


In the world of cryptocurrency, newbies are curious and want to learn more about the mining process. This guide will help newbies enter the mining field safely and efficiently. Whether you want to earn an income through mining or learn more about the principles of blockchain technology, this guide will provide you with a systematic understanding from scratch.
1. Blockchain is the underlying technology behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. It is a distributed, immutable ledger that records all transactions. Miners play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain by verifying transactions and ensuring network security.
2. Cryptocurrency mining is the process of verifying blockchain transactions through hash rate and obtaining digital currency rewards. In blockchain networks that utilize the proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism, such as Bitcoin, miners employ specialized equipment to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to successfully verify a transaction block receives a reward.
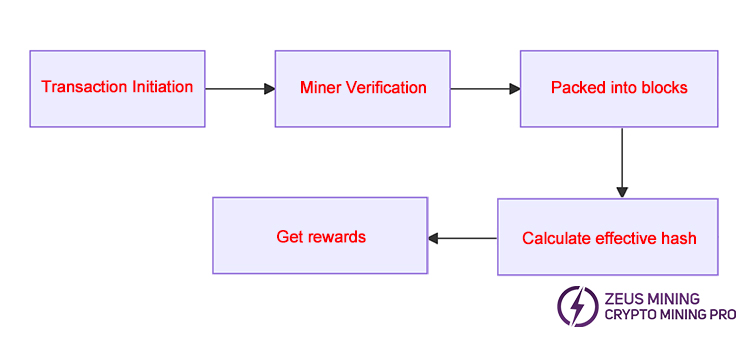
1. Proof-of-Work: A consensus mechanism that requires miners to solve cryptographic puzzles to verify transactions and create new blocks, thereby ensuring the security and integrity of the network.
2. Block: An independent unit of the blockchain. Each block contains a set of transactions, and once added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed.
3. Algorithm: Each cryptocurrency has a unique algorithm, which is a cryptographic function that crypto miners and the network use to create secure and unique hash values.
4. Hash rate: Hash rate is a measure of a blockchain network's mining and transaction processing capabilities. It represents the number of hash calculations a device or network can perform per second. A higher hash rate increases the likelihood that miners will solve cryptographic puzzles faster.
5. Hash value: A hash value is a unique, fixed-length string of numbers and letters. Miners will continuously generate hash values through the hash rate.
6. Nonce: Miners repeatedly change this number to get different hash values until they find a hash value that meets the network's requirements.
7. Number of cryptocurrencies: The number of cryptocurrencies varies. Some currencies have no upper limit, while others have a regular reduction in number. For example, Bitcoin halving is an event that occurs approximately every four years, when the mining reward is halved.
8. Node: A participant in a cryptocurrency network.
1. Choose a currency: Select the currency that suits our needs, such as Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, etc. Click to view the most suitable cryptocurrency for miners in 2025 to learn more. Research the reputation and long-term viability of cryptocurrencies and choose a currency that is profitable for us. Mining less well-known cryptocurrencies may be riskier, especially if their value fluctuates wildly or lacks community support.
2. Hardware Requirements: Purchase popular, high-hash-rate miners that can mine our currency, such as the Antminer S21e XP Hyd 3U, Antminer L9, and IceRiver ALEO AE3, among others. Ensure that we find mining hardware that considers both efficiency and price. Miners with a strong hash rate may be able to get cryptocurrency block rewards, but home mining is challenging to compete with large-scale mining farms.
3. Energy consumption: Understand the electricity costs in our area and the energy consumption of the hardware, which will affect the profit of mining.
4. Mining pool options: Consider whether we want to join a mining pool or mine alone. The income of the mining pool is more stable; however, our income will be divided among the entire mining pool. Solo mining may not be profitable for a long time, but once the reward is obtained, it will be exclusive.
5. Network difficulty: Understand the current mining difficulty of the cryptocurrency. The higher the difficulty, the more intense the competition, and the lower the reward. The higher the difficulty.
6. Install mining monitoring software: Mining monitoring software connects our miners to the cryptocurrency network, such as CGMiner and BFGMiner. It can support our advanced functions, such as remote monitoring, fan speed adjustment, and overclocking, among others.
7. Create a cryptocurrency wallet: We can choose between a software wallet and a hardware wallet to securely store our mining rewards. Software wallets, such as Bitcoin wallets, can be created by searching the official website wallet.bitcoin.com. Hardware wallets, such as Ledger, can provide an extra layer of security by storing private keys offline.
8. Profit calculator: This tool is used to estimate the potential benefits and costs of cryptocurrency mining. It is usually calculated based on current market conditions, hardware performance, and operating costs to help us evaluate the feasibility of mining. Some large manufacturers, such as Antminer and Canaan, provide dedicated calculators. Alternatively, we can choose from general calculators, such as WhatToMine and CryptoCompare.
9. Tax and compliance considerations: Different countries and regions have varying regulatory policies regarding cryptocurrency mining. Most countries regard mining income as taxable income and require miners to declare mining income and pay corresponding taxes. Some countries prohibit or restrict mining activities, primarily due to energy consumption considerations. Large-scale mining may require the registration of a business entity.
1. Follow the miner manual step by step. Unbox and check the hardware, connect the power supply and network, and update the miner firmware.
2. Find the miner's IP address, and enter it into the Google browsing page to access the miner's background.
3. Next, enter the mining configuration, which depends on whether we want to join a mining pool or mine alone.
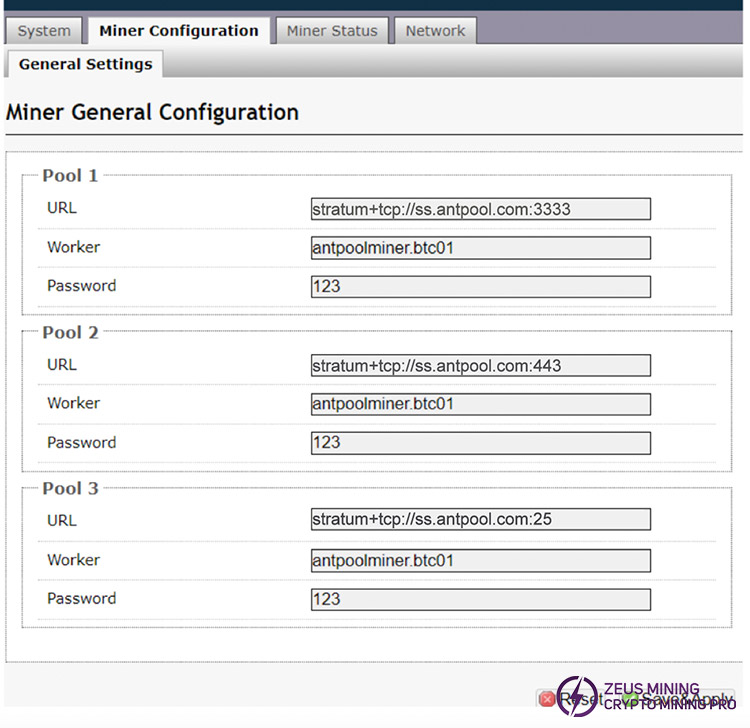
If it is a mining pool:
• Enter the mining pool URL provided by the mining pool
• Miner ID and password: a unique identifier in the mining pool
• Fill in the wallet address: mining rewards will be sent here
• Save the settings and restart the miner; the miner will connect to the mining pool and start running. For a more detailed process of mining pool settings, please refer to the article What Is Binance Pool And How To Set Up?
If it is solo mining:
• We need to install and run a full node, ensuring it is running and synchronized with the entire blockchain. This process may take some time.
• Enter the full node connection details, including the IP address and port of the whole node, as well as the wallet address.
• Save the configuration and restart the miner: the miner will now start trying to solve blocks independently and verify transactions through our full node. Here, we can refer to the article "How to Solo Mine Bitcoin?"
4. Start the mining monitoring software to detect the hash rate, temperature, and rejection rate indicators. Adjust overclocking and fan settings based on operating data, and establish a regular maintenance and optimization plan.
5. Cooling and ventilation: ASIC miners generate a significant amount of heat, so it is essential to dissipate it effectively. Place the miner in a well-ventilated area, or consider using additional cooling equipment to prevent overheating and maximize performance.
1. Stay informed about current mining industry trends and continually learn about the latest developments and technologies in the industry.
2. Flexibly adjust strategies to adapt to changes, and evaluate personal budgets and risk tolerance.
3. Participating in mining communities and forums (such as BitcoinTalk) is a good way to get the latest information.
4. Analyze the current prospects and challenges of the mining industry and develop a sustainable mining strategy.
ZEUS MINING offers a guide to cryptocurrency mining, helping beginners safely launch their mining careers and achieve stable returns. If novices are considering entering the world of cryptocurrency mining, it is crucial to assess whether it is a profitable endeavor. This article can also serve as a way to understand cryptocurrency, learn about distributed networks, and explore decentralized finance.
Q: How to effectively deal with the heat generated by ASIC miners?
A: Industrial-grade ventilation systems can extend the life of equipment by up to 40%. For home mining, consider a dedicated water cooling solution or utilize waste heat for heating in winter.
Q: Why does cryptocurrency mining make noise?
A: The noise is emitted by the cooling fan. Crypto mining is highly energy-intensive and generates significant heat, necessitating the use of fans to keep the hardware running smoothly. We can choose a low-noise model or add a silencer to reduce noise.
Q: Is Bitcoin mining profitable?
A: Bitcoin mining can be profitable; however, due to high electricity costs and intense competition, it is typically challenging for home miners.
Disclaimer:
For cryptocurrency tutorial purposes only, not investment advice. This website is not responsible for the actions taken by readers based on the information in this article.