


The new ElphaPex FP-103 power supply unit (PSU) is used to replace the irreparable failed part of the DG1+ miner and restore its performance.This article will describe various troubleshooting methods for this power supply and how to use testing tools to pinpoint the problem.
I. Requirements for the repair platform
1. Constant temperature soldering iron above 80W (soldering temperature 300-350℃) with a pointed tip for soldering small surface-mount components such as resistors and capacitors, and a knife-shaped tip for soldering and replacing through-hole components (soldering temperature 380-420℃).
2. Hot air gun for chip removal and soldering; be careful not to heat for too long to avoid PCB blistering (soldering temperature 260℃).
3. AC controllable power supply/voltage regulator (output 200-250V, current limit 0-30A) for power-on testing of BC442A18-01.
Alternatively, a 100W incandescent light bulb can be connected in series with the AC live wire for safety.
4. Electronic load (4KW power, 0-50V voltage range). Alternatively, a power resistor load matching 4kW can be used.
5. Multimeter, desoldering gun, tweezers, V9-1.2 test fixture with dedicated power supply and test card firmware (oscilloscope is optional).
6. Solder flux, lead-free solder wire, PCB cleaning solution and anhydrous alcohol;The PCB cleaning solution is used to clean flux residue and improve appearance after repair.
7. Thermal conductive grease (2500) for thermal conduction between MOS and heat sink after repair; thermal conductive silicone (704 silicone) for fixing and covering damaged original adhesive points on PCBA components after repair.
II. Maintenance work requirements
1. Repair personnel must possess a certain level of electronic knowledge, at least one year of repair experience, and an understanding of the working principles of switching power supplies.
2. Before opening the product casing and repairing the PCBA board, the large capacitors must be discharged. Welding can only begin after measuring with a multimeter and confirming that there is no voltage (less than 5V indicates complete discharge)! Take precautions to avoid electric shock.
3. Pay attention to proper work procedures when troubleshooting circuit components. After replacing any components, the PCB board should show no significant deformation, and the solder joints should be reliable. Check for missing components, open circuits, or short circuits in the replaced parts and surrounding areas.
4. After replacing critical components, the main circuit must be checked and measured to ensure there are no short circuits or other obvious abnormalities before applying AC voltage for testing; otherwise, there is a risk of equipment failure.
5. When applying AC 220V voltage to troubleshoot circuit signals, pay attention to safety precautions.
Maintenance personnel must meet the required qualifications:
(1) The instruments and equipment used for maintenance must meet the specified requirements;
(2) The instruments and equipment being repaired must be properly grounded, and the repair environment must comply with anti-static requirements;
(3) The materials used for maintenance must meet the specified requirements;
(4) To ensure the accuracy and traceability of the materials used for maintenance, the materials must be the production materials corresponding to the specific model, and material replacements must be confirmed as correct;
1. To prevent potential electric shock hazards, non-professional personnel should not open the casing;
2. When repairing the power adapter, maintenance personnel are required to use a dedicated casing opening tool to avoid damaging internal components;
3. After opening the product casing, the high-voltage capacitors must be discharged;
4. Electronic waste generated during product repair must not be discarded indiscriminately;
5. Defective products must be marked with a repair process card indicating the cause of the defect and placed in designated areas;
6. Repaired products must be clearly marked for identification;
7. Repaired products must be placed in the designated repaired area and undergo systematic testing before being returned to inventory.
III. The principle and structure of the circuit
1. Principle Overview
1.1 The BC442A18-01 consists of a main board, two PFC control boards, an auxiliary power supply control board, and two SR boards. Normally, it receives two 220Vac inputs and provides two DC outputs: an auxiliary output of Vaux-12V and a main voltage output of 17V-22V. Communication and control with the mining rig are performed via the I2C communication port.
1.2 The performance characteristics and application scope are described below: The BC442A18-01 is a high-efficiency DC power supply designed and manufactured by our company, featuring single-phase AC input and two DC outputs:
(1) High-efficiency, high-reliability server power supply
(2) Dual output: Main output 4200W, auxiliary output 240W
(3) Output voltage: V1/17-22V, Vsb/12.3V
(4) High-efficiency design: Full-load efficiency above 94% in the operating range
(5) AC input 200-264Vac, 16A*2
(6) Built-in fan cooling
(7) Output undervoltage, overvoltage, overcurrent, and short-circuit protection; input overvoltage and undervoltage protection; overtemperature protection
(8) I2C communication
1.3 BC442A18-01 Appearance Description
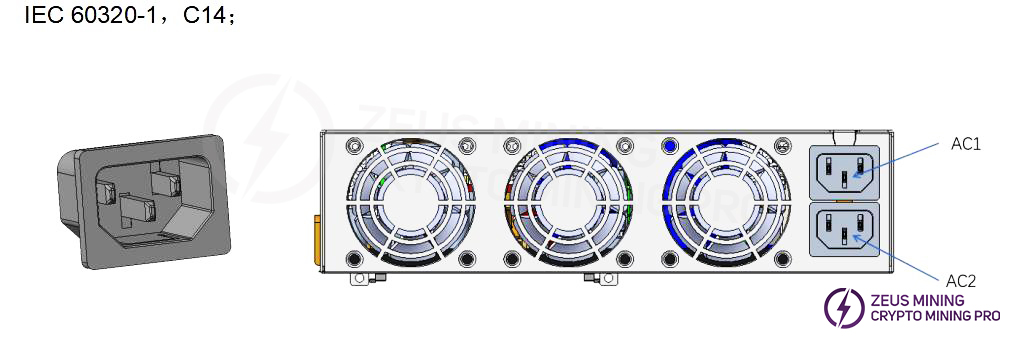
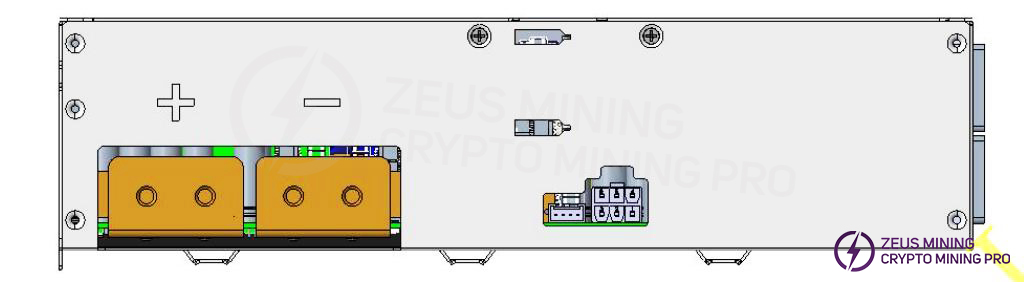
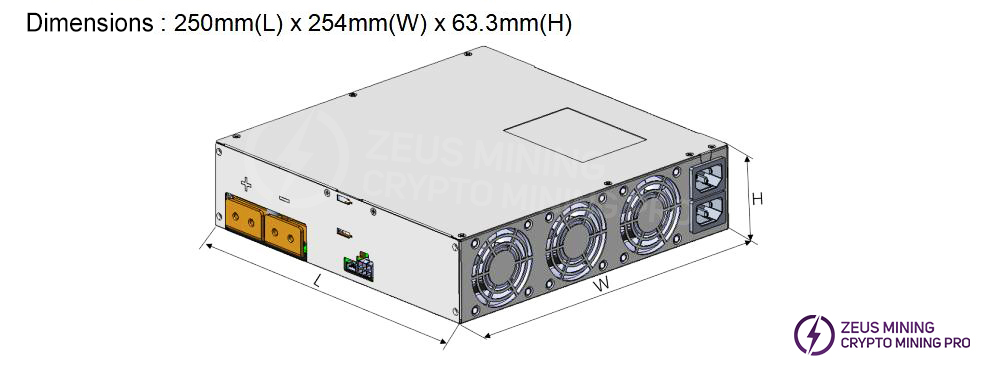
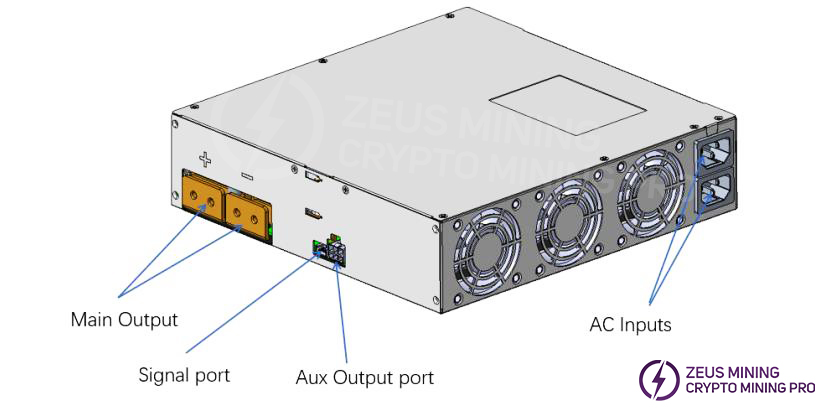
2. Troubleshooting approaches and case studies for common malfunctions
2.1 Basic Block Diagram of Power Supply Principles
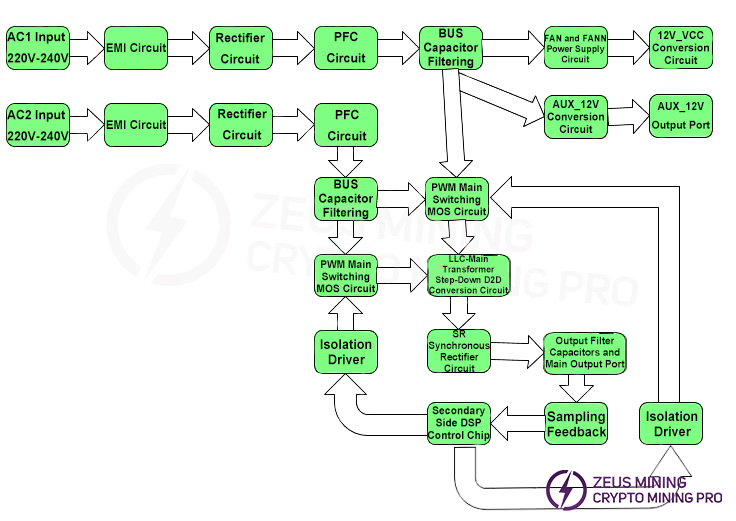
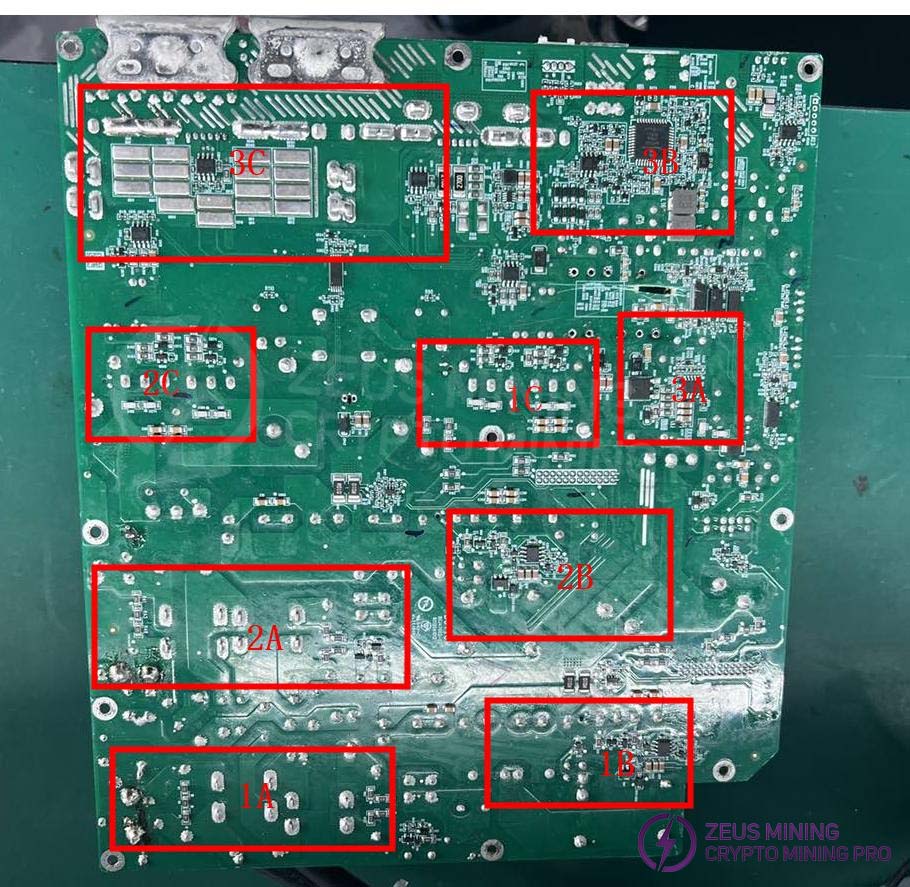
3. Power supply PCB layout
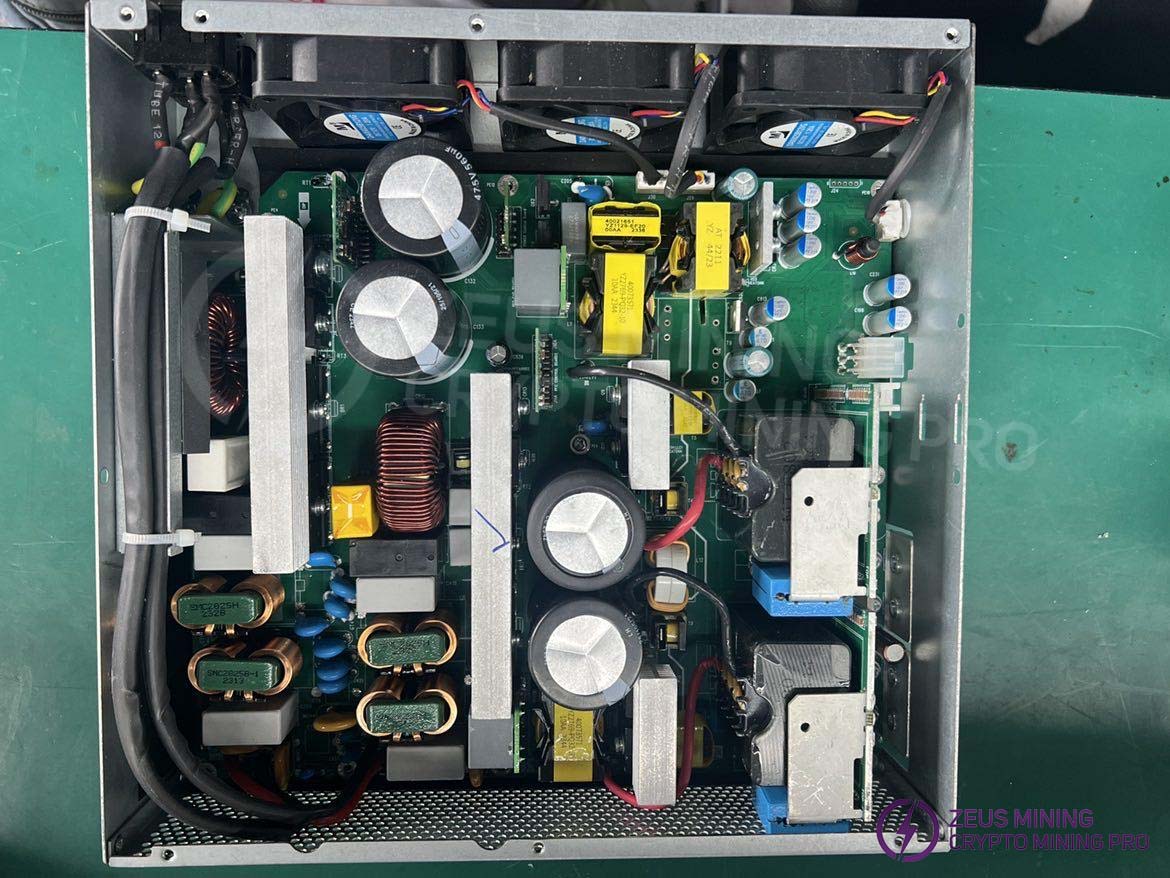
3.1 Layout Marking Description:
(1) 1A - First AC input and EMI circuit, 1B - PFC switching transistor and driver circuit, 1C - DCDC PWM driver circuit and main power MOSFET
(2) 2A - Second AC input and EMI circuit, 1B - PFC switching transistor and driver circuit, 1C - DCDC PWM driver circuit and main power MOSFET
(3) 3A - Auxiliary power supply circuit, 3B - Secondary side DSP control circuit, 3C - Main output filter capacitor and main output port
Note: The actual product images may have slight differences due to different versions, but the principle remains the same.
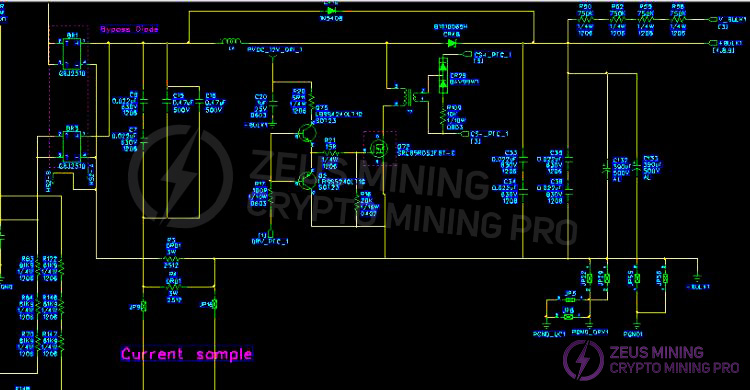
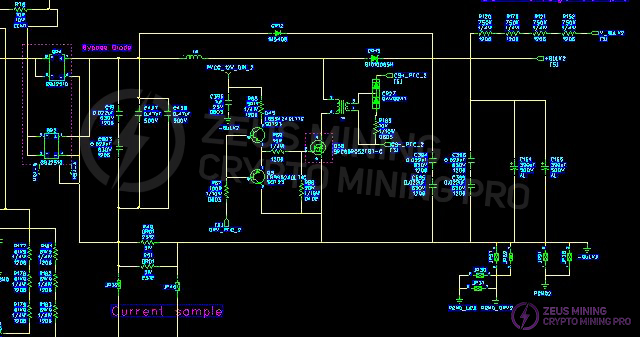
 3.2 Schematic diagram of the dual AC input EMI to PFC circuit:
3.2 Schematic diagram of the dual AC input EMI to PFC circuit:
Use a multimeter to check if the F1 fuse at the AC1 input is open, and if there are any short circuits in the BR1 & BR3 rectifier bridges, PFCMOSQ72, CR16, and CR48 (the inspection method for the other channel is the same). Pay attention to the resistors in the circuit surrounding the faulty MOSFET: the transistor may be damaged and needs to be replaced. Under normal operation, the voltage across the bus capacitors C134, C135, C132, and C133 should be 410V-450V.
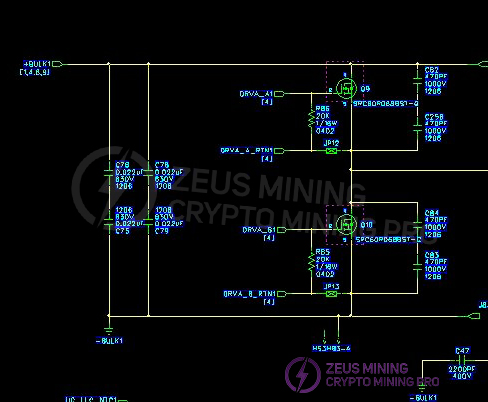
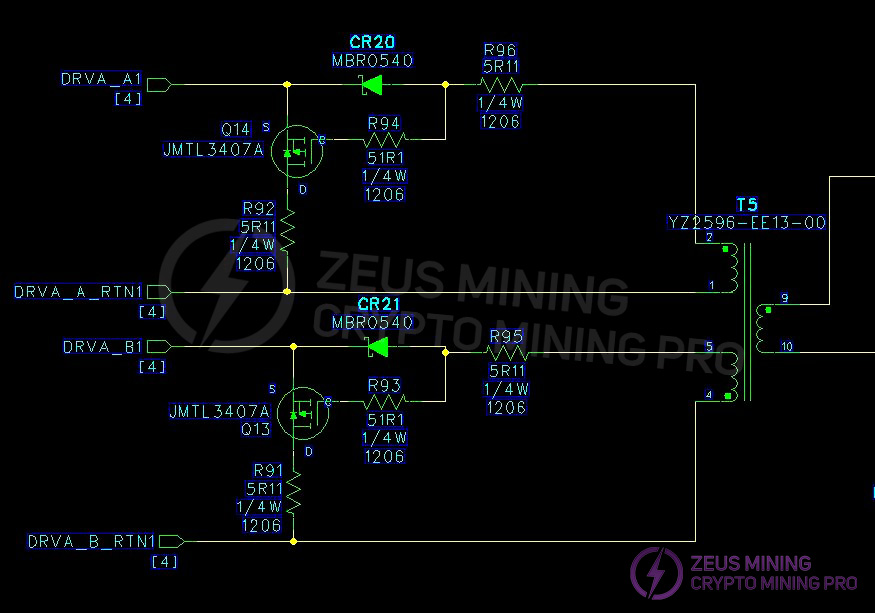
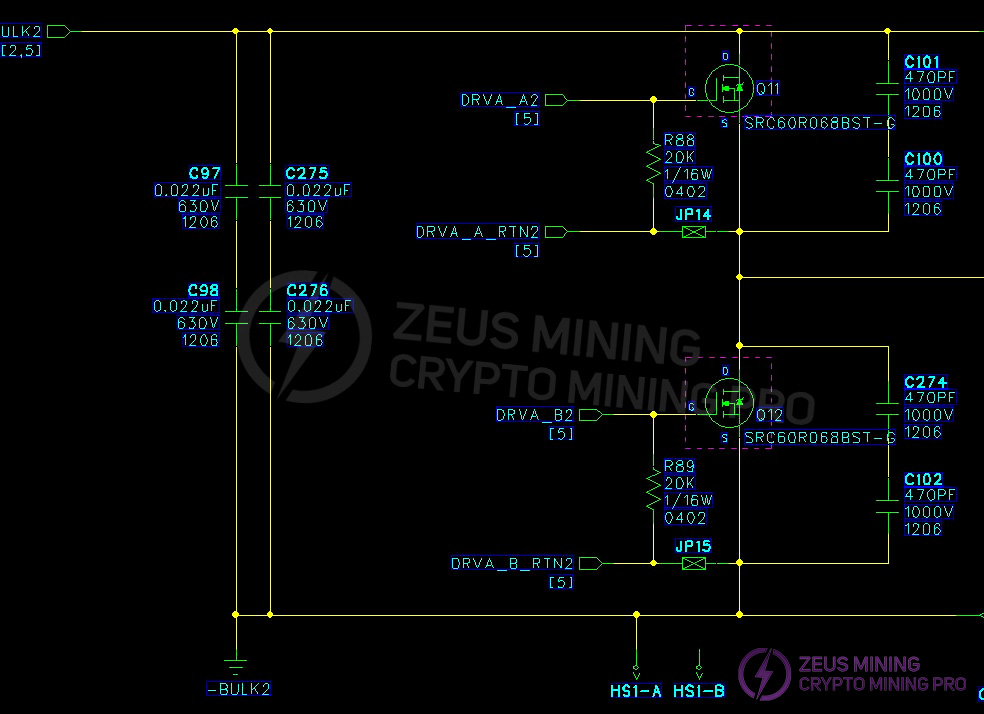
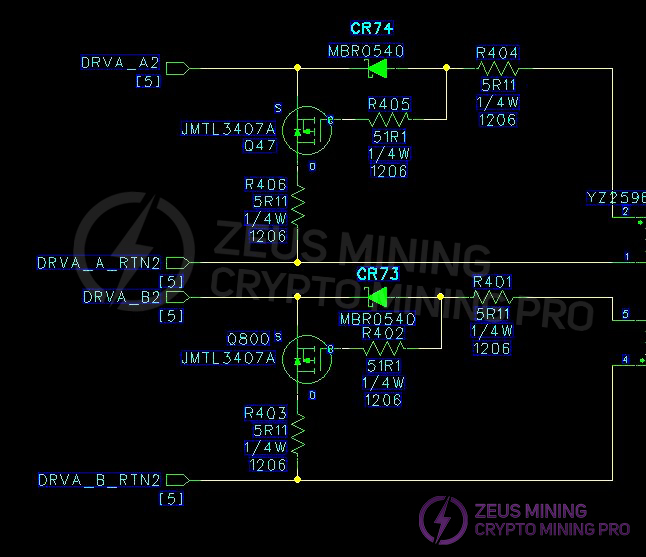
3.3 Two-channel LLC main switch DC-DC buck converter circuit and output SR synchronous rectification filter circuit:
Measurement of PWM circuit main switches MOS Q9, Q10, Q11, Q12; and surface-mount MOS Q907 and Q9 on the output SR board.

3.4 Repair steps
(1) Check the power supply's appearance for severe damage or deformation, and check if the DC fan and AC socket are damaged.
(2) Apply AC 220V power and observe if the fan rotates normally. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the output J5 terminal to see if it is 12V (12.1V-12.50V), eliminating measurement errors.
(3) Open the casing and check for arcing or burning on components and solder joints. Use a multimeter to check if the F1 fuse at the AC1 input is open. Measure if RT12 is 10 ohms, and check if the BR1 & BR3 rectifier bridges; PFCMOS Q72; CR16; CR48 are short-circuited (the other circuit is checked in the same way). Measure the main switch MOS transistors Q9; Q10; Q11; Q12 in the PWM circuit; and the SMD MOS transistors Q907; Q908; Q909; Q910; Q916; Q917; Q912; Q913; Q914; Q915; Q918; Q919 on the output SR board for short circuits. If there is a short circuit, the components need to be checked and replaced. Note that the resistors and transistors in the circuit around the faulty MOS transistor may also be damaged and need to be replaced.
(4) Check the auxiliary 12V circuit U14; Q60; CR60; CR42, CR28, CR59 and other components for short circuits or open circuits and surrounding component damage. Replace if necessary.
(5) If there are no abnormalities in the above locations, and the F1 or F2 fuses are working correctly, and the DC fan rotates after applying AC power to both circuits (if it doesn't rotate, measure if there is 12V at the fan socket; if normal, replace the fan), and there is 12V voltage at the output J5 terminal, measure whether there is DC 410V-450V at the measurement points of the two PFC large capacitors C134, C135, C132, C133. Otherwise, check if the PVCC power supply of the PFC circuit has 12V or determine if the components are damaged and replace them. If there are no abnormalities, check if the PWM circuit U12; U3 power supply VCC has 12V voltage or determine if the components are damaged and replace them.
(6) Other malfunctions require further analysis and judgment based on the technician's skills. After completing the above checks, for single power supply testing, the main DC output requires shorting pins 3 and 4 of J4. The main output should be approximately 18V.
Note that incorrect shorting may damage the chip. After replacing the defective components and verifying the soldering is correct, only then can you apply AC 220V for testing.
Note: If other circuits are checked and found to be normal, and the large capacitor has 420V, but there is no output after shorting, it may indicate that the DSP chip U49 firmware needs to be reprogrammed or the IC needs to be replaced and then reprogrammed (this type of malfunction is generally rare).
3.5 Simple troubleshooting and maintenance of common mining rig power supply failures:
Number | Fault phenomenon | Reason | Solution |
1 | The fan is not working, and there is no 18V | The AC power supply to the output is abnormal | 1. Check if the AC power cord is functioning properly and that both ends of the plug are securely connected. 2. Check if there is power in the electrical grid and that the voltage is normal. |
2 | The fan is operating normally, but there is no 18V output. | Low grid voltage Power supply protection | 1. Check if the fan is operating normally. 2. Check if the power supply's cooling air vents are blocked. 3. Check if the power supply has accumulated excessive dust internally due to prolonged use. 4. Check if the power consumption or ambient temperature exceeds the values specified in the power supply's power rating curve. |
3 | The power supply stopped outputting for a few seconds, then resumed normal operation, worked for a few minutes, and then stopped outputting again, repeating this cycle. | The power supply has entered over-temperature protection mode | 1. Check if the fan is operating normally. 2. Check if the power supply's cooling vents are blocked. 3. Check if the power supply has accumulated excessive dust due to prolonged use. 4. Check if the power consumption or ambient temperature exceeds the power supply's specified limits. |
4 | The output is normal, but the fan is not running. | The fan is broken | 1. Check if the fan is blocked by debris. 2. The fan is broken. |
5 | The power supply, which was working normally, suddenly stopped providing output and will not start up again. | Overcurrent protection has been triggered | The phenomenon of reaching the overcurrent protection limit occurs when the power supply sets the overcurrent protection to a locked state. This is to prevent the power supply from continuing to output power in case of a load abnormality, thus preventing dangerous situations such as fires. |
3.6 After the power supply unit is repaired and functioning normally, it needs to undergo ATS1 testing, hot pot burn-in for 2 hours, and ATS2 testing. Only after passing all of the above tests can it be shipped to the customer.