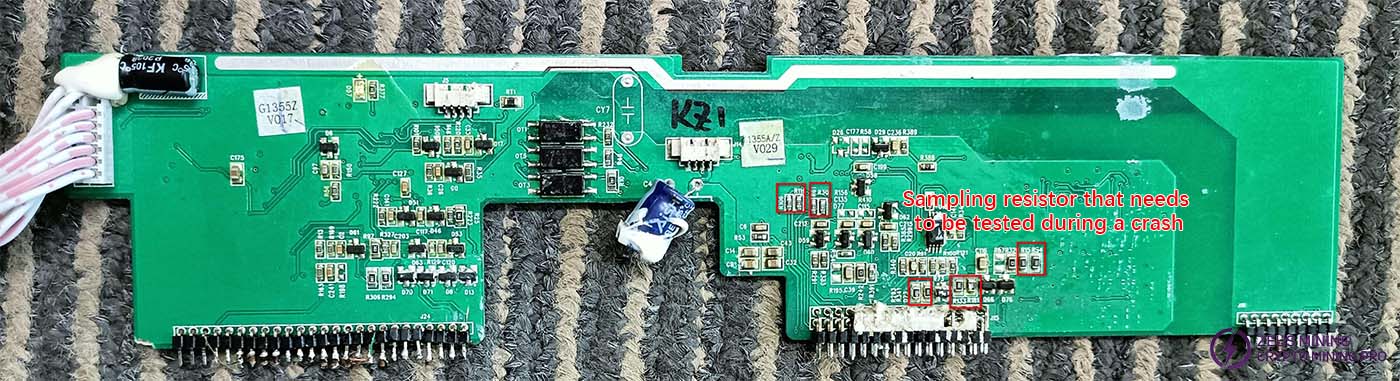
Fan driver board bottom circuit
 Auxiliary power supply voltage
Auxiliary power supply voltage
12V fan power supply board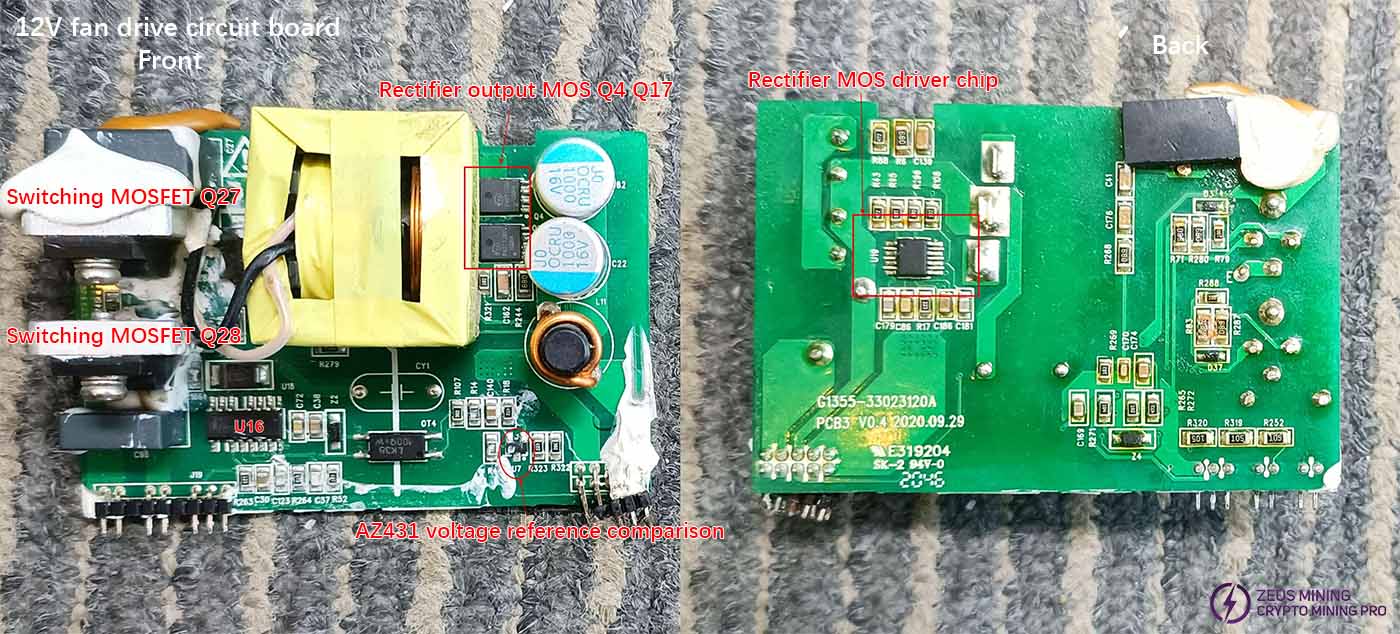
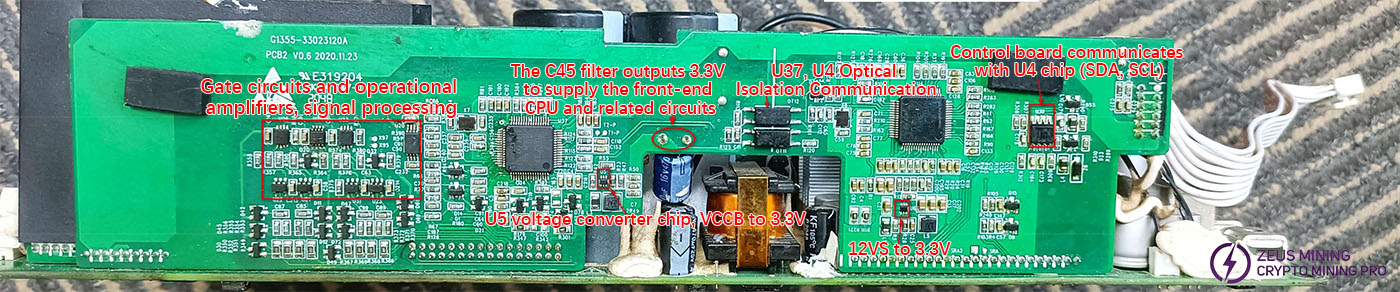
Main control board
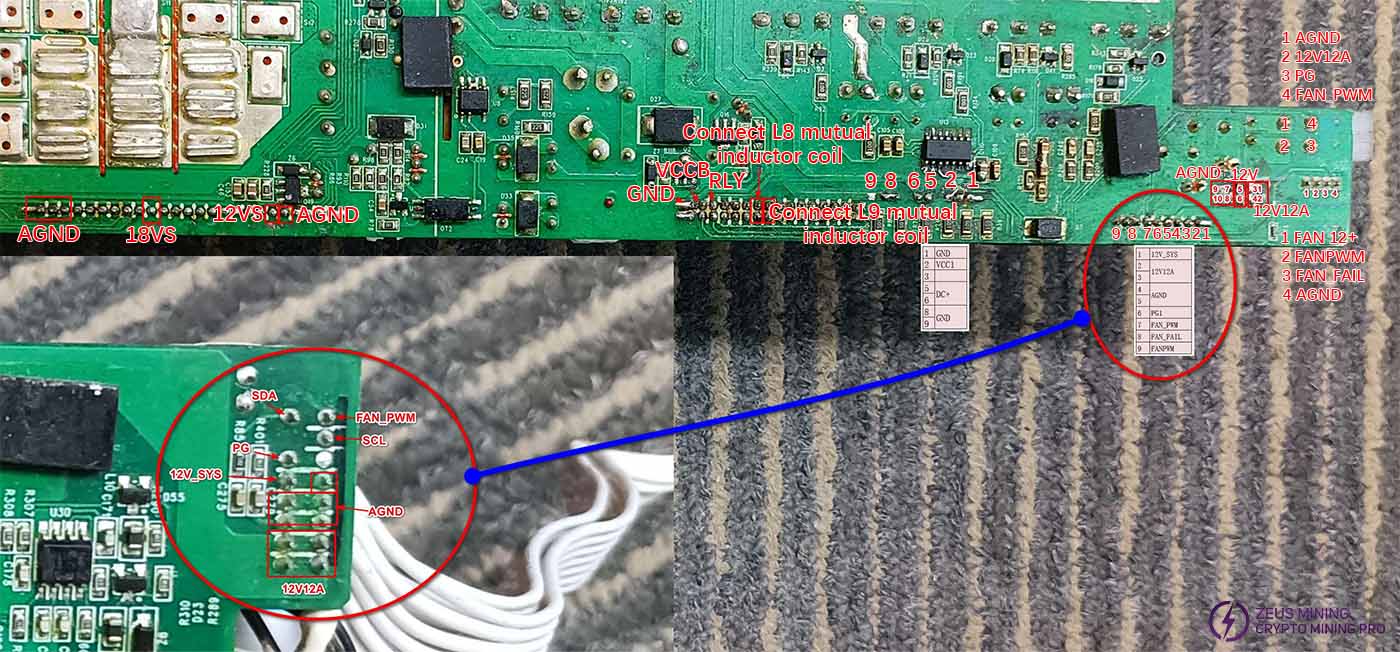
Connector pin functions
Repair Procedure:
Troubleshooting without power:
First, measure the resistance at the AC input terminal. If there is an open circuit, the fuse is blown. Perform an internal component inspection before applying power for testing. After opening the case, visually inspect for any burnt components or damaged copper traces. Replace any damaged components first.
PFC circuit inspection:
Measure the values of pins 1 and 3 of the PFC MOS transistor driver transistors Q3, Q23, Q41, and Q22 using the diode test function. The forward voltage should be approximately 0.56V, and the reverse voltage approximately 1.54V.
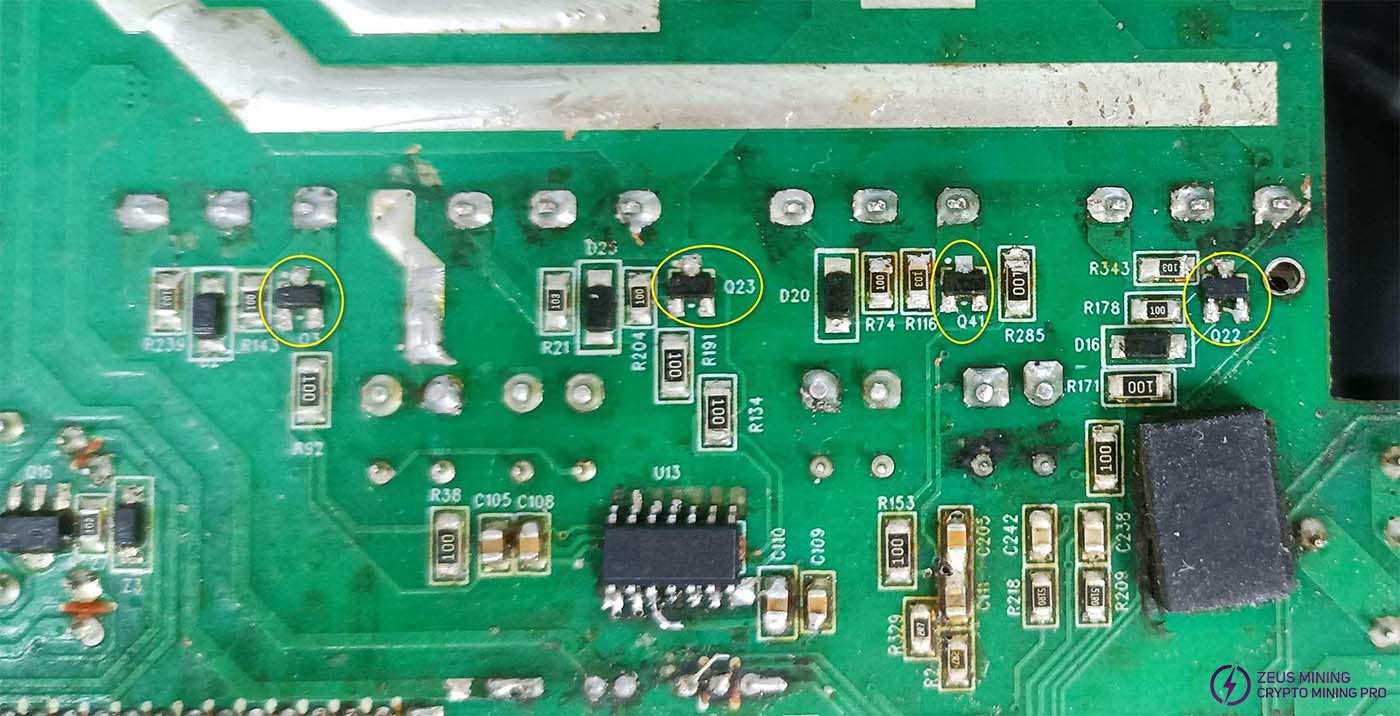
If the values at pins 1 and 3 of Q3, Q23, Q41, and Q22 are too high, consider that the 10-ohm resistor might be open-circuited. If the values are too low, the driver chips U13 and U14 might be damaged, the MOSFETs might be damaged, the four inductors RT5, RT1, RT6, and RT4 might be burned out, or the PCB traces might be broken. Use a multimeter to check the continuity between the inductors and the MOSFET pins as shown in the diagram.
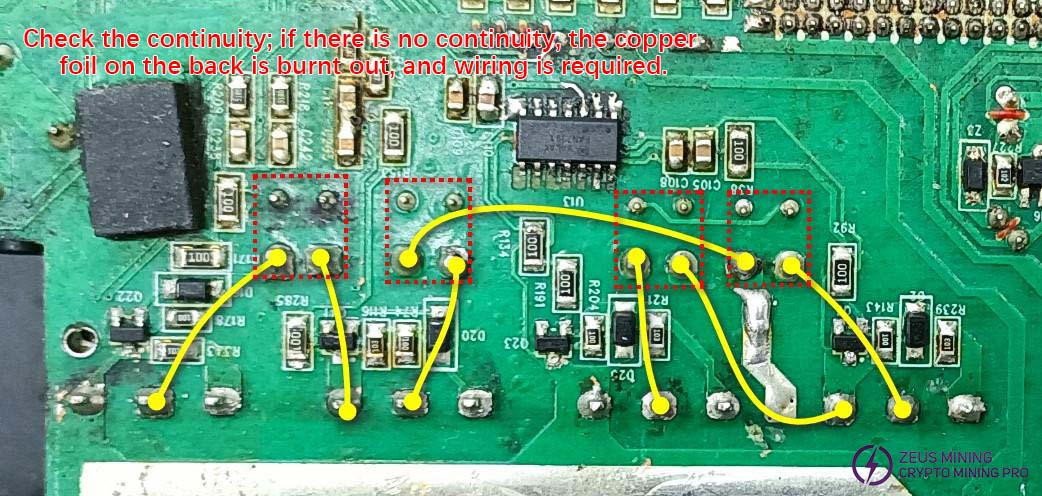
If the PFC MOSFET is faulty, the corresponding PFC driver IC usually needs to be replaced as well. When replacing the four PFC MOSFETs in the same power supply, they must all be of the same brand and model to maintain consistency.
PFC driver chips U13 and U14 troubleshooting:
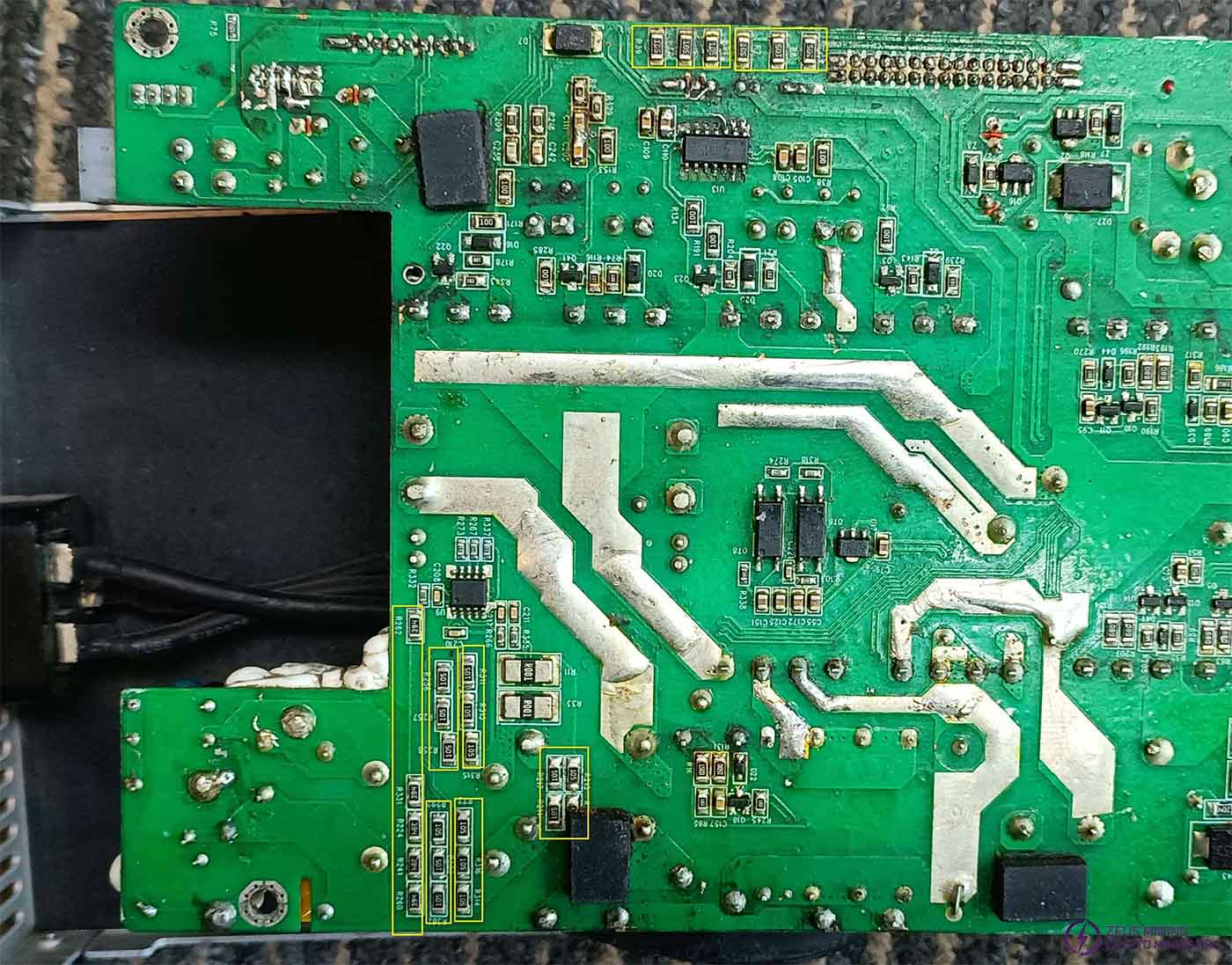
Check if there is a short circuit between (C105, C108) and (C109, C110) on U13, and between (C111, C205) on U14. Alternatively, check if the voltages are normal after power-on.
The resistance between U13's PIN1 and PIN2 to U37's Pin43 and Pin44 is normally 150 ohms. The resistance between U14's R209 and R218 and U37's pin42 and pin43 is also normally 150 ohms. The connection diagram is shown in the figure:

Checking the startup resistor and sampling feedback resistor:
The diagram shows the startup resistor and sampling resistor connected in series. For more accurate measurement, one of the resistors can be disconnected before measuring.
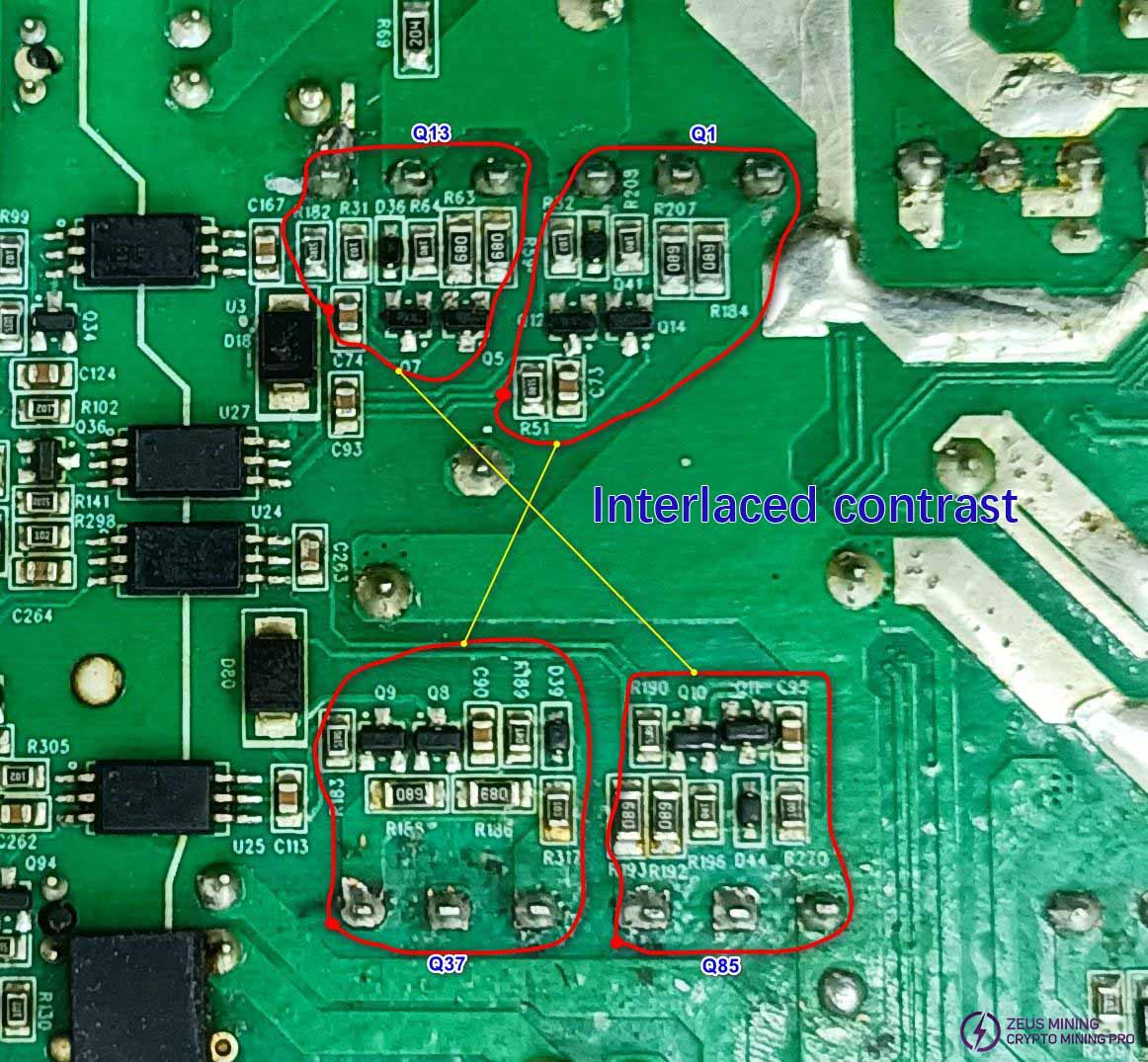
LLC Circuit Troubleshooting:
Compare the diode values of pins on MOS transistors Q1 and Q37, and Q13 and Q85. If the circuit is functioning correctly, the diode values should be approximately the same. A significantly lower value indicates a short circuit in the MOS transistor. If the value is significantly higher, further measurements of the associated push-pull driver transistors and resistors are required. Compare and measure components throughout the circuit.
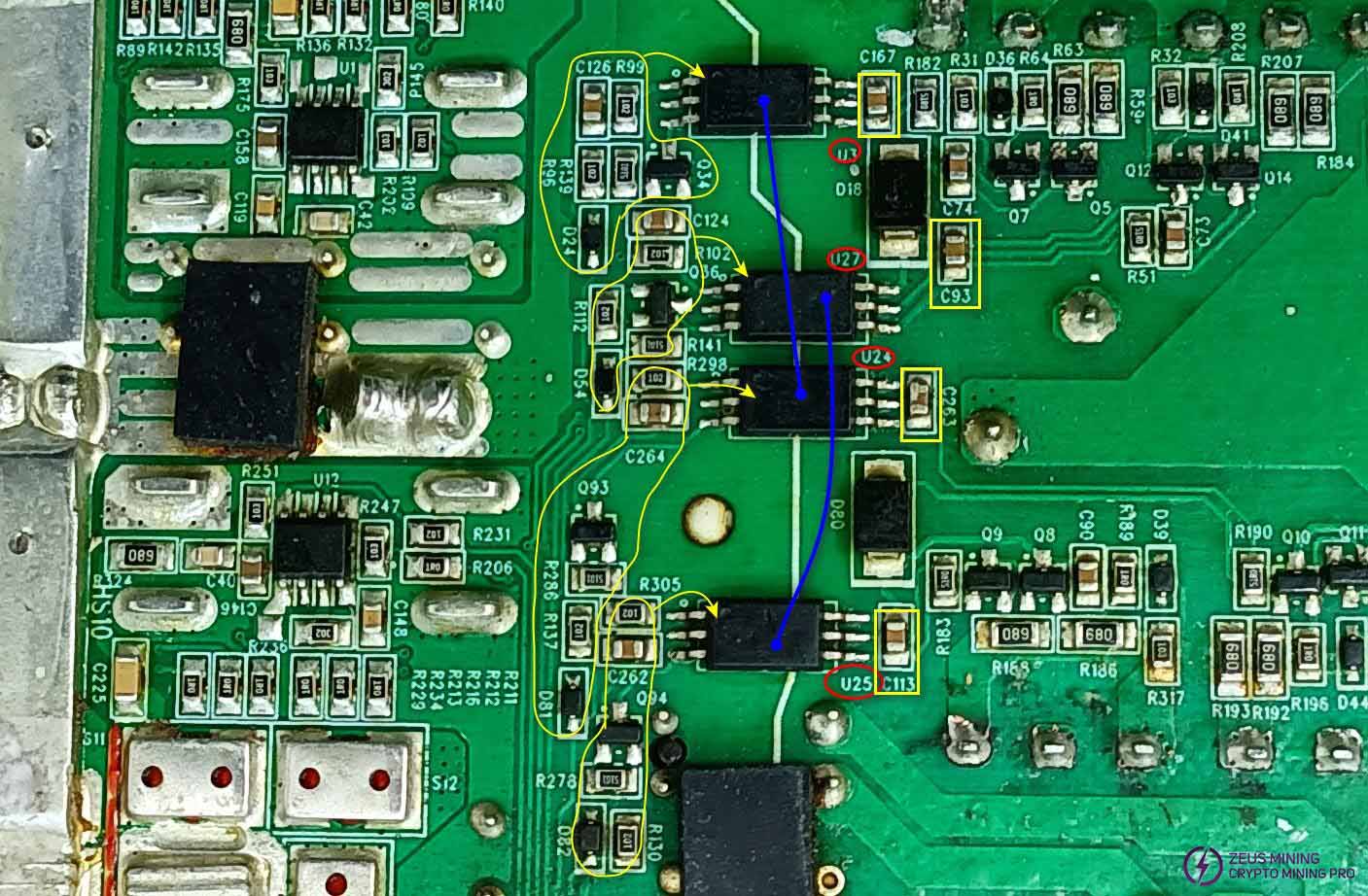
Optocoupler circuit inspection:
Compare the diode values of optocoupler circuits U3 and U24, and U27 and U25. Compare the receiving ends C167 with C263, and C93 with C113, to check for short circuits or differences in diode values. Compare the diode values of the corresponding transistors on the transmitting end: Q34 with Q93, and Q36 with Q94.
Output rectifier section check:
Problems with the output rectifier section generally do not cause the machine to crash.
Repair Procedure:
1. Measure for short circuits at the output terminals.
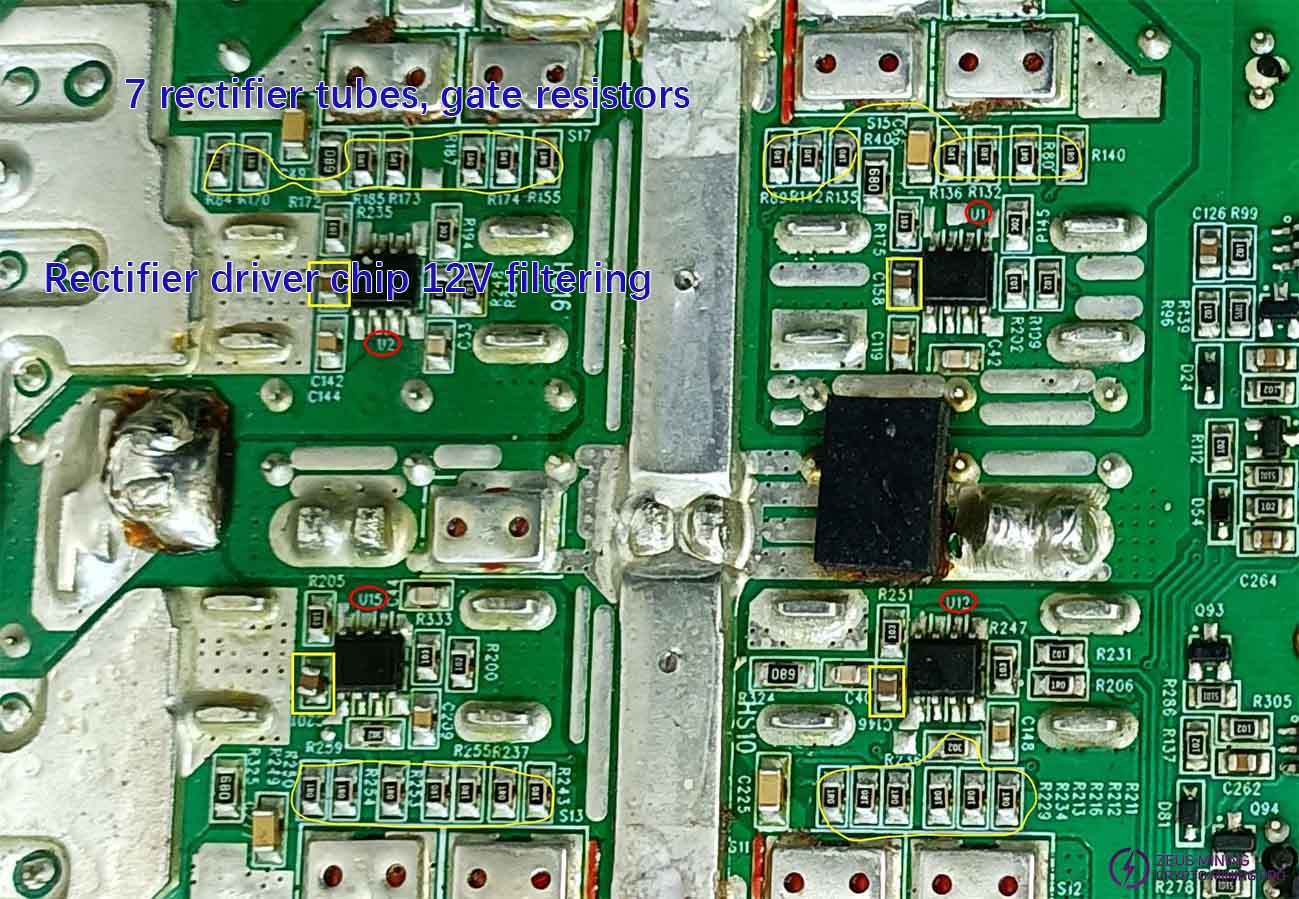
2. Rectifier driver chip fault diagnosis:
1) Measure the diode values of C142, C158, C201, and C146 to check for short circuits or abnormal resistance values.
2) Compare the diode values of the chip's pins.
3) Each rectifier group has seven 1R0 resistors, corresponding to seven MOS transistors. Measure the diode value of any resistor in each group, and compare the four groups. If the diode value of a group is abnormal, then there is a damaged MOS transistor in that group.
4) In the rectifier circuit containing damaged MOSFETs, compare the resistance values of pin 4 of each MOSFET. The MOSFET with the lowest resistance value is the damaged one. After replacing it, measure again. If there is still a difference, continue replacing the one with the lowest resistance value. If more than three MOSFETs are found to be defective after continuous checking, the entire set of rectifier MOSFETs needs to be replaced.
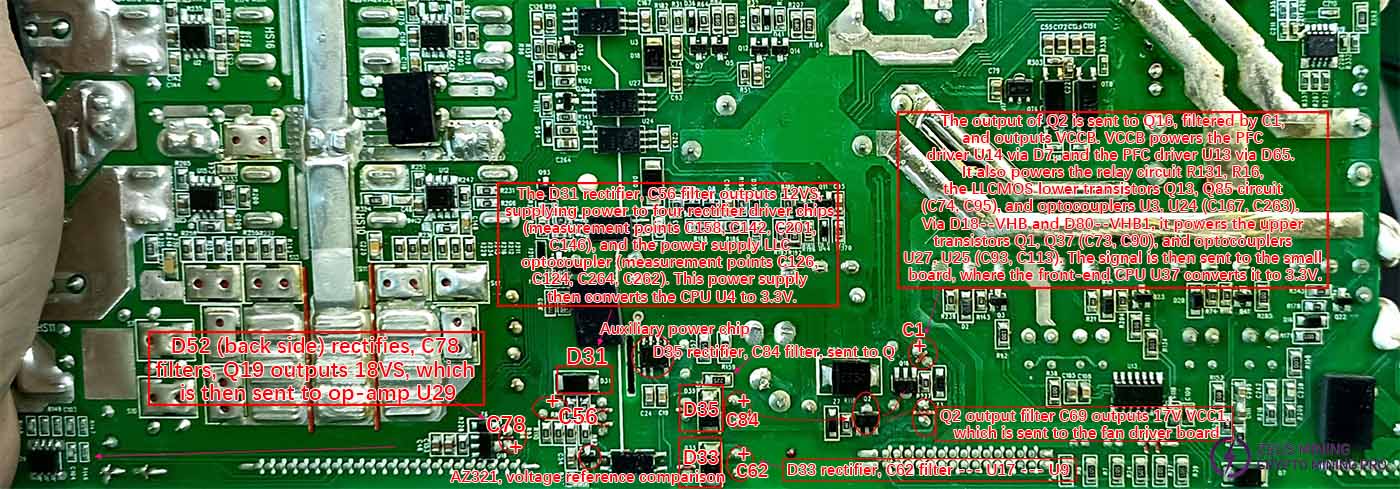
Auxiliary circuit control voltage circuit repair

Using the diode test function, compare the readings across the various filter capacitors. If there is a significant deviation in the measured values, the corresponding rectifier diode or the load circuit it supplies needs to be checked. Check the resistance to ground at pins 1, 2, and 4 of U8. D35 provides rectified output, C84 filters it, and sends it to Q2. C69 filters the output to provide VCC1, which supplies the fan auxiliary circuit. VCC1 is sent to Q16, filtered by C1 to output VCCB. D31 rectifies, C56 filters to provide 12VS. D52 rectifies, C78 filters, and sends the signal through Q19 to U29. D33 rectifies, C62 filters and sends the signal to U17, supplying power to OT6, OT8, and the meter chip U9.
After powering on, check if the output voltage across the capacitor is normal.
CPU Circuit Check:
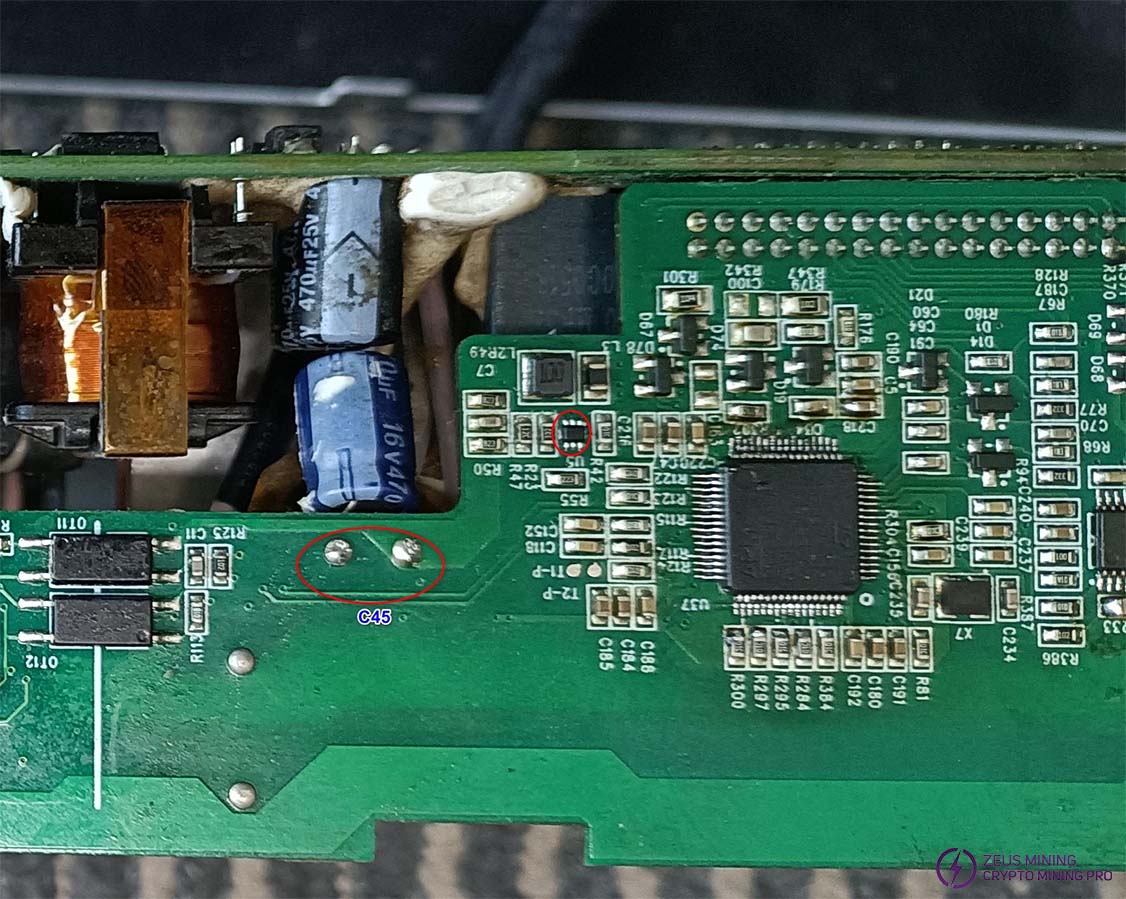
3.3V power supply is filtered by C45 and supplied to U37. Measure the value of C45 using a diode test mode. A forward voltage of approximately 0.37V and a reverse voltage between 0.6V and 0.9V is considered normal. If the measured value is outside this range, remove U37 and measure C45 again. If the measured value returns to the normal range, U37 is considered defective. If the value remains abnormal, U5 is considered defective.

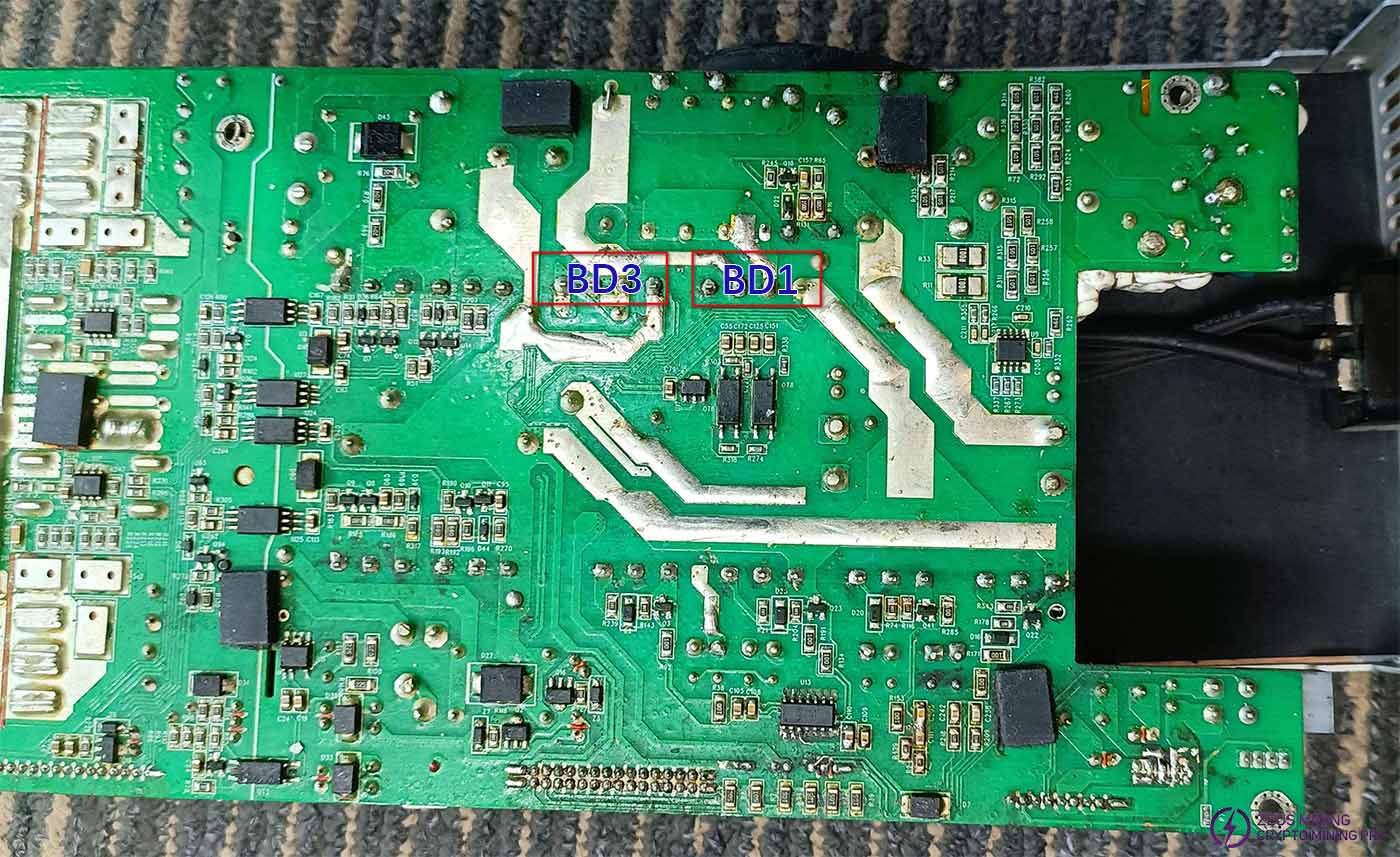
Before powering on the circuit after repair, the large filter capacitor C68 needs to be measured again using the diode test mode. The forward measurement should be around 0.48, and the reverse measurement should show an open circuit. If the measured values differ significantly, or the reverse measurement does not show an open circuit, then check the rectifier bridges BD1 and BD3 (clean the solder from the pins before measuring), and the MOSFETs of the PFC and LLC circuits.
After the above comprehensive non-powered inspection and repair, a powered-on check can be performed for confirmation:
If you hear a clicking sound from the relay closing after powering on, it should be working normally.
After powering on, measure the voltage across capacitor C86; if it's around 400V, the PFC circuit is working normally.
Check if the auxiliary control voltage C1 outputs approximately 14V (VCCB). If the output is normal, the auxiliary voltage is basically normal.
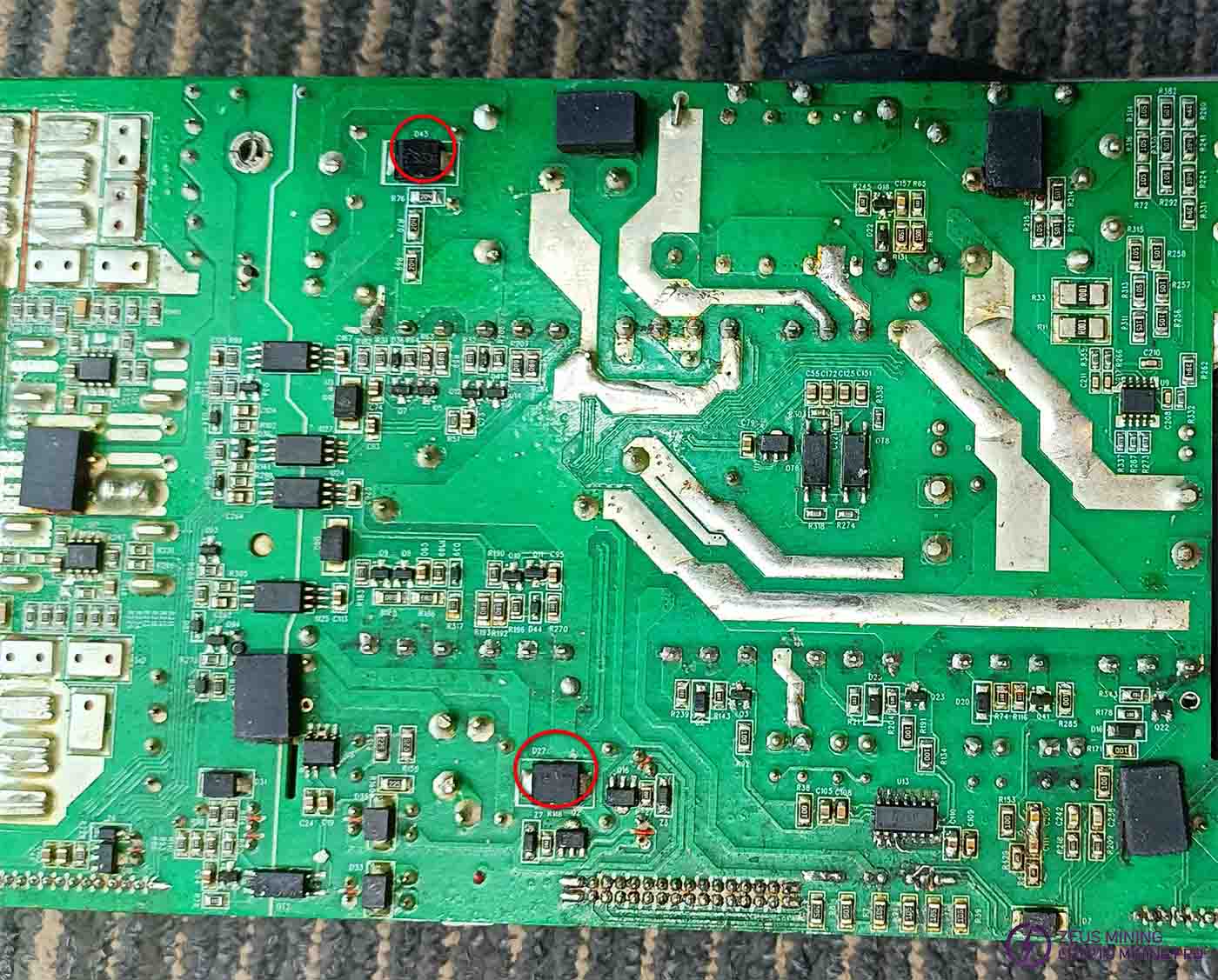
Connect the unlock control board and use a multimeter in voltage mode to measure D27 and D43 for a pulsed voltage of 12-120V. Observe whether the decimal point of the measured value periodically fluctuates. If there is no fluctuation or the fluctuation range is small, the LLC circuit on this side is not working properly.
If the output voltage is normal but the device cannot drive the load after being powered on, it may be due to the PFC or LLC working unilaterally, or due to capacitor aging. Use a capacitance meter to check the capacitance value of the capacitors, such as LLC capacitors C3, C10, C252, and C261. The total capacitance at the output should be around 20mF. If the capacitance is insufficient, replace the capacitors until the capacitance value is restored.
If the output protection is triggered after powering on, and the output voltage quickly drops to zero, check RT2, RT5, RT3, and RT4. The normal voltage should be around 3V.
Fan malfunction:
The fan inside the power supply is controlled by CPU U4. The PG signal (speed feedback signal) of the external mining rig fan is sent back to the miner control board, and the PWM signal is sent from the miner control board to the two external fans.
Check if the pins of the ribbon cable connecting the power supply control board to the miner control board are properly connected to the corresponding pins on the power supply mainboard. If a connection is broken due to burning, a jumper wire can be used to connect the corresponding pins.
Check for damage to the feedback components at the output of R3 and C204 caused by screw tightening.

CPU:
Front-end MCU U37: The programmed MCU chip can be replaced. The back-end MCU U4 requires parameter calibration after replacement and cannot be replaced arbitrarily.
Differences between P221C and P222C:
P221C output voltage: 12VDC, P222C output voltage: 14VDC. The programs in the back-end CPU U4 of the two power supplies are different, and the capacitance and voltage rating of the output filter capacitors are also different. Other parts remain the same.
Dear Customers,
Hello everyone, as China is about to usher in the Spring Festival, international logistics will be suspended. Zeus Mining is scheduled to stop shipping on February 11, 2026, and start the Spring Festival holiday from February 12 to February 23, 2026 (GMT+8). Pre-sales and after-sales service will reply to the information on February 24, 2026, and shipping will resume on February 24, 2026. Thank you for your support and trust in 2025. In 2026 and the future, we will bring better products and services to our friends.
Best wishes,
ZEUS MINING CO., LTD.