


I. Download and install
1. The official Canaan download address is: https://download.canaan-creative.com/fms/. Unless otherwise specified, please download the latest version's zip file to your local computer. Version release notes and user manuals can also be found in the download directory.Applicable to version 2.0.2 and later.
2. Unzip the downloaded zip file to your desired location. No installation is required; simply double-click the fmsapp.exe filein the directory to start FMS. For convenience, you can create a shortcut to fmsapp.exe in a suitable location for quick access.
filein the directory to start FMS. For convenience, you can create a shortcut to fmsapp.exe in a suitable location for quick access.
II. Starting FMS
1. If you created a desktop shortcut, you can start FMS by double-clicking the desktop shortcut. If not, please go to the unzipped directory and double-click the fmsapp.exe file to start FMS. Administrator privileges are not required.
2. The main interface of FMS after startup looks like this:
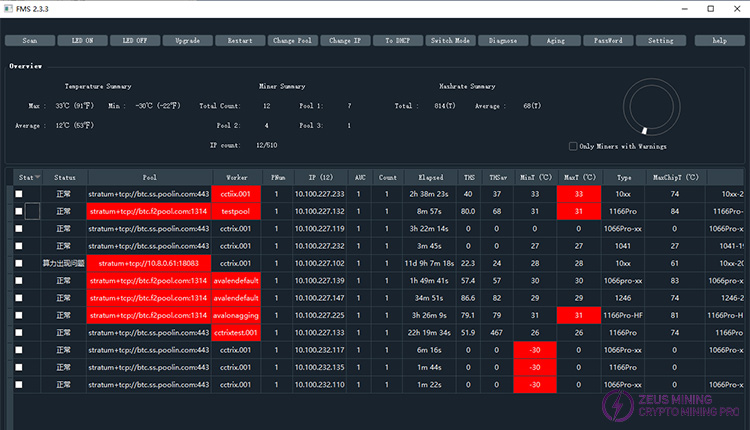
If this is the first time launching the application or if you've just started your computer, you might see the mouse cursor change to a waiting state and the interface appear unresponsive. This indicates that FMS is initializing. This usually takes a few seconds, after which the normal main interface will be displayed. If the FMS executable file in the same location is launched multiple times, it will actually share the same configuration, which can easily lead to interference. Please avoid launching multiple instances. If you want to launch multiple FMS instances with different configurations on the same computer, please copy the entire directory to different paths to create multiple FMS executable directories. Each FMS in a different path will use an independent configuration.
III. Main Interface Introduction
The main interface is roughly divided into four areas: Scanning Dynamics Area, Function Button Area, Overview Area, and Miner Information Area. These are shown in the following images:
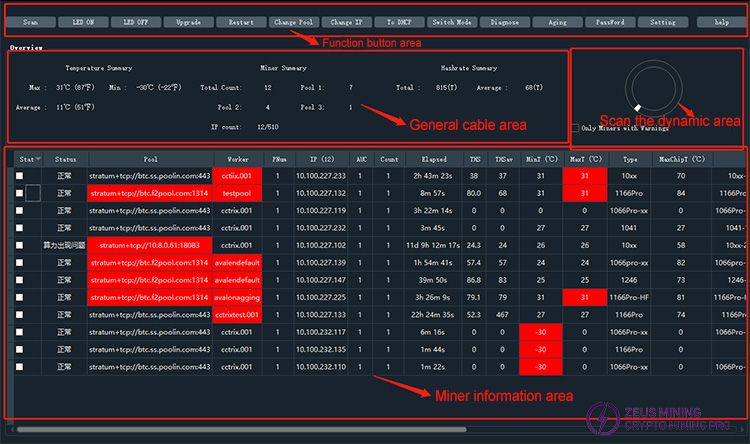
The exact version number of the currently installed FMS will be displayed in the title bar at the top.
 | Manual scan |
 | Turn on lights in bulk |
 | Turn off lights in bulk |
 | Batch firmware upgrade |
 | Batch switching of mining pools |
 | Batch set static IP addresses |
 | Reset DHCP |
 | Select high/low power mode |
 | Remote diagnosis |
 | aging |
 | Change password |
 | Configuration Settings |
V. Overview section
Temperature Summary | Max | Maximum air inlet temperature |
Min | Minimum air inlet temperature | |
Average | Average inlet air temperature | |
Miner Summary | Total Count | Number of miners currently detected |
Miner Overview | Pool 1 | The number of miners working in pool #1 |
Pool 2 | The number of miners working in pool #2 | |
Pool 3 | The number of miners working in pool #3 | |
IP Count | Number of IPs with data / Total number of IPs | |
Hashrate Summary | Total | Total hashrate of all miners |
Average | Average hashrate of all miners |
VI. Miner Information Section
This is a table displaying miner information, with each row representing a unique IP address. For miners like the Avalon8 or Avalon9, which don't have their own IP addresses, each row represents a Raspberry Pi. For miners like the Avalon10, which do have their own IP addresses, each row represents a single miner.
The specific meaning of each column is shown in the table below:
State | Select status; function buttons only apply to selected miners |
Status | Miner status and reasons for any problems |
Pool&Worker | Name of the pool and worker |
Number of Miners in Pool | The number of miners in the pool |
IP | IP address; the total number of IPs in the current network segment will be displayed in parentheses in this column header |
AUC count | AUC count (not applicable to A10) |
Miner count | The total number of miners under the IP address |
Elapsed Time | The running time since the last power-on or restart |
Real-Time Hashrate(T) | Real-time hashrate, in T/second |
Average Hashrate(T) | Average hashrate, in T/second |
Miner | Miner type |
Max chip Temperature(℃) | Temperature(℃): Maximum chip temperature |
Ver | Full version number |
If you double-click the IP address cell, you can directly open the backend page of that IP address in your browser.
If you double-click the Real-Time Hashrate cell, a window will pop up listing the real-time hashrate of each miner under that IP address.
When you first install and use the software, the miner information area will be blank. You need to go to the IP range settings page in the settings dialog box (explained later) to set the IP scanning range to see the miner information.
VII. Features and Usage
1. Settings
Clicking the button will take you to the settings interface, the default page is shown below:
button will take you to the settings interface, the default page is shown below:
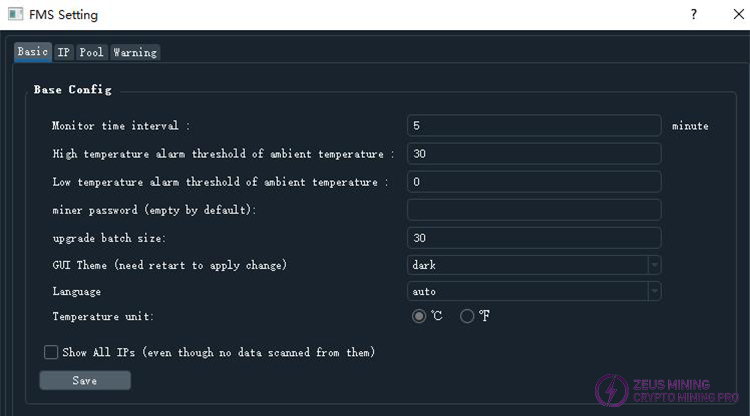
The entire settings interface consists of four sub-pages, which are described below.
1)Basic Settings Interface
As shown in the image above, it contains some basic settings. Any modifications require clicking the "Save" button to take effect. If you make changes on this page but do not save them before closing the window, all changes will be lost.
The "Monitor time interval" setting determines the time interval for the background scanning of miners, in minutes. For example, setting it to 1 means the background will scan all miner information every minute. It can be a decimal number, such as 2.5, representing two and a half minutes. It can also be set to a value less than 1. When the number of scannable miners is large, it is recommended to increase the scanning interval appropriately to prevent FMS from occupying excessive system resources.
The "High temperature alarm threshold of ambient temperature" is used to set the high-temperature alarm threshold for the air intake temperature.
This setting is effective for all types of miners. Please distinguish it from the Warning settings that will be explained later. If the air intake temperature of a miner exceeds the value set here, the maximum air intake temperature cell in the miner information table for that miner's IP address will be marked with a red background, similar to the image below:
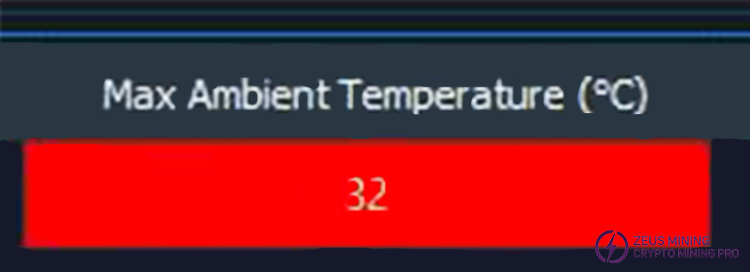
The ambient temperature low temperature alarm threshold is similar to the one above, setting the minimum allowable air inlet temperature. Please note that the units of these two settings depend on the Temperature unit setting below.
GUI Theme (need restart to apply change) is used to set the theme style of the graphical interface. Currently, there are two themes available: dark and light. A restart of FMS is required for the change to take effect.
Temperature unit is used to set the unit for temperature display and settings. The default is Celsius (°C). Please note that temperature-related settings will not be automatically converted when the unit is changed here. Therefore, after changing the unit here, please also modify the corresponding temperature settings to the converted values in the new unit.
Show All IPs (even though no data scanned from them) is used to set whether to display all IP addresses.
When checked, the miner information table will list those IPs from which no data was scanned on a separate line (the cells will be left blank or show 0).
This option is useful if you want to see which IPs did not have miners scanned.
When you have made changes that need to be saved, please click the Save button to save them.
2)IP Range Settings Interface
The interface is similar to the image below:
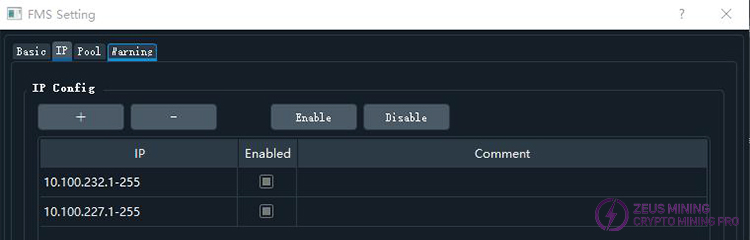
This section configures the IP address range that FMS can scan. Each row in the table represents a range; the IP column shows the configured IP range, and the Enabled column indicates whether this range is enabled (true means enabled, false means disabled). Only enabled IP ranges will be scanned by FMS.
To add a new IP range, please click the button. A dialog box will then appear, similar to the image below:
button. A dialog box will then appear, similar to the image below:
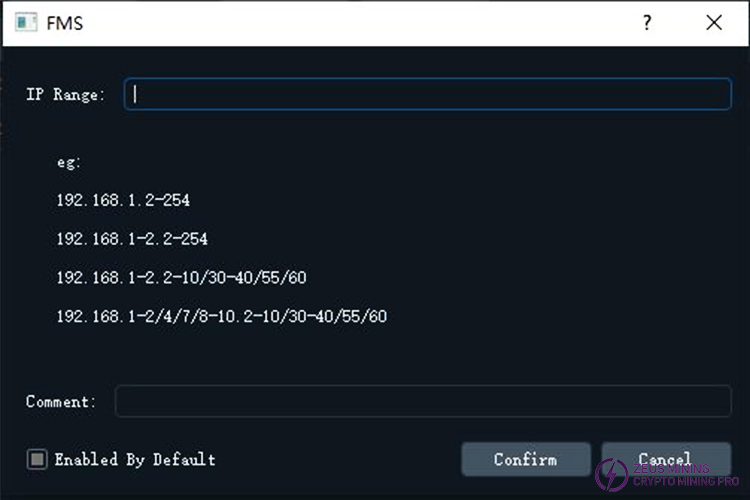
In the IP Range edit box, you can enter the IP range you want to add. It supports the following formats:
a. Range: A hyphen can be used in any byte to represent a range.
For example:
192.168.1-3.5 represents the four IP addresses: 192.168.1.5, 192.168.2.5, 192.168.3.5, and 192.168.4.5. Ranges can be used in multiple bytes simultaneously.
For example: 192.168.1-2.5-6
represents the four addresses: 192.168.1.5, 192.168.1.6, 192.168.2.5, and 192.168.2.6.
b. Multiple group separation: A slash can be used in any byte to separate multiple ranges or single values.
For example: 192.168.1-2.4-5/8/10/14-15
represents the 12 IP addresses: 192.168.1.4, 192.168.1.5, 192.168.1.8, 192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.14, 192.168.1.15,
192.168.2.4, 192.168.2.5, 192.168.2.8, 192.168.2.10, 192.168.2.14, and 192.168.2.15.
The "eg:" section in the dialog box also provides simple examples of the available formats.
Enabled By Default : This checkbox indicates whether to enable it by default. Checking it means that the added item will be enabled, it will be disabled after adding.
: This checkbox indicates whether to enable it by default. Checking it means that the added item will be enabled, it will be disabled after adding.
Click the Confirm button to confirm the addition.
button to confirm the addition.
To delete, enable, or disable certain IP ranges, you need to first highlight the IP ranges you want to operate on. The Ctrl+A shortcut for selecting all, and holding down Shift for continuous selection or holding down Ctrl for individual selection, are supported. Then, clicking the button will delete the selected rows, clicking the
button will delete the selected rows, clicking the button will enable the selected rows, and clicking the
button will enable the selected rows, and clicking the button will disable the selected rows. These changes take effect immediately and do not require separate saving.
button will disable the selected rows. These changes take effect immediately and do not require separate saving.
Double-clicking an IP cell or comment cell allows direct editing; clicking anywhere else completes the editing. Comments are used to add custom information to an IP range, solely for the convenience of collaboration and understanding among users; it does not affect the scanning function itself.
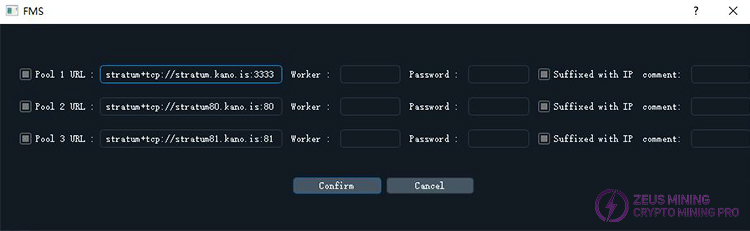
3) Pool Settings Interface
This is where you configure the mining pool information that will be used in the future. Note that this will not actually change the current mining pool of any mining machine, but only sets up the settings for switching mining pools, saving you the trouble of re-entering the mining pool information every time.
The interface is shown in the image below:
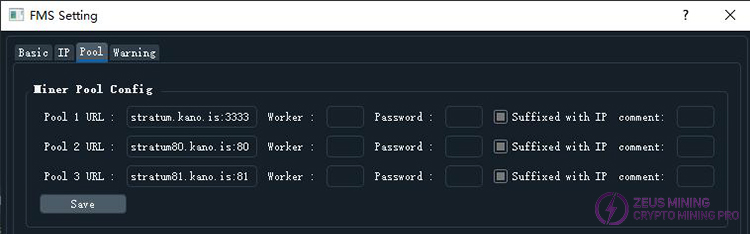
A maximum of three pools can be configured in total. Each setting includes the pool address, miner name, and password, as well as a "Suffixed with IP" checkbox. If "Suffixed with IP" is checked, the miner's IP address (or the IP address of the associated Raspberry Pi) will be used as a suffix to the miner name. This allows you to see the IP address in the "Pool & Worker" column of the miner information table, and also on the pool's own webpage, making it easier to distinguish the statistics of each miner. This option is checked by default.
If you make any changes on this page, please click the Save button to save them; otherwise, all changes will be lost when you close the settings page.
4) Warning Settings Interface
This interface is used to precisely control which cells in the miner information table should be marked with a warning color (red). It contains several warning rules. Each row represents a warning rule, including four parts: Field (checked field), Ver Prefix (version prefix), Operator (comparison rule), and Value (threshold value). When a miner's complete version starts with the version prefix in the rule,
this rule will be applied to that miner. When displaying the miner's information, warning indicators will be displayed based on all warning rules that can be applied to it.
The interface is similar to the image below:
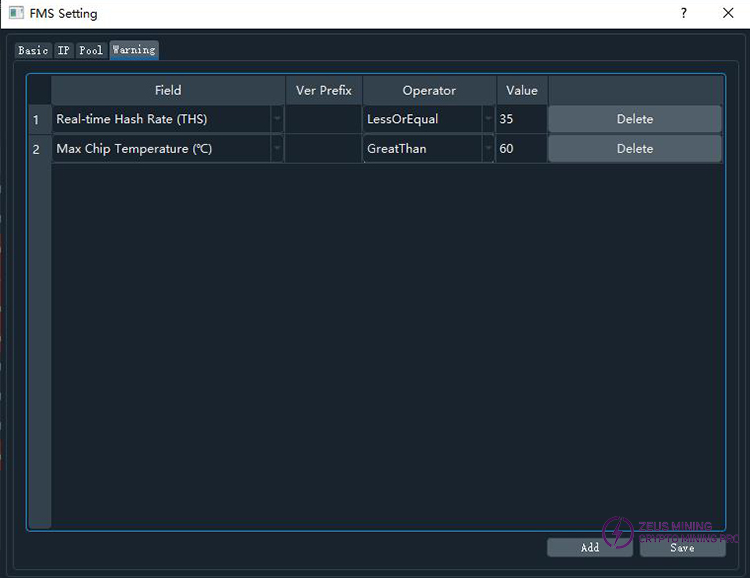
The following examples illustrate the application of the rules. In the image, the first rule has an empty version prefix, indicating that it applies to all miners. This rule means that if the miner's Real-Time Hash Rate (real-time hash rate in THS) is LessThan or Equal to 35, the real-time hash rate cell will be marked with a warning color. The second rule has a version prefix of 10RT, meaning that this rule only applies when the miner's full version number (Ver column) starts with 10RT.
This rule means that if the miner's Max Chip Temperature field is GreaterThan 60, the maximum chip temperature field will be marked with a warning color.
Currently supported fields include real-time hash rate, maximum chip temperature, and maximum air inlet temperature. Other fields with warning value may be added in the future.
Currently supported comparison rules include: LessThan or Equal to, Less Than, Greater Than or Equal to, Greater Than, and Equal to.
If you need to add a new rule, please click the button at the bottom of the page.
button at the bottom of the page.
If you need to delete a rule, please click the button on the far right of that rule in the table.
button on the far right of that rule in the table.
If you have made any additions, deletions, or modifications, please click Save; otherwise, the changes will be lost when you close the settings dialog box.
5) Firmware Upgrade
Users select the corresponding miner on the main interface and click the button. A selection box will then pop up.
button. A selection box will then pop up.
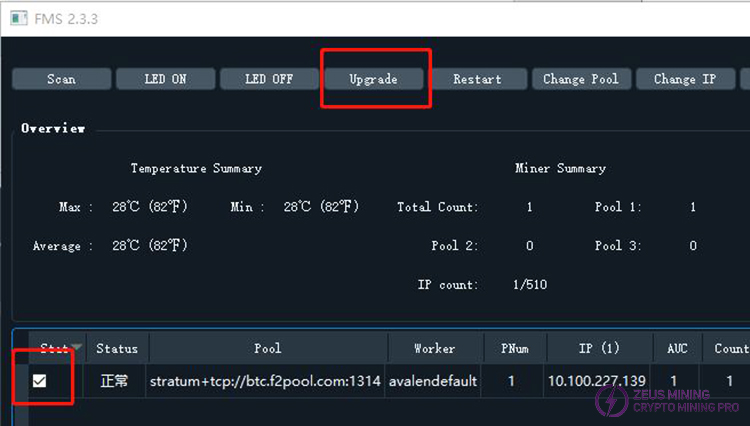
When selecting multiple miners for batch upgrading, the latest version of FMS will first prompt you to select the model of the firmware to be upgraded.
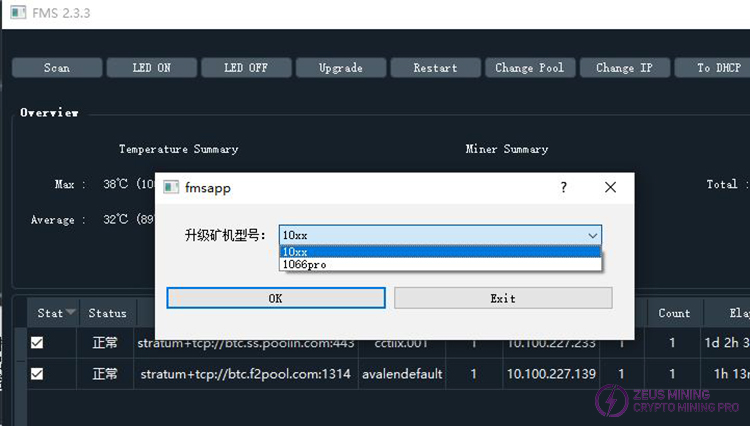
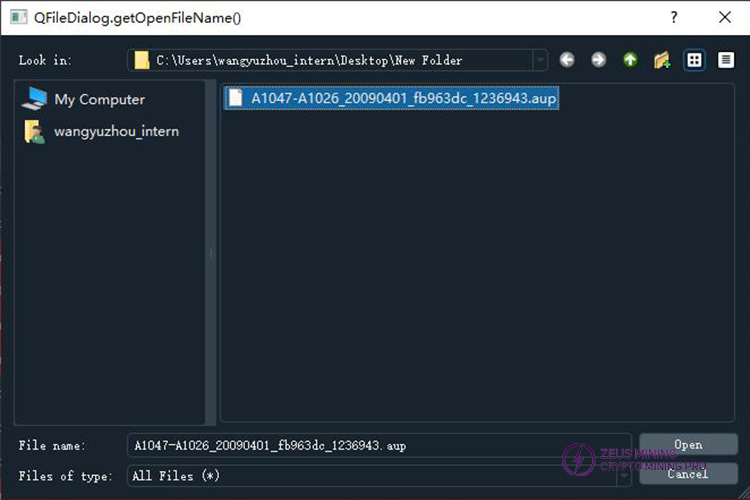
Select the firmware you want to upgrade, then click "Open" to start the update.
Upgrade loading progress bar
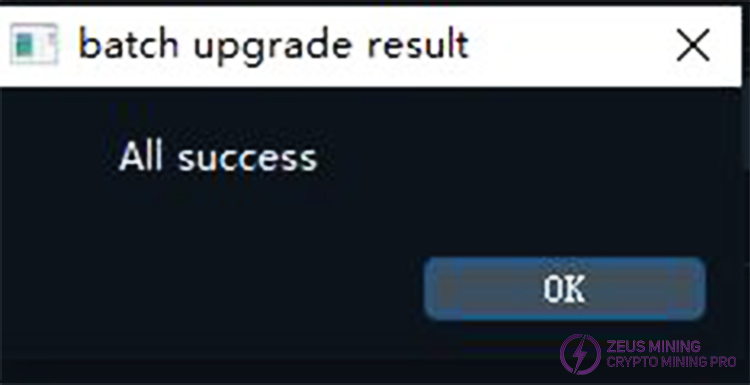
After the update is complete, a dialog box will pop up to inform you of the results. If all updates are successful, it will display "All upgrades were successful."
Otherwise, it will list all the IP addresses where the upgrade failed.
6) Batch Switching Lights
First, select one or more miners from the list using the checkboxes in the "State" column, then click the "LED ON" button to turn on the LED lights on these miners. A progress bar will be displayed during the process. After the progress bar disappears, a dialog box will pop up to inform you whether the lights have been successfully turned on. After successful activation, the LED lights will flash yellow and green (some models will show a steady white light).
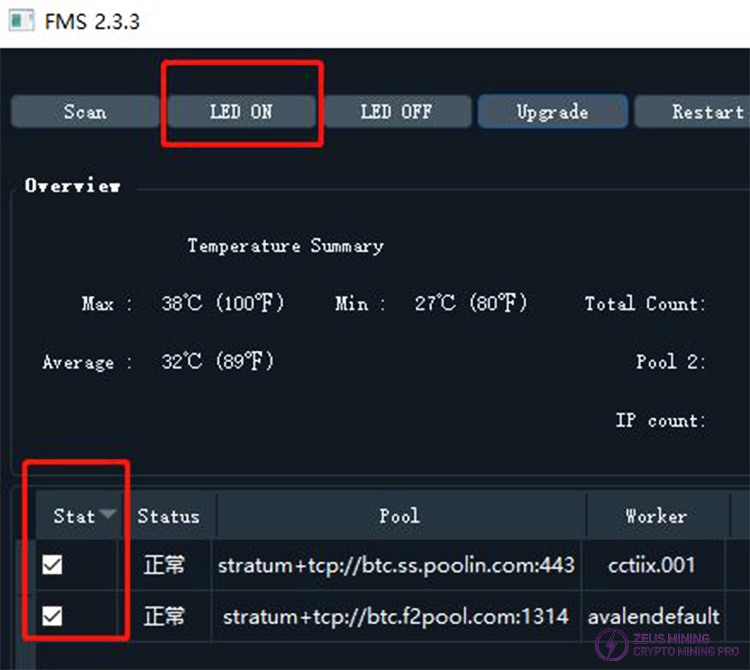
7) Batch Restart
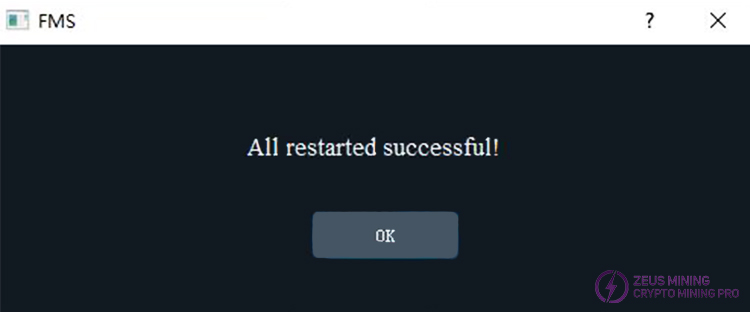
First, select one or more miners from the list using the checkboxes in the "State" column, and then click the "Restart" button to restart these miners. A progress bar will be displayed during the restart process. After the progress bar disappears, a dialog box will pop up to inform you whether the restart was successful. After a successful restart, the miners will need some time to enter a normal mining state. During this time, FMS may not be able to detect these newly restarted miners.
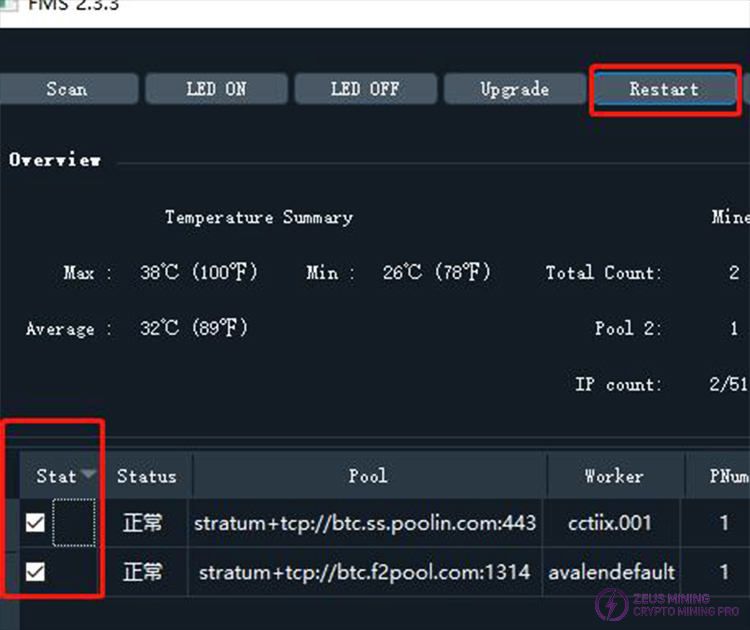
After clicking "start," you will be prompted to choose whether to upgrade the selected miner.
Restart successful
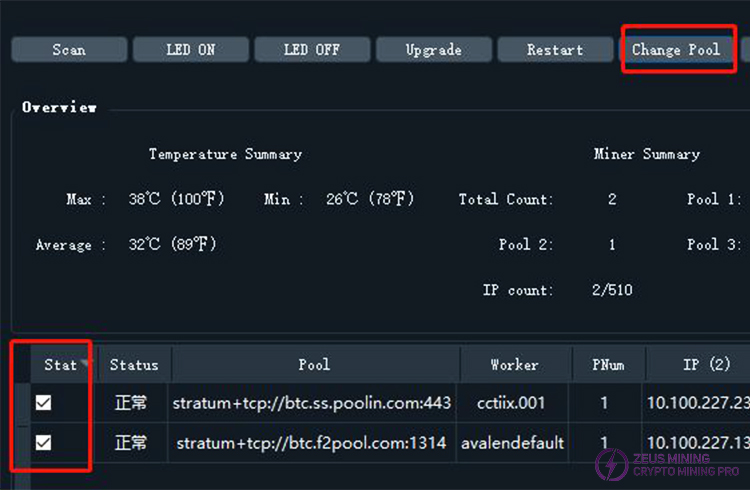
8) Batch Pool Switching
First, select one or more miners from the miner list using the checkboxes in the "State" column, then click the "Change Pool" button. A dialog box will pop up to configure the pool. After confirmation, FMS will perform the pool switching operation on the selected miners. A progress bar will be displayed during the pool switching process. After the progress bar disappears, a dialog box will pop up to inform you whether the pool switching was successful. After successful pool switching, the miners will restart and require some time to enter a normal mining state. During this time, FMS may not be able to detect these miners that have just switched pools.
9) Batch Setting Static IP Addresses
Step 1: Launch the batch static IP setting dialog box. Select multiple miners that require static IP addresses, and then click the button to enter the static IP address setting dialog box:
button to enter the static IP address setting dialog box:
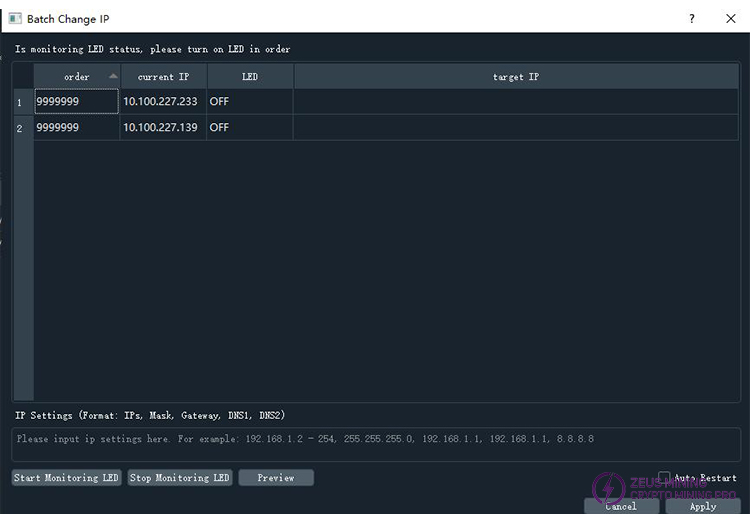
The top row here displays various results or error messages, and the table below shows information about the selected miner. The "Order" column indicates the order in which the miner was manually switched on; 999999 means it has not yet been manually switched on. The "Current IP" column shows the miner's current IP address; the "LED" column shows the miner's current real-time LED status, where ON means the light is on, and OFF means the light is off (Note: OFF only means the light is not illuminated, the LED is actually still lit with another color); the "Target IP" column shows the IP address to which it will be changed.
Step 2: Switching on the lights
When you see that all LED statuses in the table are OFF, the message will usually be as follows:

At this point, you can begin manually activating the miners one by one according to the configured IP address sequence. To activate a machine, briefly press the small protruding button on the miner (Note: Avalon10 miners also have another recessed button used for factory reset; please do not confuse the two). When you see the red light illuminate and then immediately turn off automatically, it indicates that the FMS system has detected the activation and recorded the event. If the light does not turn off automatically, please wait a moment, as there may be a slight delay in the FMS scanning process. If it does not turn off after 10 seconds, it may indicate that you have activated the wrong machine (this miner is not among those selected), or there may be a communication problem with the miner; please check it separately. Each time a selected miner is detected as activated, the FMS will display the status in real-time and automatically turn off the light. A message similar to the following will be displayed in the notification bar:

The first part of the information shows the current IP address of the detected miner, and the last number indicates its position in the sequence of being powered on.
After all miners have been powered on, a dialog box will pop up asking if you want to continue modifying the power-on sequence:
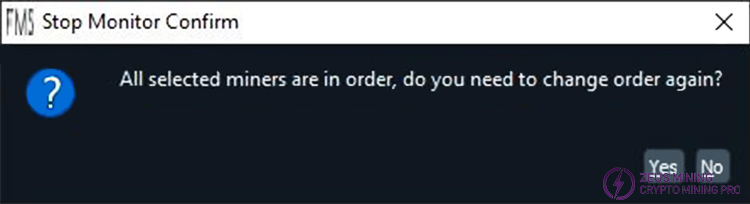
If the lighting sequence is confirmed to be correct, you can select "No" to stop further scanning. If you are unsure, or if you find the sequence is incorrect,
you can select "Yes" to relight the lights and change the sequence. The purpose of stopping the scan is to prevent accidental touches of the lights from affecting the currently determined sequence. If you want to restart the scan after stopping it, you can click the button on the dialog box. Clicking the
button on the dialog box. Clicking the button at any time will stop the scan and prevent the effects of accidental touches of the lights. If the lighting sequence is incorrect, you can relight the first incorrect miner; FMS will then clear the sequence numbers of all miners that were lit after this miner. This is equivalent to relighting the miners with the incorrect sequence one by one again.
button at any time will stop the scan and prevent the effects of accidental touches of the lights. If the lighting sequence is incorrect, you can relight the first incorrect miner; FMS will then clear the sequence numbers of all miners that were lit after this miner. This is equivalent to relighting the miners with the incorrect sequence one by one again.
Step 3: Set IP Address Range
Once all miners have been assigned sequential numbers, you can configure the static IP address range. Below the table is the editing box for setting the static IP address range. Each line represents a set of IP address settings. Multiple lines are allowed. Each line of settings includes the IP range, subnet mask, gateway IP address, primary DNS address, and secondary DNS address, separated by commas.
For example: 192.168.193.2-5,255.255.255.0,192.168.193.1,114.114.114.114,202.106.0.20
This indicates an IP range from 192.168.193.2 to 192.168.193.5, a total of 4 available addresses, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, a gateway of 192.168.193.1, a primary DNS of 114.114.114.114, and a secondary DNS of 202.106.0.20. The IP range format is the same as the IP range format in the FMSIP range settings. Additionally, it supports default prefixes: If the currently selected miners already have IP addresses within the same network segment, then the first few bytes of the configured IP address range can be omitted. The omitted bytes will take the same value as the corresponding part of the current IP address.
For example, if the current IP addresses all start with 192.168.3, then writing 5.7-10 is equivalent to writing 192.168.5.7-10. The sequence of IP addresses expressed in each line will be used to set the static IP addresses of the miners in order. If the number of IP addresses in the first line is insufficient, the addresses will be taken sequentially from the second line, and so on for subsequent lines. Please specify the static IP range according to the order in which the lights are illuminated. After editing, proceed to the next step. (In fact, IP settings can be edited at any time, not necessarily after the lights have finished illuminating.)
Step 4: Preview
After editing the settings, you can click the button to preview the settings. FMS will extract the static IP sequence values based on the content in the IP settings box and fill them into the "Target IP" column in ascending order of "Order," making it easy to confirm whether the results meet expectations. If there are any errors in the IP range settings, the preview action will fail, and an error message will be displayed at the top. If the preview fails, all values in the "Target IP" column will become empty. Please re-edit the IP range settings and preview again. After a successful preview, you can proceed to the next step.
button to preview the settings. FMS will extract the static IP sequence values based on the content in the IP settings box and fill them into the "Target IP" column in ascending order of "Order," making it easy to confirm whether the results meet expectations. If there are any errors in the IP range settings, the preview action will fail, and an error message will be displayed at the top. If the preview fails, all values in the "Target IP" column will become empty. Please re-edit the IP range settings and preview again. After a successful preview, you can proceed to the next step.
Step 5: Execute the Change
After confirming that all static IP address mappings are correct, click the button to start the static IP address setting process.
button to start the static IP address setting process.
FMS will simultaneously modify the static IP settings of all miners according to the mappings in the table. If you need FMS to restart the miners after the settings are applied, please check the box. If you do not check this box, FMS will only set the new static IP addresses on the miners; these settings will only take effect after a power cycle or a batch restart. The batch static IP setting function can also be used to modify the IP address of a single miner. If only one miner is selected, the lighting step is not necessary; simply set the IP address and execute the change.
box. If you do not check this box, FMS will only set the new static IP addresses on the miners; these settings will only take effect after a power cycle or a batch restart. The batch static IP setting function can also be used to modify the IP address of a single miner. If only one miner is selected, the lighting step is not necessary; simply set the IP address and execute the change.
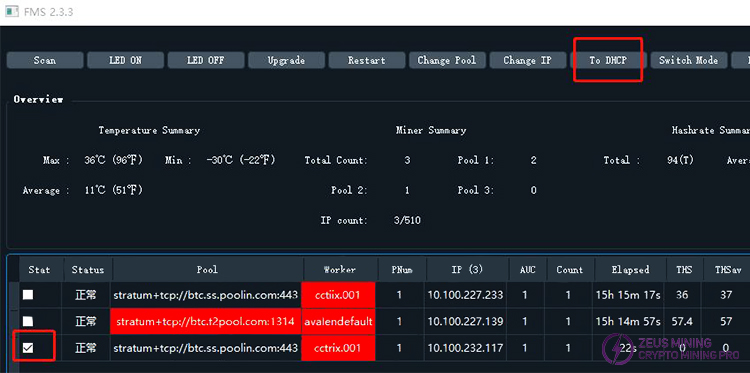
10) Reset DHCP
Select the machine you want to reconfigure DHCP for, then click .
.
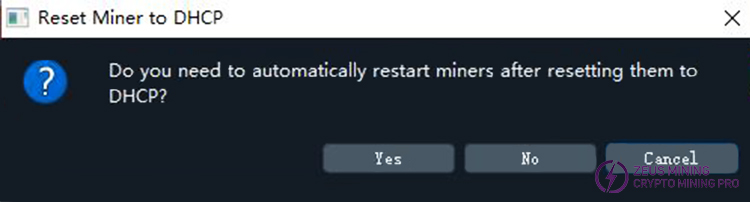
After clicking the button, a dialog box will pop up asking if you want to configure DHCP and restart; click the YES button.
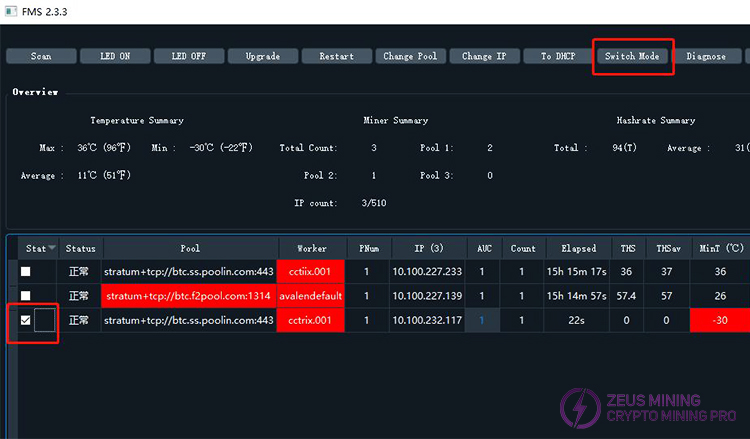
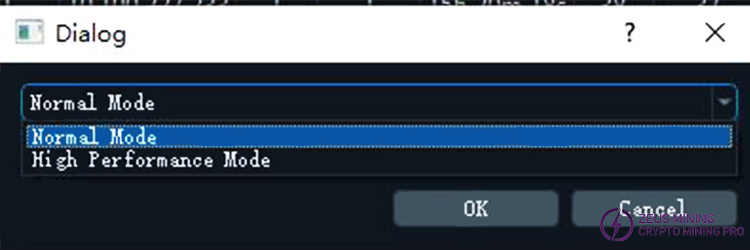
11) Batch modification of miner operating mode
Select the machines whose operating mode you want to modify, then click , and select the operating mode. Normal Mode is for low power consumption, and High Performance Mode is for high performance.
, and select the operating mode. Normal Mode is for low power consumption, and High Performance Mode is for high performance.
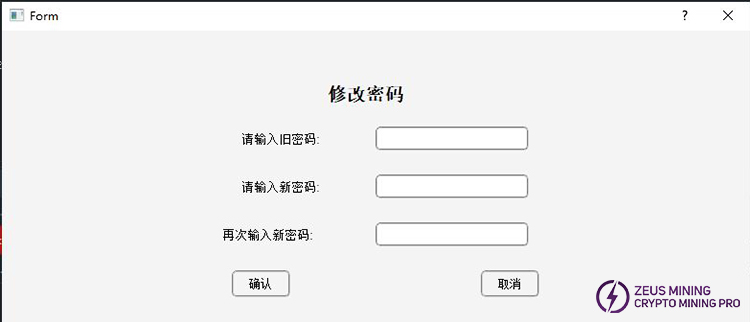
12) Change Password
In the status section, select a machine whose password you want to change, click the [ ] button to bring up the change dialog box, and then change the password.
If you forget your password before making any changes, you can click the button and enter a command to display the current password.
button and enter a command to display the current password.

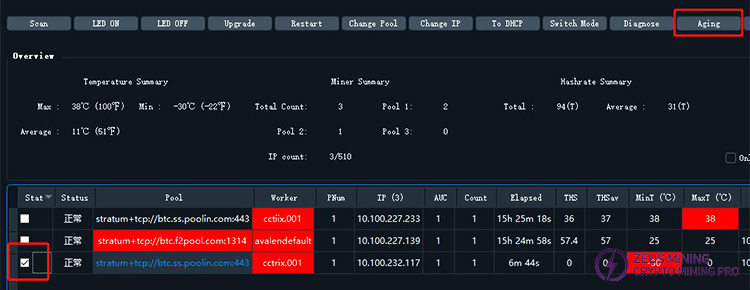
13) Batch Miner Aging Test
In the status section, select a machine to perform the aging test on, and click the button to start the aging process.
button to start the aging process.
If the settings are successful, "All success" will pop up.
14) Configuration Import and Export
The “config” directory located in the same directory as “fmsapp.exe” is where all the configuration files are stored. Backing up or restoring this directory will effectively export or import the configuration settings.
For more products and information, please click to join our official Telegram channel.